Synergy of Satellite, In Situ and Modelled Data for Addressing the Scarcity of Water Quality Information for Eutrophication Assessment and Monitoring of Swedish Coastal Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- to evaluate horizontal coastal-open sea gradients of CHL-a and SD derived from MERIS (monthly averages) between 2002–2012 and to validate them against in situ data and to apply a correction if necessary and subsequently,
- (2)
- to evaluate the results against corresponding water quality parameters derived from the SCM, and
- (3)
- to investigate the degree of coupling between two sets of independently acquired data—i.e., satellite vs. modelled and thereby to infer information about nutrient status from satellite data.
- (4)
- Another objective is to assess which of the discussed method is best able to depict changes in phytoplankton phenology.
2. Materials and Methods
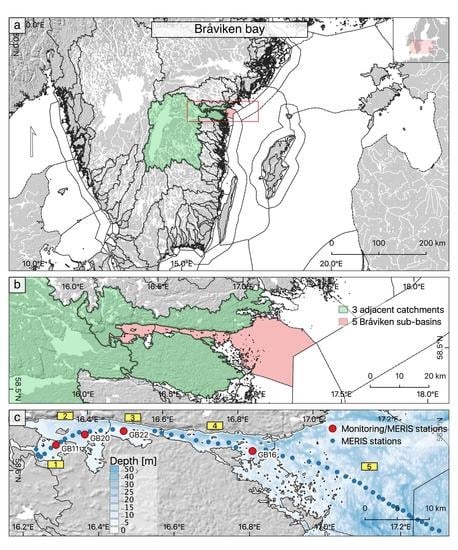
2.1. Area of Investigation
2.2. National Monitoring Data
2.3. Satellite-Derived Water Quality Data
Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MERIS) Data Processing
2.4. Application of a Calibration Algorithm for MERIS CHL-a Data Derived from FUB
2.5. Derived Water Quality Estimates from the Swedish Coastal Zone Model (SCM)
2.5.1. Parameterization of CHL-a in the SCM
2.5.2. Parameterization of Secchi Depth in the SCM
2.5.3. Parameterization of Total Nitrogen in the SCM
2.6. Horizontal Transects from the Inner Bay out into the Open Sea
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Horizontal CHL-a Gradients along the Near-Coastal-to-Open Sea Transects
3.2. Horizontal SD Gradients along the Near-Coastal-to-Open Sea Transects
3.3. Comparison between MERIS and SCM
3.4. Evaluation of CHL-a Derived from MERIS versus CHL-a Derived from the SCM
3.5. Evaluation of Secchi Depth Derived from MERIS versus Modelled Secchi Depth
3.6. Relationship between Calibrated CHL-a (MERIS) and Modelled Total Nitrogen (SCM)
4. Discussion
4.1. Synergy between MERIS, In Situ and SCM Data
4.2. Potential Advantages and Challenges for Monitoring Water Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harvey, E.T.; Walve, J.; Andersson, A.; Karlson, B.; Kratzer, S. The Effect of Optical Properties on Secchi Depth and Implications for Eutrophication Management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, P.; Gilpin, L.; Svendsen, H.; Erlandsson, C.P.; Larsson, U.; Kratzer, S.; Fouilland, E.; Janzen, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Grenz, C.; et al. Eutrophication and some European waters of restricted exchange. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1635–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, S.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Eutrophication in the Baltic Sea—An integrated thematic assessment of the effects of nutrient enrichment and eutrophication in the Baltic Sea region. In Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings 115B; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission – HELCOM: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. State of the Baltic Sea – Second HELCOM holistic assessment 2011-2016. In Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings 155; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission – HELCOM: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saaltink, R.; van der Velde, Y.; Dekker, S.C.; Lyon, S.W.; Dahlke, H.E. Societal, land cover and climatic controls on river nutrient flows into the Baltic Sea. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2014, 1, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golterman, H.L.; de Oude, N.T. Eutrophication of Lakes, Rivers and Coastal Seas BT—Water Pollution. In Water Pollution; Allard, B., Craun, G.F., de Oude, N.T., Falkenmark, M., Golterman, H.L., Lindstrom, T., Piver, W.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 79–124. ISBN 978-3-540-46685-7. [Google Scholar]
- Boesch, D.F.; Hecky, R.; O’Melia, C.; Schindler, D.; Seitzinger, S. Eutrophication of Swedish Seas; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency Naturvårdsverket: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006; ISBN 9162055097.
- Boesch, D.; Carstensen, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Skjoldal, H.R.; Voss, M. Eutrophication of seas along Sweden’s West Coast. In Report no. 5898; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2008; 79p, ISBN 978-91-620-5898-2. [Google Scholar]
- Vahtera, E.; Conley, D.J.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Kuosa, H.; Pitkänen, H.; Savchuk, O.P.; Tamminen, T.; Viitasalo, M.; Voss, M.; Wasmund, N.; et al. Internal Ecosystem Feedbacks Enhance Nitrogen-fixing Cyanobacteria Blooms and Complicate Management in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 2007, 36, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.; Dippner, J.W.; Humborg, C.; Hürdler, J.; Korth, F.; Neumann, T.; Schernewski, G.; Venohr, M. History and scenarios of future development of Baltic Sea eutrophication. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österblom, H.; Hansson, S.; Larsson, U.; Hjerne, O.; Wulff, F.; Elmgren, R.; Folke, C. Human-induced trophic cascades and ecological regime shifts in the baltic sea. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Therese Harvey, E.; Philipson, P. The use of ocean color remote sensing in integrated coastal zone management—A case study from Himmerfjärden, Sweden. Mar. Policy 2014, 43, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. The Baltic Sea Action Plan (BSAP). In Proceedings of the HELCOM Ministerial Meeting of the Helsinki Commission, Krakow, Poland, 15 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzer, S.; Håkansson, B.; Sahlin, C. Assessing Secchi and photic zone depth in the Baltic Sea from satellite data. Ambio 2003, 32, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Tett, P. Using bio-optics to investigate the extent of coastal waters: A Swedish case study. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Communities; Water Framework Directive (WFD). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Dramework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. Official Journal of the European Communities 2000, L327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Naturvårdsverket. Naturvårdsverkets Författningssamling; NFS 2006:1; Naturvårdsverket: 2004; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006. (In Swedish)
- Rantajärvi, E.; Olsonen, R.; Hällfors, S.; Leppänen, J.M.; Raateoja, M. Effect of sampling frequency on detection of natural variability in phytoplankton: Unattended high-frequency measurements on board ferries in the Baltic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 55, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, T.; Kratzer, S.; Philipson, P. Satellite-based water quality monitoring for improved spatial and temporal retrieval of chlorophyll-a in coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Abaunza, J.M.; Kratzer, S.; Höglander, H. Using MERIS data to assess the spatial and temporal variability of phytoplankton in coastal areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 38, 2004–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.; Dahné, J.; Strömqvist, J.; Arheimer, B. Modelling Tools: From Sweden to Pan-European Scales for European WFD Data Requirements. In Proceedings of the BALWOIS 4th International Conference (BALWOIS 2010), Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia, 25–29 May 2010; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, T.; White, G.N.; Zhai, L.; Sathyendranath, S.; Roy, S. The phenology of phytoplankton blooms: Ecosystem indicators from remote sensing. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3057–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikas, K.; Reinart, A. Validation of the MERIS products on large European lakes: Peipsi, Vänern and Vättern. Hydrobiologia 2008, 599, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyryliuk, D. Total Suspended Matter Derived from MERIS Data as an Indicator of Coastal Processes in the Baltic Sea. Master’s Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kyryliuk, D.; Kratzer, S. Evaluation of Sentinel-3A OLCI products derived using the Case-2 Regional CoastColour Processor over the Baltic Sea. Sensors 2019, 16, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westman, Y.; Pettersson, O.; Wingqvist, E. Arbete med SVAR version 2016, Svenskt Vattenarkiv - en databas vid SMHI; Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute: Norrköping, Sweden, 2017. (In Swedish)
- Gullstrand, M.; Löwgren, M.; Castensson, R. Water issues in comprehensive municipal planning: A review of the Motala River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 69, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMHI SVAR2012_2. Available online: https://www.smhi.se/data/hydrologi/sjoar-och-vattendrag/ladda-ner-data-fran-svenskt-vattenarkiv-1.20127 (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- Copernicus EU-DEM v1.1—Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/imagery-in-situ/eu-dem/eu-dem-v1.1/view (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- SMHI SHARKweb Database. Available online: https://sharkweb.smhi.se (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- SMHI Havsmiljödata-Marine Environmental Data | SMHI. Available online: https://www.smhi.se/data/oceanografi/havsmiljodata (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- Schroeder, T.; Schaale, M.; Fischer, J. Retrieval of atmospheric and oceanic properties from MERIS measurements: A new Case-2 water processor for BEAM. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5627–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P.; Stedmon, C.A.; Markager, S. Modeling absorption by CDOM in the Baltic Sea from season, salinity and chlorophyll. Mar. Chem. 2006, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Vinterhav, C. Improvement of MERIS level 2 products in baltic sea coastal areas by applying the improved Contrast between Ocean and Land Processor (ICOL)—Data analysis and validation. Oceanologia 2010, 52, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Abaunza, J.M.; Kratzer, S.; Brockmann, C. Evaluation of MERIS products from Baltic Sea coastal waters rich in CDOM. Ocean Sci. 2014, 10, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florén, K.; Philipson, P.; Strömbeck, N.; Nyström Sandman, A.; Isaeus, M.; Wijkmark, N. Satellite-Derived Secchi Depth for Improvement of Habitat Modelling in Coastal Areas; AquaBiota Report 2012-02; AquaBiota Water Research: Stockholm, Sweden, 2012; ISBN 978-91-85975-18-1. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA CCI Land Cover ATBD. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Pre-Processing Year 3- 1.1. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=2ahUKEwjHp5CIirHkAhWC7GEKHUQmDE0QFjAAegQIABAC&url=http%3A%2F%2Fcci.esa.int%2Ffiledepot_download%2F253%2F288&usg=AOvVaw2EW4EEGJCQNw1lFzmPstQG (accessed on 20 July 2019).
- Brockmann, C.; Paperin, M.; Danne, O.; Ruescas, A. Multi-Sensor Cloud Screening and Validation: IdePix and PixBox. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Space Agency Living Planet Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Philipson, P.; Kratzer, S.; Ben Mustapha, S.; Strömbeck, N.; Stelzer, K. Satellite-based water quality monitoring in Lake Vänern, Sweden. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3938–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommersom, A.; Kratzer, S.; Strömbeck, N.; Philipson, P. Characterisation of the Optical Properties of Lake Vänern, Sweden, for Improved Water Quality Mapping by Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstract and Poster Presentation at Ocean Optics, Glasgow, UK, 8–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arheimer, B.; Nilsson, J.; Lindström, G. Experimenting with coupled hydro-ecological models to explore measure plans and water quality goals in a semi-enclosed Swedish Bay. Water 2015, 7, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlberg, J.; Marmefelt, E.; Brandt, M.; Hjerdt, N.; Lundholm, K. HOME Vatten i Norra Östersjöns Vattendistrikt Integrerat Modellsystem för Vattenkvalitetsberäkningar; SMHI, Oceanografi Rapport Nr. 93; Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute: Norrköping, Sweden, 2008. (In Swedish)
- Edman, M.; Eilola, K.; Almroth-Rosell, E.; Meier, H.E.M.; Wåhlström, I.; Arneborg, L. Nutrient Retention in the Swedish Coastal Zone. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almroth-Rosell, E.; Edman, M.; Eilola, K.; Markus Meier, H.E.; Sahlberg, J. Modelling nutrient retention in the coastal zone of an eutrophic sea. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 5753–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R software for statistical computing (version 3.6.0). 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 20 July 2019).
- Cristina, S.; Goela, P.; Icely, J. Assessment of water-leaving reflectances of oceanic and coastal waters using MERIS satellite products off the southwest coast of Portugal. J. Coast. 2009, II, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Z.P.; Du, K.P.; Arnone, R. A model for the diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance. J. Geophys. Res. C Ocean. 2005, 110, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Kyryliuk, D.; Brockmann, C. Inorganic Suspended Matter as an indicator of terrestrial influence in Baltic Sea coastal areas—Algorithm development, validation and ecological relevance. 2019. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Kyryliuk, D. Baltic Sea from Space. The Use of Ocean Color Data to Improve our Understanding of Ecological Drivers Across the Baltic Sea basin—Algorithm Development, Validation and Ecological Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences, Faculty of Science, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Communities; Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Marine Environmental Policy. Official Journal of the European Union 2008, L164, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vinterhav, C. Remote Sensing of Baltic Coastal Waters Using MERIS—A Comparison of Three Case-2 Water Processors. Master’s Thesis, Deapartment of Physical Geography, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bukanova, T.; Kopelevich, O.; Vazyulya, S.; Bubnova, E.; Sahling, I. Suspended matter distribution in the south-eastern Baltic Sea from satellite and in situ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 9317–9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyryliuk, D.; Kratzer, S. Summer Distribution of Total Suspended Matter Across the Baltic Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohde, T.; Siegel, H.; Gerth, M. Validation of MERIS Level-2 products in the Baltic Sea, the Namibian coastal area and the Atlantic Ocean. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raag, L.; Sipelgas, L.; Uiboupin, R. Analysis of natural background and dredging-induced changes in TSM concentration from MERIS images near commercial harbours in the Estonian coastal sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6764–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Arst, H.; Paavel, B.; Laas, A.; Nõges, T. Spatial and temporal variations in coloured dissolved organic matter in large and shallow Estonian waterbodies. Boreal Environ. Res. 2009, 14, 959–970. [Google Scholar]
- Vaičiūtė, D.; Bresciani, M.; Bučas, M. Validation of MERIS bio-optical products with in situ data in the turbid Lithuanian Baltic Sea coastal waters. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 63568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.; Babin, M.; Hembise, O.; Mangin, A.; Garnesson, P. Ocean transparency from space: Validation of algorithms estimating Secchi depth using MERIS, MODIS and SeaWiFS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2986–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikas, K.; Kratzer, S. Improved retrieval of Secchi depth for optically-complex waters using remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Dellwig, O.; Kuliński, K.; Omstedt, A.; Pollehne, F.; Rehder, G.; Savchuk, O. Biogeochemical cycles BT—Biological Oceanography of the Baltic Sea; Snoeijs-Leijonmalm, P., Schubert, H., Radziejewska, T., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 87–122. ISBN 978-94-007-0668-2. [Google Scholar]
- Brockmann, C.; Doerffer, R.; Peters, M.; Stelzer, K.; Embacher, S.; Ruescas, A. Evolution of the C2RCC neural network for Sentinel 2 and 3 for the retrieval of ocean colour products in normal and extreme optically complex waters. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; Volume 740, pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Vodacek, A.; Blough, N.V.; DeGrandpre, M.D.; DeGrandpre, M.D.; Nelson, R.K. Seasonal variation of CDOM and DOC in the Middle Atlantic Bight: Terrestrial inputs and photooxidation. Limnology and Oceanography 1997, 42, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hägg, H.E.; Lyon, S.W.; Wällstedt, T.; Mörth, C.M.; Claremar, B.; Humborg, C. Future nutrient load scenarios for the Baltic Sea due to climate and lifestyle changes. Ambio 2014, 43, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, S.W.; Meidani, R.; van der Velde, Y.; Dahlke, H.E.; Swaney, D.P.; Mörth, C.M.; Humborg, C. Seasonal and regional patterns in performance for a Baltic Sea Drainage Basin hydrologic model. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerberg, I.; Gustavsson, H.; Sonesten, L. Impact of discharge data uncertainty on nutrient load uncertainty. EGU Gen. Assem. Conf. Abstr. 2016, 18, 12039. [Google Scholar]
- Rönnback, P.; Sonesten, L.; Wallin, M. Ämnestransporter under Vårflöden i Ume älv och Kalix älv; Institutionen för vatten och miljö, Sveriges Lantbruksuniversitet, SLU: Uppsala, Sweden, 2009. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar]
- Kratzer, S.; Brockmann, C.; Moore, G. Using MERIS full resolution data to monitor coastal waters—A case study from Himmerfjarden, a fjord-like bay in the northwestern Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2284–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Tamminen, T.; Lehtinen, S.; Jürgens, K.; Labrenz, M.; Viitasalo, M. The pelagic food web. In Biological Oceanography of the Baltic Sea; Snoeijs-Leijonmalm, P., Schubert, H., Radziejewska, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 281–332. ISBN 978-94-007-0668-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kahru, M.; Leppanen, J.M.; Rud, O. Cyanobacterial blooms cause heating of the sea surface. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 101, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Moore, G. Inherent Optical Properties of the Baltic Sea in Comparison to Other Seas and Oceans. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernes, C. Change Beneath the Surface: An In-Depth Look at Sweden’s Marine Environment; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2005; ISBN 9162012460.












| Water Body (no) | Water Body Name in English (In Swedish) | Monitoring Station | No of ‘Pins’ per Waterbody |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pampusfjärden (Pampusfjärden) | GB11 | 7 |
| 2 | Inner Bråviken (Inre Bråviken) | GB20 | 6 |
| 3 | Mid-Bråviken (Mellersta Bråviken) | GB22 | 5 |
| 4 | Outer Bråviken (Yttre Bråviken) | GB16 | 9 |
| 5 | Bråviken coastal waters (Bråvikens kustvatten) | None | 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kratzer, S.; Kyryliuk, D.; Edman, M.; Philipson, P.; Lyon, S.W. Synergy of Satellite, In Situ and Modelled Data for Addressing the Scarcity of Water Quality Information for Eutrophication Assessment and Monitoring of Swedish Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172051
Kratzer S, Kyryliuk D, Edman M, Philipson P, Lyon SW. Synergy of Satellite, In Situ and Modelled Data for Addressing the Scarcity of Water Quality Information for Eutrophication Assessment and Monitoring of Swedish Coastal Waters. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(17):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172051
Chicago/Turabian StyleKratzer, Susanne, Dmytro Kyryliuk, Moa Edman, Petra Philipson, and Steve W. Lyon. 2019. "Synergy of Satellite, In Situ and Modelled Data for Addressing the Scarcity of Water Quality Information for Eutrophication Assessment and Monitoring of Swedish Coastal Waters" Remote Sensing 11, no. 17: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172051
APA StyleKratzer, S., Kyryliuk, D., Edman, M., Philipson, P., & Lyon, S. W. (2019). Synergy of Satellite, In Situ and Modelled Data for Addressing the Scarcity of Water Quality Information for Eutrophication Assessment and Monitoring of Swedish Coastal Waters. Remote Sensing, 11(17), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172051