A Study of Vertical Structures and Microphysical Characteristics of Different Convective Cloud–Precipitation Types Using Ka-Band Millimeter Wave Radar Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Data
2.2. Data Processing and Cloud–Precipitation Microphysical Parameter Retrieval
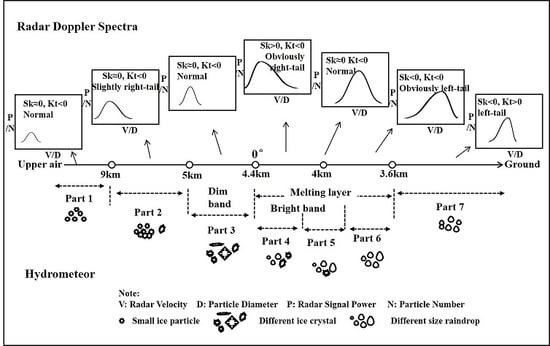
2.2.1. Radar Doppler Spectra Processing
2.2.2. Cloud–Precipitation Microphysical Parameter Retrieval
2.2.3. Parsivel Data Post-Processing
3. Results
3.1. Weather Background and Convection Evolution
3.2. Vertical Structures and Microphysical Properties of Different Convections
3.2.1. Multi-Cell Convection
3.2.2. Isolated-Cell Convection
3.2.3. Convective–Stratiform Mixed Cloud–Precipitation
3.2.4. Warm Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Didlake, A.C.; Kumjian, M.R. Examining polarimetric radar observations of bulk microphysical structures and their relation to vortex kinematics in hurricane Arthur (2014). Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 4521–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, K.; Keil, C.; Weissmann, M. Impact of radar data assimilation and orography on predictability of deep convection. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasic, S.; Lin, C.A.; Zawadzki, I. Evaluation of precipitation from numerical weather prediction models and satellites using values retrieved from radars. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 3750–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Clothiaux, E.E.; Miller, M.A.; Albrecht, B.A.; Stephens, G.L.; Ackerman, T.P. Millimeter-wavelength radars: New frontier in atmospheric cloud and precipitation research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1608–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropfli, R.A.; Kelly, R.D. Meteorological research applications of mm-wave radar. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1996, 59, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Verlinde, J.; Gilbert, C.; Tongue, J.; Lehenbauer, G. Cloud detection using the WSR-88D: An initial evaluation. Preprints, 28th Conf. on Radar Meteorology, Austin, TX. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 28, 442–443. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, P.V.; Funk, N.T.; Weiss, R. Evaluation of a 35-GHz radar for cloud physics research. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1985, 2, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossard, E.E.; Snider, J.B.; Clothiaux, E.E.; Martner, B.J.; Gibson, S.; Kropfli, R.A.; Frisch, A.S. The potential of 8-mm radars for remotely sensing cloud drop size distributions. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1997, 13, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Albrecht, B.A.; Lhermitte, R.; Savtchenko, A. Radar observations of updrafts, downdrafts, and turbulence in fair weather cumuli. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.P.; Martner, B.E.; Post, M.J.; Kropfli, R.A.; Welsh, D.C.; Widener, K.B. An unattended cloud profiling radar for use in climate research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.P.; Pezoa, S.; Fairall, C.; Ayers, T.; Brewer, A.; Williams, C. A motion-stabilized W-band radar for shipboard observations of marine boundary-layer clouds. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2012, 143, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Mark, A.M.; Edward, P.L.; Karen, L.J.; Eugene, E.C.; Kenneth, P.M.; Kevin, B.W.; Bruce, A.A. The atmospheric radiation measurement program cloud profiling radars: Second-generation sampling strategies, processing, and cloud data products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1199–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, G.M.; Schwartz, S.E. The Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) program: Programmatic background and design of the cloud and radiation test bed. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 75, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, T.J.; Fu, Q.; Comstock, J.M. Cloud effect on radiative heating rate profiles over Darwin using ARW and A-train radar/lidar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5637–5654. [Google Scholar]
- Haeffelin, M.; Barthès, L.; Bock, O.; Boitel, C.; Bony, S.; Bouniol, D.; Drobinski, P. SIRTA, a ground-based atmospheric observatory for cloud and aerosol research. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Hogan, R.J.; O’Connor, E.J.; Brooks, M.E.; Delanoe, J.; Donovan, D.P.; Eastment, J.D. Cloudnet-continuous evaluation of cloud profiles in seven operational models using ground-based observations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Zheng, J.F.; Ruan, Z. Comprehensive radar observations of clouds and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and preliminary analysis of cloud properties. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, K.; Wu, J.; Wang, B. A method for retrieving vertical air velocities in convective clouds over the Tibetan Plateau from TIPEX-III Cloud Radar Doppler spectra. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.H.; Sui, C.H.; Fan, J.W.; Fan, J.W.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhong, L.Z. A study of cloud microphysics and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau by radar observations and cloud-resolving models simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 13735–13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Vane, D.G.; Boain, R.J.; Mace, G.G.; Sassen, K.; Wang, Z.; Illingworth, A.J.; O’connor, E.J.; Rossow, W.B.; Durden, S.L.; et al. The CloudSat mission and the A-Trian. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1771–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerrow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Mace, G.G. Cirrus Microphysical Properties and Air Motion Statistics Using Cloud Radar Doppler Moments. Part I: Algorithm Description. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1690–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Albrecht, B. The Turbulence Structure in a Continental Stratocumulus Cloud from Millimeter-Wavelength Radar Observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémillard, J.; Fridlind, A.M.; Ackerman, A.S.; Tselioudis, G.; Kollias, P.; Mechem, D.B.; Chandler, H.E.; Luke, E.; Wood, R.; Witte, M.K.; et al. Use of cloud radar Doppler spectra to evaluate stratocumulus drizzle size distributions in large-eddy simulations with size-resolved microphysics. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 3264–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, S.; Shupe, M.; Djalalova, I.; Feingold, G.; Poellot, M. The Retrieval of Stratus Cloud Droplet Effective Radius with Cloud Radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokol, Z.; Mináˇrová, J.; Novák, P. Classification of Hydrometeors Using Measurements of the Ka-Band Cloud Radar Installed at the Milešovka Mountain (Central Europe). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sassen, K. Cloud Type and Macrophysical Property Retrieval Using Multiple Remote Sensors. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1665–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Kollias, P.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Long, C.N.; Kalesse, H.; Chandra, A.; Kumar, V.V.; Protat, A. Stratiform and convective precipitation observed by multiple radars during the DYNAMO/AMIE experiment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 2503–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Johnson, K.; Liu, Y.; Wiscombe, W. High resolution retrieval of liquid water vertical distributions using collocated Ka-band and W-band cloud radars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L24807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, R.J.; Jakob, C.; Illingworth, A.J. Comparison of ECMWF Winter-Season Cloud Fraction with Radar-Derived Values. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2001, 40, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, G.L.; Wood, N.B. Properties of Tropical Convection Observed by Millimeter-Wave Radar Systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, B.; Raymond, D.J.; Grubišić, V.; Davis, C.A.; Barth, M.C.; Detwiler, A.; Klein, P.M.; Lee, W.; Markowski, P.M.; MullenDore, G.L.; et al. Recommendations for in situ and remote sensing capabilities in atmospheric convection and turbulence. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 2463–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Zheng, J.F.; Wu, J.Y. A Ka-band solid-state transmitter cloud radar and data merging algorithm for its measurements. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, J.F.; Gao, W.H. Comparing and merging observation data from Ka-band cloud radar, C-band frequency-modulated continuous wave radar and ceilometer systems. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.A.; Meneghini, R.; Kozu, T. The shape-slope relation in observed gamma raindrop size distributions: Statistical error or useful information? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, X. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distributions observed in East China during the Asian summer monsoon season using 2-D video distrometer and micro rain data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Peterson, W.A.; Gatlin, P.; Wingo, M. Comparison of raindrop size distribution measurements by collocated disdrometers. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1672–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monique, P.; Amadou, S.Y.; Axel, G. Statistical characteristics of the noise power spectral density in UHF and VHF wind profilers. Radio Sci. 1997, 32, 1229–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J. Algorithms for Doppler Spectral Density Data Quality Control and Merging for the Ka-Band Solid-State Transmitter Cloud Radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Rémillard, J.; Luke, E.; Szyrmer, W. Cloud radar Doppler spectra in drizzling stratiform clouds:1. Forward modeling and remote sensing applications. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Szyrmer, W.; Rémillard, J.; Luke, E. Cloud radar Doppler spectra in drizzling stratiform clouds:2. Observations and microphysical modeling of drizzle evolution. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Fan, Y.W.; Li, F.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, X. The attenuation correction for a 35GHz ground-based cloud radar. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2013, 32, 325–330. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y. Attenuation-Based Estimates of Rainfall Rates Aloft with Vertically Pointing Ka-band Radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.R. An extension of the Z-R relation for Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the 11th Weather Radar Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 14–18 September 1964; pp. 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, D.; Amayenc, P. A New Method for Deducing Hydrometeor-Size Distributions and Vertical Air Motions from Doppler Radar Measurements at Vertical Incidence. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gossard, E.E. Measurement of cloud droplet size spectra by Doppler radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1994, 11, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupe, M.D.; Kollias, P.; Matrosov, S.Y.; Schneider, T.L. Deriving mixed-phase cloud properties from Doppler radar spectra. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The terminal velocity of fall for water droplets in stagnant air. J. Meteorol. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, G.B.; Du, T.P.S. Terminal velocity of raindrops aloft. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1969, 8, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ding, H.; Dong, X.; Cao, J.; Su, T. Applications of QC and Merged Doppler Spectral Density Data from Ka-Band Cloud Radar to Microphysics Retrieval and Comparison with Airplane in Situ Observation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Raindrop size distribution measurements at 4,500 m on the Tibetan Plateau during TIPEX-III. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11092–11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procù, F.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Prodi, F.; Caracciolo, C. Rain drop size distribution over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2014, 150, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Tokey, A. PARSIVEL snow observations: A critical assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuter, S.E.; Houze, R.A. Measurements of raindrop size distributions over the Pacificwarmpool and implications for Z–R relations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Ulbrich, C.W. Path and area integrated rainfall measurement by microwave in the 1~3 cm band. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1977, 16, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, E.P.; Kollias, P.; Karen, L.J.; Clothiaux, E.E. A Technique for the Automatic Detection of Insect Clutter in Cloud Radar Returns. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1498–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görsdorf, U.; Volker, L.; Matthias, B.; Gerhard, P.; Dmytro, V.; Vladimir, V.; Vadim, V. A 35-GHz polarimetric doppler radar for long-term observations of cloud parameters-description of system and data processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; May, P.T.; Shupe, M.D. Rainfall profiling using atmospheric radiation measurement program vertically pointing 8-mm wavelength radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 1478–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Albrecht, B. Vertical velocity statistics in fair weather cumuli at the ARM TWP Nauru climate research facility. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 6590–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, E.P.; Kollias, P. Separating Cloud and Drizzle Radar Moments during Precipitation Onset Using Doppler Spectra. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Bansemer, A.; Matrosov, S. The 94 GHz radar dim band: Relevance to ice cloud properties and CloudSat. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L03802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, P.; Albrecht, B.A.; Marks, F.D. Cloud radar observations of vertical drafts and microphysics in convective rain. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, R.S.; Srivastava, R.C. Doppler Radar Observations of Drop-Size Distributions in a Thunderstorm. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]














| Items | Technical Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Radar system | Doppler, solid-state, depolarization | |
| Frequency | 33.44 GHz | |
| Wavelength | 8.9 mm | |
| Transmitted peak power | ≥100 W | |
| Antenna gain | 53 dB | |
| Beam width | 0.3 degree | |
| Pulse width | 0.2 , 12 | |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 8333 Hz | |
| Gate number | 510 | |
| Sensitivity | −38 dBZ at 5 km | |
| Resolutions | Horizontal resolution | 26 m at 5 km |
| Vertical resolution | 30 m | |
| Temporal resolution | ~9 s (adjustable) | |
| Detectable range | Height | 150 m–15.3 km |
| Measurable reflectivity range | −50–30 dBZ | |
| Unambiguous velocity range | −18.54–+18.54 | |
| Measurements | Original data | Doppler velocity spectra |
| Spectral moments | Reflectivity, mean Doppler velocity, spectrum width, linear depolarization ratio | |
| Items | Technical Specifications |
|---|---|
| Sensor type | Laser |
| Frequency | 50 KHz |
| Operating power | ≥2 W |
| Sampling height | 1.4 m |
| Sampling area | 54 cm2 |
| Measurable particle type | Solid, mixed, liquid |
| Measurable particle diameter range | 0.062–24.5 mm (32 channels) |
| Measurable particle falling speed | 0.05–20.8 (32 channels) |
| Measurement | Particle size (32 channels), particle falling speed (32 channels), particle number, rain rate, reflectivity, accumulated rain amount |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Che, Y. A Study of Vertical Structures and Microphysical Characteristics of Different Convective Cloud–Precipitation Types Using Ka-Band Millimeter Wave Radar Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151810
Zheng J, Zhang P, Liu L, Liu Y, Che Y. A Study of Vertical Structures and Microphysical Characteristics of Different Convective Cloud–Precipitation Types Using Ka-Band Millimeter Wave Radar Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(15):1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151810
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jiafeng, Peiwen Zhang, Liping Liu, Yanxia Liu, and Yuzhang Che. 2019. "A Study of Vertical Structures and Microphysical Characteristics of Different Convective Cloud–Precipitation Types Using Ka-Band Millimeter Wave Radar Measurements" Remote Sensing 11, no. 15: 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151810
APA StyleZheng, J., Zhang, P., Liu, L., Liu, Y., & Che, Y. (2019). A Study of Vertical Structures and Microphysical Characteristics of Different Convective Cloud–Precipitation Types Using Ka-Band Millimeter Wave Radar Measurements. Remote Sensing, 11(15), 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151810