Evaluation of CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H Cloud Cover Climate Data Records over Europe with ECA&D Ground-Based Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. CLARA-A2
2.2. ISCCP-H
2.3. Summary of Differences between CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H
2.4. ECA&D Surface Observations
3. Results
3.1. Climatologies and Differences of CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H
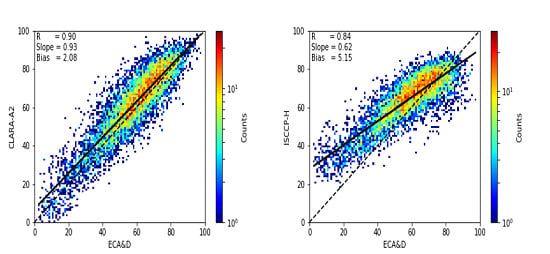
3.2. Validation against ECA&D Ground Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norris, J.R.; Allen, R.J.; Evan, A.T.; Zelinka, M.D.; O’Dell, C.W.; Klein, S.A. Evidence for climate change in the satellite cloud record. Nature 2016, 536, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bony, S.; Stevens, B.; Frierson, D.M.W.; Jacob, C.; Kageyama, M.; Pincus, R.; Shepherd, T.G.; Sherwood, S.C.; Siebesma, A.P.; Sobel, A.H.; et al. Clouds, circulation and climate sensitivity. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. 2013: Clouds and aerosols. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Doschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 571–657. [Google Scholar]
- Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.G.; King, M.D.; Wind, G.; Amarasinghe, N.; Marchant, B.; Arnold, G.T.; Zhang, Z.B.; Hubanks, P.A.; Holz, R.E.; et al. The MODIS Cloud Optical and Microphysical Products: Collection 6 Updates and Examples from Terra and Aqua. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 502–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Foster, M.J.; Walther, A.; Zhao, X. The Pathfinder Atmospheres Extended (PATMOS-x) AVHRR Climate Dataset. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.G.; Hanschmann, T.; Stengel, M.; Meirinh, J.F. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, CM SAF Cloud, Albedo, Radiation data record, AVHRR-based, Edition 2 (CLARA-A2); Cloud Products (level-1 to level-3); Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring (CM SAF): Darmstadt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, K.G.; Antilla, K.; Trentmann, J.; Stengel, M.; Meirink, J.F.; Devasthale, A.; Hanschmann, T.; Kothe, S.; Jääskeläinen, E.; Sedlar, J.; et al. CLARA-A2: The second edition of the CM SAF cloud and radiation data record from 34 years of global AVHRR data. Atmos Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5809–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.H.; Knapp, K.R.; Inamdar, A.; Hankinns, W.; Rossow, W.B. The International Cloud Climatology Project H-Series climate data record product. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Walker, A.; Golea, V.; Knapp, K.R.; Young, A.; Inamdar, A.; Hankins, B. NOAA’s Climate Data Record Program: International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project Climate Data Record; H-Series; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2016.
- Karl, T.R.; Steuer, P.M. Increased cloudiness in the United States during the first half of the Twentieth Century: Fact or fiction? Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, M.; Sun, B. Trends in US total cloud cover from a homogeneity-adjusted dataset. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 4959–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Calbó, J.; Wild, M. Increasing cloud cover in the 20th century: Review and new findings in Spain. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.H.; Hewitson, B.; Busuioc, A.; Chen, A.; Gao, X.; Held, I.; Jones, R.; Kolli, R.K.; Kwon, W.-T.; Laprise, R.; et al. Regional Climate Projections. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Enriquez-Alonso, A.; Calbó, J.; González, J.A.; Wild, M.; Folini, D.; Norris, J.R.; Vicente-Serano, S.M. Fewer Clouds in the Mediterranean: Consistency of observations and climate simulations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 414715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsias, G.; Lolis, C.J. A study on the total cloud cover variability over the Mediterranean region during the period 1979-2014 with the use of the ERA-Interim database. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerkötter, R.; Köning, C.; Bissoli, P.; Gesell, G.; Mannstein, H. A 14-year European Cloud Climatology from NOAA/AVHRR data in comparison to surface observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L15103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez-Alonso, A.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Calbó, J.; González, J.A.; Norris, J.R. Cloud Cover climatologies in the Mediterranean obtained from satellites, surface observations, reanalyses, and CMIP5 simulations: Validation and future scenarios. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levizzani, V.; Pinelli, F.; Pasqui, M.; Melani, S.; Laing, A.G.; Carbone, R.E. A 10-year climatology of warm-season cloud patterns over Europe and the Mediterranean from Meteosat IR observations. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Baena-Calatrava, R.; Echave-Calvo, I.; Connell, B.H.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; López-Moreno, J.I. A daytime over land algorithm for computing AVHRR convective cloud climatologies for the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. Int. J. Clim. 2013, 33, 2113–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.G. A 10-year cloud climatology over Scandinavia derived from NOAA Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer imagery. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1023–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, M.; Kriebel, K.T. Alpine cloud climatology using long-term NOAA-AVHRR satellite data. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2001, 57, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.R.; Wild, M. Trends in aerosol radiative effects over Europe inferred from observed cloud cover, solar “dimming,” and solar “brightening”. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D08214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.G.; Eastman, R.M.; Hahn, C.J. A Survey of Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types over Land from Surface Observations, 1971–96. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas, M.; Li, L.Z.; Kanakidou, M.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Seze, G.; Le Treut, H. Winter weather regimes over the Mediterranean region: their role for the regional climate and projected changes in the twenty-first century. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, E.; Lolis, C.J.; Papadimas, C.D.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Bartzokas, A. On the intra-annual variation of cloudiness over the Medirranean region. Atmos. Res. 2017, 208, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.G.; Riihelä, A.; Müller, R.; Meirink, J.F.; Sedlar, J.; Stengel, M.; Lockhoff, M.; Trentmann, J.; Kaspar, F.; Hollmann, R.; et al. CLARA-A1: A cloud, albedo, and radiation dataset from 28 yr of global AVHRR data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5251–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybbroe, A.; Thoss, A.; Karlsson, K.-G. NWCSAF AVHRR cloud detection and analysis using dynamic thresholds and radiative transfer modeling. Part 1: Algorithm description. J. Appl. Meteor. 2005, 44, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Evan, A.T.; Foster, M.J.; Walther, A. A naive Bayesian cloud-detection scheme derived from CALIPSO and applied within PATMOS-x. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasthale, A.; Raspaud, M.; Schlundt, C.; Hanschmann, T.; Finkensieper, S.; Dybbroe, A.; Hörnquist, S.; Håkansson, N.; Stengel, M.; Karlsson, K.-G. PyGAC: An open-source, community-driven Python interface to preprocess the nearly 40- year AVHRR Global Area Coverage (GAC) data record. GSICS Quartherly Newsl. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Schiffer, R.A. Advances in understanding clouds from ISCCP. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2261–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Ferrier, J. Evaluation of long-term calibrations of the AVHRR visible radiances. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 744–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Garder, L.C. Cloud Detection Using Satellite Measurements of Infrared and Visible Radiances for ISCCP. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 2341–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossow, W.B.; Walker, A.W.; Garder, L.C. Comparison of ISCCP and other Cloud Amounts. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 2394–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Schiffer, R.A. ISCCP Cloud Data Products. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1991, 72, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.; Hardy, E.; Roach, J.; Witmer, R. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data; Technical Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1976.
- Van der A, R.J.; Allaart, M.A.F.; Eskes, H.J. Multi sensor reanalysis of total ozone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11277–11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OSI SAF: The EUMETSAT OSI SAF Sea Ice Concentration Algorithm; Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, SAF/OSI/CDOP/DMI/SCI/MA/189, Version 1.5; EUMETSAT: Darmstadt, Germany, 2016.
- Moody, E.G.; King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F. Spatially complete global spectral surface albedos: Value-added datasets derived from Terra MODIS land products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 43, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, S.W.; Borbas, E.E.; Knuteson, R.O.; Stephenson, G.R.; Huang, H.-L. Development of a Global Infrared Land Surface Emissivity Database for Application to Clear Sky Sounding Retrievals from Multi-spectral Satellite Radiance Measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Matthews, J.L.; Ho, S.-P.; Yang, Q.; Bates, J.J. Algorithm Development of Temperature and Humidity Profile Retrievals for Long-Term HIRS Observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Rosenlof, K.; Hassler, B.; Hurst, D.; Read, W.; Vömel, H.; Selkirk, H.; Fujiwara, M.; Damadeo, R. The Stratospheric Water and Ozone Satellite Homogenized (SWOOSH) database: A long-term database for climate studies. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, A.; Tilley, F.; Ferguson, M.; Allegrino, A. NOAA operational sounding products for advanced TOVS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4615–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, S.; O’Donnel, D.; Stier, P.; Kloster, S.; Zhang, K.; Schmidt, H.; Rast, S.; Giorgetta, M.; Eck, T.F.; Stevens, B. MAC-v1: A new global aerosol climatology for climate studies. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2013, 5, 704–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.A.; Frei, A. Seasonal variability of Northern Hemisphere snow extent using visible satellite data. Prof. Geogr. 2000, 52, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.D.; Robinson, D.A. Northern Hemisphere spring snow cover variability and change over 1922–2010 including an assessment of uncertainty. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breivik, L.-A.; Eastwood, S.; Lavergne, T. Use of C-Band Scatterometer for Sea Ice Edge Identification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Crawford, J.P.; Drinkwater, M.R.; Eppler, D.T.; Farmer, L.D.; Jentz, R.R.; Wackerman, C.C. Aircraft active and passive microwave validation of sea ice concentration from the Defense Meteorological Program Special Sensor Microwave Imager. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 21989–22008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, T.R.; Merchant, J.W.; Ohlen, D.O.; Brown, J.F. Development of land-cover characteristics database for the conterminous U.S. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Wijngaard, J.B.; Konnen, G.P.; Böhm, R.; Demarée, G.; Gocheva, A.; Mileta, M.; Pashiardis, S.; Hejkrlik, L.; Kern-Hansen, C.; et al. Daily dataset of 20th-century surface air temperature and precipitation series for the European climate assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.-G.; Devasthale, A. Inter-Comparison and Evaluation of the Four Longest Satellite-Derived Cloud Climate Data Records: CLARA-A2, ESA Cloud CCI V3, ISCCP-HGM, and PATMOS-x. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddux, B.C.; Ackerman, S.A.; Platnick, S. Viewing Geometry Dependencies in MODIS Cloud Products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.R. What can cloud observations tell us about climate variability? Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 94, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.R.; Evan, A.T. Empirical Removal of Artifacts from the ISCCP and PATMOS-x Satellite Cloud Records. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.J.; Rossow, W.B.; Warren, S.G. ISCCP cloud properties associated with standard cloud types identified in individual surface observations. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, A.J.; Lindsay, R.W.; Vavrus, S.; Francis, J.A. Arctic Clouds in Multiyear Satellite Data Sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1845–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, L.A.; Temini, M.; Youssef, W.; Weston, M.; Al Mandous, A. Assessment of Total Cloud Amounts and Analysis of Cloud Cover Climatology over the Arabian Peninsula. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2018, 20, EGU2018-7909. [Google Scholar]
- Boers, R.; Brandsma, T.; Siebesma, A.P. Impact of aerosols and clouds on decadal trends in all-sky solar radiation over the Netherlands (1966–2015). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8081–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, K.-G.; Håkansson, N. Characterization of AVHRR global cloud detection sensitivity based on CALIPSO-CALIOP cloud optical thickness information: Demonstration of results based on the CM SAF CLARA-A2 climate data record. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Su, Z.; Calvet, J.-C.; Manninen, T.; Swinnen, E.; Schulz, J.; Roebeling, R.; Poli, P.; Tan, D.; Riihelä, A.; et al. Analysis of current validation practices in Europe for space-based Climate Data Records of Essential Climate Variables. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 42, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, A.; Bell, W.; Brocca, L.; Bulgin, C.E.; Burdanowitz, J.; Calbet, X.; Donner, R.V.; Ghent, D.; Gruber, A.; Kaminski, T.; et al. Validation practices for satellite-based Earth observation data across communities. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 779–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z.; Timmermans, W.J.; Zeng, Y.; Schulz, J.; John, V.O.; Roebeling, R.A.; Poli, P.; Tan, D.; Kaspar, F.; Kaiser-Weiss, A.K.; et al. An overview of European efforts in generating climate data records. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| CLARA-A2 | ISCCP-H | |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Climate Data Records (FCDRs) | Based on an AVHRR GAC FCDR described in [7], including shortwave calibration with MODIS Collection 6 as a reference, removal of corrupt data, and noise reduction for AVHRR channel 3b. | Generated by applying HBT tables to B1U geostationary satellite data and AVHRR GAC radiances. |
| Cloud Detection Algorithms | Based on an upgraded version (patch 1) of the PPS (Polar Platform System) Version 2014 cloud processing package. | Improved version of the D-series algorithm with applied modifications that mostly serve to reduce uncertainties. |
| Ancillary data | Various parameters from ERA-Interim (atmospheric temperature and humidity profiles, surface skin temperature, integrated water vapor, snow cover), land use from Unites States Geological Survey (USGS) in [35], surface elevation from GTOPO30 (http://edcdaac.usgs.gov/gtopo30/), total ozone column from [36], sea ice observations from (OSI SAF, 2016) [37], and MODIS-based surface albedo [38] and surface emissivity [39]. | Atmospheric temperature-humidity profiles (HIRS, SAGE, MLS) [40,41], total column ozone abundance (TOMS, OMI, SBUV, TOVS) [42], tropospheric and stratospheric aerosol optical properties (MACv.1, SAGEII) [43], land snow cover (NOAA) [44,45] and ocean sea ice cover (OSI-SAF, SSM/I) [46,47], land surface type (MODIS IGBP) [48] and topographic height information (USGS EROS) and land water mask (USGS AVHRR). |
| Satellites | Combines day and night measurements from all available satellites. The number of satellites varies from one in the early part of the record to at least four in the last decade. With each satellite having two (daytime plus nighttime) or—towards higher latitudes—more overpasses over a specific location per day. | Between 55°S and 55°N geostationary satellites are used. At higher latitudes, ISCCP uses both morning and afternoon polar orbiting satellites simultaneously for the gridded data products. |
| Spectral Channels | Incorporates six spectral channels. | Incorporates one VIS and one IR channel. |
| Satellite | Start | End | Equatorial Overpass Time | In CLARA-A2 | In ISCCP-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOAA-7 | 24 Aug 1981 | 7 Jun 1986 | 0230 PM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-8 | 3 May 1983 | 31 Oct 1985 | 0730 AM | no | yes |
| NOAA-9 | 25 Feb 1985 | 11 May 1994 | 0230 AM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-10 | 17 Nov 1986 | 17 Sep 1991 | 0730 AM | no | yes |
| NOAA-11 | 8 Nov 1988 | 13 Sep 1994 | 0200 AM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-12 | 14 May 1991 | 15 Dec 1994 | 0730 AM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-14 | 30 Dec 1994 | 23 May 2007 | 0130 PM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-15 | 13 May 1998 | 31 Dec 2012 | 0730 AM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-16 | 21 Sep 2000 | 9 Jun 2014 | 0200 PM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-17 | 24 Jun 2002 | 31 Dec 2012 | 1000 AM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-18 | 30 Aug 2005 | 31 Dec 2012 | 0200 PM | yes | yes |
| NOAA-19 | 2 Jun 2009 | 31 Dec 2012 | 0200 PM | yes | yes |
| MetOp-A | 20 Jun 2007 | 31 Dec 2012 | 0930 AM | yes | yes |
| MET-2 | Jul 1983 | Jul 1988 | no | yes | |
| MET-3 | Aug 1988 | Apr 1990 | no | yes | |
| MET-4 | May 1990 | Jan 1994 | no | yes | |
| MET-5 | Feb 1994 | Dec 2006 | no | yes | |
| MET-6 | Mar 1997 | May 1998 | no | yes | |
| MET-7 | Jun 1998 | Dec 2012 | no | yes | |
| MSG-1 | Jul 2006 | Apr 2007 | no | yes | |
| MSG-2 | May 2007 | Dec 2012 | no | yes |
| ECA&D Station | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| Tromsø (1) | 69.65°N | 18.93°E |
| Oslo-Blindern (2) | 59.94°N | 10.72°E |
| Stockholm (3) | 59.35°N | 18.05°E |
| Eskdalemuir (4) | 55.32°N | 03.20°W |
| Groningen (5) | 53.12°N | 06.58°E |
| De Bilt (6) | 52.10°N | 05.18°E |
| Heathrow (7) | 51.48°N | 00.45°E |
| Wien (8) | 48.23°N | 16.35°E |
| München-Botanischer Garten (9) | 48.16°N | 11.50°E |
| Geneve-Observatoire (10) | 46.25°N | 06.13°E |
| Lugano (11) | 46.00°N | 08.97°E |
| Zagreb-Gric (12) | 45.82°N | 15.98°E |
| Belgrade (13) | 44.80°N | 20.47°E |
| A Coruña (14) | 43.37°N | 08.42°W |
| Bilbao-Aeropuerto (15) | 43.30°N | 02.91°W |
| Zaragoza-Aeropuerto (16) | 41.66°N | 01.01°W |
| Barcelona-Aeropuerto (17) | 41.29°N | 02.07°E |
| Madrid-Barajas (18) | 40.47°N | 03.56°W |
| Corfu (19) | 39.62°N | 19.92°E |
| Athens-Hellinikon (20) | 37.90°N | 23.75°E |
| Sevilla-San Pablo (21) | 37.42°N | 05.88°W |
| Heraklion (22) | 35.33°N | 25.18°E |
| ECA&D Station | MAE | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLARA-A2—ECA&D | ISCCP-H—ECA&D | CLARA-A2—ECA&D | ISCCP-H—ECA&D | |
| Tromsø | 7.0 | 6.2 | 9.0 | 7.8 |
| Oslo-Blindern | 7.2 | 5.8 | 9.3 | 7.6 |
| Stockholm | 6.2 | 6.2 | 8.2 | 8.0 |
| Eskdalemuir | 4.3 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 6.2 |
| Groningen | 6.7 | 10.4 | 8.8 | 12.4 |
| De Bilt | 4.7 | 7.8 | 6.4 | 9.7 |
| Heathrow | 7.2 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 8.5 |
| Wien | 4.8 | 9.2 | 6.6 | 10.8 |
| München-Botanischer Garten | 6.6 | 9.2 | 8.6 | 11.1 |
| Geneve-Observatoire | 4.2 | 8.3 | 6.2 | 10.2 |
| Lugano | 5.7 | 10.4 | 8.0 | 12.5 |
| Zagreb-Gric | 4.6 | 6.8 | 6.2 | 8.7 |
| Belgrade | 8.7 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 11.9 |
| A Coruña | 5.9 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 8.7 |
| Bilbao-Aeropuerto | 7.7 | 7.2 | 10.4 | 9.6 |
| Zaragoza-Aeropuerto | 5.9 | 8.6 | 7.8 | 9.8 |
| Barcelona-Aeropuerto | 5.7 | 9.1 | 7.5 | 10.8 |
| Madrid-Barajas | 9.7 | 9.7 | 11.8 | 11.2 |
| Corfu | 8.5 | 13.1 | 11.4 | 15.3 |
| Athens-Hellinikon | 7.0 | 16.7 | 12.6 | 18.7 |
| Sevilla-San Pablo | 8.1 | 8.4 | 10.5 | 10.2 |
| Heraklion | 6.8 | 11.7 | 9.2 | 14.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tzallas, V.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Benas, N.; Meirink, J.F.; Matsoukas, C.; Stackhouse, P., Jr.; Vardavas, I. Evaluation of CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H Cloud Cover Climate Data Records over Europe with ECA&D Ground-Based Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020212
Tzallas V, Hatzianastassiou N, Benas N, Meirink JF, Matsoukas C, Stackhouse P Jr., Vardavas I. Evaluation of CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H Cloud Cover Climate Data Records over Europe with ECA&D Ground-Based Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(2):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020212
Chicago/Turabian StyleTzallas, Vasileios, Nikos Hatzianastassiou, Nikos Benas, Jan Fokke Meirink, Christos Matsoukas, Paul Stackhouse, Jr., and Ilias Vardavas. 2019. "Evaluation of CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H Cloud Cover Climate Data Records over Europe with ECA&D Ground-Based Measurements" Remote Sensing 11, no. 2: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020212
APA StyleTzallas, V., Hatzianastassiou, N., Benas, N., Meirink, J. F., Matsoukas, C., Stackhouse, P., Jr., & Vardavas, I. (2019). Evaluation of CLARA-A2 and ISCCP-H Cloud Cover Climate Data Records over Europe with ECA&D Ground-Based Measurements. Remote Sensing, 11(2), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020212