Measuring Marine Plastic Debris from Space: Initial Assessment of Observation Requirements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
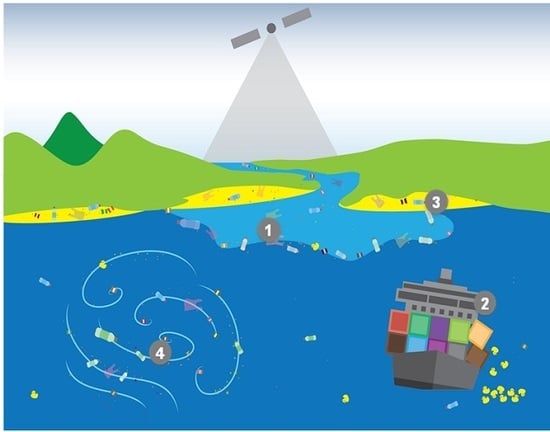
- Question 1 (Q1): What are the magnitude, location and temporal variability of the sources and pathways into the marine environment of marine plastic debris?
- Question 2 (Q2): What are the abundance, horizontal distribution and composition of marine plastic debris, and how do these attributes change over time?
- Question 3 (Q3): Where does marine plastic debris tend to accumulate?
- Question 4 (Q4): How is marine plastic debris transported and what are the dominant physical processes influencing its fate?
- Question 5 (Q5): What role do biological, chemical and photochemical interactions play in controlling the movement and degradation of marine plastic debris?
2. Processes Controlling Marine Plastic Debris Relevant to Satellite Remote Sensing
3. Remote Sensing Methods with Potential for Marine Plastic Debris Detection
3.1. Passive Methods: Radiometry and Imaging Spectrometry
3.2. Active Sensors: LIDAR and RADAR
4. Challenges and Opportunities for Remote Sensing Detection of Marine Plastic Debris
- Challenge 1: to define the SNR for spectroradiometric detection of marine plastic debris.
- Challenge 2: to evaluate remote sensing capabilities on the shoreline.
- Opportunity 2: to exploit synergy between high spectral resolution and high spatial resolution current and planned remote sensing methods.
- Challenge 3: to develop remote sensing methods to specifically detect floating marine plastic debris.
- Opportunity 3: indices to detect floating algae, in combination with other sources of information could be used to separate among floating objects.
- Challenge 4: to liaise with current mission planning to enhance the role of marine plastic debris detection in the requirements specifications.
- Opportunity 4: to coordinate development of the remote sensing system for marine plastic debris at an international level, such that the specific requirements can be fed at the initial stage of development of future observation systems.
5. Conclusions, Implications and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Disclaimer
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergman, M.; Gutow, L.; Klages, M. Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregory, M.; Ryan, P. Pelagic plastic and other seaborne persistent synthetic debris: A review of Southern Hemisphere perspectives. In Marine Debris—Sources, Impacts and Solutions; Coe, J., Rogers, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 46–66. [Google Scholar]
- Erni-Cassola, G.; Zadjelovic, V.; Gibson, M.I.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Distribution of plastic polymer types in the marine environment; A meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.R.; Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.; Blackford, J.; Lewis, C.; Lenton, T.M.; Galloway, T.S. Marine microplastic debris: A targeted plan for understanding and quantifying interactions with marine life. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L. Plastics in the Marine Environment. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sa, L.; Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, F.; Rocha, T.L.; Futter, M.N. Studies of the effects of microplastics on aquatic organisms: What do we know and where should we focus our efforts in the future? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, S.C.; Thompson, R.C. The impact of debris on marine life. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, Á.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Sebille, E.; Wilcox, C.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Hardesty, B.D.; van Franeker, J.A.; Eriksen, M.; Siegel, D.; Galgani, F.; Law, K.L. A global inventory of small floating plastic debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlasticsEurope. The Facts 2016 An analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; Association of Plastics Manufacturers: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgani, F. Marine litter, future prospects for research. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardesty, B.D.; Harari, J.; Isobe, A.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Potemra, J.; van Sebille, E.; Vethaak, A.D.; Wilcox, C. Using Numerical Model Simulations to Improve the Understanding of Micro-plastic Distribution and Pathways in the Marine Environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximenko, N.; Chao, Y.; Moller, D. Developing a remote sensing system to track marine debris. EOS 2016, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.G.; Moore, C.J.; van Franeker, J.A.; Moloney, C.L. Monitoring the abundance of plastic debris in the marine environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maximenko, N.; Corradi, P.; Law, K.L.; Van Sebille, E.; Garaba, S.P.; Lampitt, R.S.; Galgani, F.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Goddijn-Murphy, L.; Veiga, J.M.; et al. Toward the Integrated Marine Debris Observing System. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, C.R.; Meister, G. Mission Requirements for Future Ocean Colour Sensors; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, M.M.; Diner, D.J.; Bézy, J.L. Planning for a spaceborne Earth Observation mission: From user expectations to measurement requirements. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sathyendranath, S. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal and Other Optically-Complex Waters; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I. Measuring the Oceans from Space: The Principles and Methods of Satellite Oceanography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- González-Fernández, D.; Hanke, G. Toward a Harmonized Approach for Monitoring of Riverine Floating Macro Litter Inputs to the Marine Environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emmerik, T.; Kieu-Le, T.C.; Loozen, M.; van Oeveren, K.; Strady, E.; Bui, X.T.; Egger, M.; Gasperi, J.; Lebreton, L.; Nguyen, P.D.; et al. A Methodology to Characterize Riverine Macroplastic Emission Into the Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acha, E.M.; Piola, A.; Iribarne, O.; Mianzan, H. Ecological Processes at Marine Fronts: Oases in the Ocean; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Horner-Devine, A.R.; Jay, D.A.; Orton, P.M.; Spahn, E.Y. A conceptual model of the strongly tidal Columbia River plume. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Nash, J.D.; Bruland, K.W.; Peterson, W.T.; MacCready, P.; Lessard, E.J.; Jay, D.A.; Banas, N.S.; Baptista, A.M.; et al. River Influences on Shelf Ecosystems: Introduction and synthesis. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing to assess spatial distribution of water quality characteristics in large rivers: The Mississippi River and its tributaries in Minnesota. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Shipping Council. Containers Lost at Sea—Update 2017; World Shipping Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, X. Projet Lostcont: Les conteneurs perdus par les navires dans le golfe de Gascogne et ses abords. Bull. d’information du Cedre 2009, 25, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Critchell, K.; Lambrechts, J. Modelling accumulation of marine plastics in the coastal zone; what are the dominant physical processes? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 171, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoellein, T.; Rojas, M.; Pink, A.; Gasior, J.; Kelly, J. Anthropogenic Litter in Urban Freshwater Ecosystems: Distribution and Microbial Interactions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Spatial Patterns of Plastic Debris along Estuarine Shorelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.W.G. Coastal Environments: An Introduction to the Physical, Ecological, and Cultural Systems of Coastlines; Academic Press Limited: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Giardino, A.; Schrijvershof, R.; Nederhoff, C.M.; de Vroeg, H.; Brière, C.; Tonnon, P.K.; Caires, S.; Walstra, D.J.; Sosa, J.; van Verseveld, W.; et al. A quantitative assessment of human interventions and climate change on the West African sediment budget. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippiatt, S.; Opfer, S.; Arthur, C. Marine Debris Monitoring and Assessment; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOSORR46; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013; p. 82.
- Opfer, S.; Arthur, C.; Lippiatt, S. NOAA Marine Debris Shoreline Survey Field Guide; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012; p. 15.
- OSPAR-Commission. Guideline for Monitoring Marine Litter om Beaches in the OSPAR Area; OSPAR: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- TSG-ML. Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas; Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2013; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, M.; Clemens, T.; Förster, H.; Harder, T.; Fleet, D.; Gaus, S.; Grave, C.; Flegel, I.; Schrey, E.; Hartwig, E. Statistical analyses of the results of 25 years of beach litter surveys on the south-eastern North Sea coast. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 109, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Vicente, V.; Clark, J.R.; Lindeque, P.K.; Simis, S.G.H.; Donnelly, R. Application Analysis Report and Marine Litter Mission Requirements Document. V3.1; European Space Agency—ESTEC: Noordvijk, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.R. Accumulation and Subduction of Buoyant Material at Submesoscale Fronts. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, E.A.; Shcherbina, A.Y.; Klymak, J.M.; Molemaker, J.; Novelli, G.; Guigand, C.M.; Haza, A.C.; Haus, B.K.; Ryan, E.H.; Jacobs, G.A. Ocean convergence and the dispersion of flotsam. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hörig, B.; Kühn, F.; Oschütz, F.; Lehmann, F. HyMap hyperspectral remote sensing to detect hydrocarbons. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, F.; Oppermann, K.; Hörig, B. Hydrocarbon Index—An algorithm for hyperspectral detection of hydrocarbons. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafutto, R.D.M.; de Souza Filho, C.R.; de Oliveira, W.J. Hyperspectral remote sensing detection of petroleum hydrocarbons in mixtures with mineral substrates: Implications for onshore exploration and monitoring. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaba, S.P.; Dierssen, H.M. An airborne remote sensing case study of synthetic hydrocarbon detection using short wave infrared absorption features identified from marine-harvested macro- and microplastics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaba, S.P.; Aitken, J.; Slat, B.; Dierssen, H.M.; Lebreton, L.; Zielinski, O.; Reisser, J. Sensing Ocean Plastics with an Airborne Hyperspectral Shortwave Infrared Imager. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11699–11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddijn-Murphy, L.; Dufaur, J. Proof of concept for a model of light reflectance of plastics floating on natural waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaba, S.; Dierssen, H. Spectral Reference Library of 11 Types of Virgin Plastic Pellets Common in Marine Plastic Debris. Data Set. 2017. Available online: https://ecosis.org/search/polymers/%5B%5D/0/6 (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Kokaly, R.F.; Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Livo, K.E.; Hoefen, T.M.; Pearson, N.C.; Wise, R.A.; Benzel, W.M.; Lowers, H.A.; Driscoll, R.L.; et al. USGS Spectral Library Version 7; Report 1035; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Labrie, D.; Chylek, P. Refractive indices of water and ice in the 0.65- to 2.5-μm spectral range. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3531–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transon, J.; d’Andrimont, R.; Maugnard, A.; Defourny, P. Survey of hyperspectral earth observation applications from space in the sentinel-2 context. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.W.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S.; et al. An overview of approaches and challenges for retrieving marine inherent optical properties from ocean color remote sensing. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drinkwater, R.; Rebhan, H. Sentinel-3: Mission Requirements Document; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cetnic, I.; McClain, C.R.; Werdell, P.J. (Eds.) Pre-Aerosols, Clouds, and Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Mission Science Definition Team Report; NASA, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018; Volume 2.
- Topouzelis, K.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Garaba, S.P. Detection of floating plastics from satellite and unmanned aerial systems (Plastic Litter Project 2018). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 79, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hank, T.B.; Berger, K.; Bach, H.; Clevers, J.G.; Gitelson, A.; Zarco-Tejada, P.; Mauser, W. Spaceborne imaging spectroscopy for sustainable agriculture: Contributions and challenges. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 40, 515–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Brando, V.; Gege, P.; Pinnel, N.; Hochberg, E.; Knaeps, E.; Reusen, I.; Doerffer, R.; Bresciani, M.; Braga, F. Imaging spectrometry of inland and coastal waters: State of the art, achievements and perspectives. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 40, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churnside, J.H.; Thorne, R.E. Comparison of airborne lidar measurements with 420 kHz echo-sounder measurements of zooplankton. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 5504–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, C.A.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Hu, Y.; Hair, J.W.; Schulien, J.A. Spaceborne lidar in the study of marine systems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2018, 10, 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, V.; Palombi, L.; Lognoli, D.; Masini, A.; Simeone, E. Experimental tests and radiometric calculations for the feasibility of fluorescence LIDAR-based discrimination of oil spills from UAV. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 61, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ljungholm, M.; Malmqvist, E.; Bianco, G.; Hansson, L.; Svanberg, S.; Brydegaard, M. Inelastic hyperspectral lidar for profiling aquatic ecosystems. Laser Photonics Rev. 2016, 10, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, M.T. Characterization of high-density polyethylene using laser-induced fluorescence (LIF). J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piruska, A.; Nikcevic, I.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, C.; Heineman, W.R.; Limbach, P.A.; Seliskar, C.J. The autofluorescence of plastic materials and chips measured under laser irradiation. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzichino, V.; Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Ruggiero, L. Characterization and discrimination of plastic materials using laser-induced fluorescence. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Hu, Y.; Hostetler, C.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Rodier, S.; Hair, J.W.; Trepte, C. Space-based lidar measurements of global carbon stocks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4355–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Lehner, S. Algorithm for Sea Surface Wind Retrieval From TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2928–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Runge, H.; Suchandt, S.; Kahle, R.; Rossi, C.; Bell, P. Quality Assessment of Surface Current Fields From TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X Along-Track Interferometry and Doppler Centroid Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, M.; Koiwa, M.; Aoki, Y. Applicability of SAR to Marine Debris Surveillance After the Great East Japan Earthquake. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiacomo, P.M.; Washburn, L.; Holt, B.; Jones, B. Coastal pollution hazards in southern California observed by SAR imagery: Stormwater plumes wastewater plumes and natural hydrocarbon seeps. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, D.; Del Frate, F.; Jones, C. Multi-frequency and polarimetric quantitative analysis of the Gulf of Mexico oil spill event comparing different SAR systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Ostrovsky, L.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Komori, S.; Tamura, H. Dynamics and early post-tsunami evolution of floating marine debris near Fukushima Daiichi. Nat. Geosci 2017, 10, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrunes, S.; Brekke, C.; Eltoft, T. Characterization of Marine Surface Slicks by Radarsat-2 Multipolarization Features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5302–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekner, J.; Dorf, M.C. Why some things are darker when wet. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Voss, K.J. Bidirectional reflectance study on dry, wet, and submerged particulate layers: Effects of pore liquid refractive index and translucent particle concentrations. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 8753–8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guo, X. Remote sensing of terrestrial non-photosynthetic vegetation using hyperspectral, multispectral, SAR, and LIDAR data. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 40, 276–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierssen, H.M. Hyperspectral Measurements, Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Correction of Whitecaps and Foam From Visible to Shortwave Infrared for Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Lewis, M.; Johnson, B. Influence of bubbles on scattering of light in the ocean. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 6525–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaeps, E.; Dogliotti, A.; Raymaekers, D.; Ruddick, K.; Sterckx, S. In situ evidence of non-zero reflectance in the OLCI 1020nm band for a turbid estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Feng, L.; Hardy, R.F.; Hochberg, E.J. Spectral and spatial requirements of remote measurements of pelagic Sargassum macroalgae. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoux, J.; Chome, G.; Jackques, D.; Waldner, F.; Bellemans, N.; Matton, N.; Lamarche, C.; d’Andrimont, R.; Defourny, P. Sentinel-2’s Potential for Sub-Pixel Landscape Feature Detection. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Ruz, T.; Uribe, D.; Taylor, R.; Amézquita, L.; Guzmán, M.C.; Merrill, J.; Martínez, P.; Voisin, L.; Mattar, B.C. Anthropogenic marine debris over beaches: Spectral characterization for remote sensing applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Brell, M.; Chan, J.C.W.; Giardino, C.; Gomez-Dans, J.; Mielke, C.; Morsdorf, F.; Segl, K.; Yokoya, N. Synergies of Spaceborne Imaging Spectroscopy with Other Remote Sensing Approaches. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 40, 657–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, H.; McManus, G.B.; Chlus, A.; Qiu, D.; Gao, B.C.; Lin, S. Space station image captures a red tide ciliate bloom at high spectral and spatial resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14783–14787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; English, D.; Han, X.; Naar, D.; Lapointe, B.; Brewton, R.; Hernandez, F. Remote Sensing of Sargassum Biomass, Nutrients, and Pigments. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 12,359–12,367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurekin, A.A.; Loveday, B.R.; Clements, O.; Quartly, G.D.; Miller, P.I.; Wiafe, G.; Adu Agyekum, K. Operational Monitoring of Illegal Fishing in Ghana through Exploitation of Satellite Earth Observation and AIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Pinnel, N. Feasibility Study for an Aquatic Ecosystem Earth Observing System; Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization: Canberra, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hestir, E.; Ade, C.; Turpie, K.; Roberts, D.A.; Siegel, D.; Miller, R.J.; Humm, D.; Izenberg, N.; Keller, M. Satellite sensor requirements for monitoring essential biodiversity variables of coastal ecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Marine Process | Spatial | Temporal | Related to Question (Q) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial Extent (max) | Required Spatial Resolution of Observations | Lifetime of Process (max) | Required Frequency of Observations | ||
| River discharge | ∼100 km | ∼20 m | ∼1 month | at least every 12 h | Q1 |
| Spills | ∼100 km | ∼20 m | ∼1 month | at least every 24 h | Q1 |
| Shoreline accumulation | ∼1000 km | ∼20 m | ∼10 year | at least every 30 d | Q1, Q2, Q3 |
| Submesoscale convergence filaments | ∼10 km | 100 m | ∼10 d | at least every 24 h | Q2, Q3 |
| Sensor | NIR Bands (nm) | Spatial Resolution (GSD in m) | Revisit Time Interval (in days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OLCI (Sentinel-3) | 900; 1020 | 300 (max) | 1 |
| PACE | 940; 1038; 1250; 1378; 1615; 2130; 2260 | 1000 | 2 |
| MSI (Sentinel-2) and OLI (Landsat-8) | 1373; 1613; 2202 | 10 (max) | 5 |
| PRISMA | 920 to 2500 | 30 | 7 to 14 |
| ENMap | SWIR I (950–1390) SWIR II (1480–1760) SWIR III (1950–2450) | 30 | 4 |
| SHALOM | 920 to 2500 | 10 | 4 |
| HyspIRI | 1400 to 2510 | 30 | 16 |
| HYPXIM | 1100 to 2500 | 8 | 3 to 5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Vicente, V.; Clark, J.R.; Corradi, P.; Aliani, S.; Arias, M.; Bochow, M.; Bonnery, G.; Cole, M.; Cózar, A.; Donnelly, R.; et al. Measuring Marine Plastic Debris from Space: Initial Assessment of Observation Requirements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202443
Martínez-Vicente V, Clark JR, Corradi P, Aliani S, Arias M, Bochow M, Bonnery G, Cole M, Cózar A, Donnelly R, et al. Measuring Marine Plastic Debris from Space: Initial Assessment of Observation Requirements. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(20):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202443
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Vicente, Víctor, James R. Clark, Paolo Corradi, Stefano Aliani, Manuel Arias, Mathias Bochow, Guillaume Bonnery, Matthew Cole, Andrés Cózar, Rory Donnelly, and et al. 2019. "Measuring Marine Plastic Debris from Space: Initial Assessment of Observation Requirements" Remote Sensing 11, no. 20: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202443
APA StyleMartínez-Vicente, V., Clark, J. R., Corradi, P., Aliani, S., Arias, M., Bochow, M., Bonnery, G., Cole, M., Cózar, A., Donnelly, R., Echevarría, F., Galgani, F., Garaba, S. P., Goddijn-Murphy, L., Lebreton, L., Leslie, H. A., Lindeque, P. K., Maximenko, N., Martin-Lauzer, F. -R., ... Vethaak, A. D. (2019). Measuring Marine Plastic Debris from Space: Initial Assessment of Observation Requirements. Remote Sensing, 11(20), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202443