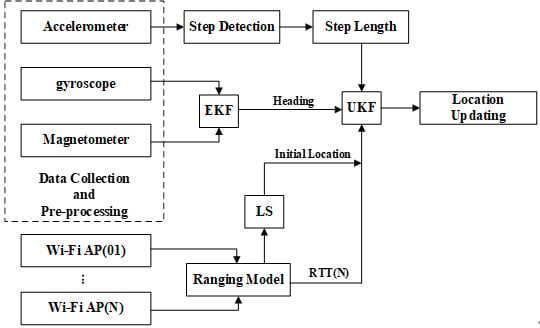
A Robust Dead Reckoning Algorithm Based on Wi-Fi FTM and Multiple Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- To improve the traditional multi-sensor-based dead reckoning method, a multi-pattern-based step detection and location updating algorithm is proposed in order to adapt to complex indoor walking modes.
- (2)
- A real-time ranging model based on Wi-Fi FTM is presented which can effectively reduce the Wi-Fi ranging error caused by clock deviation, non-line-of-sight (NLOS), and multipath propagation.
- (3)
- Based on the fusion of Wi-Fi ranging model and multi-pattern-based dead reckoning method, DRWMs is proposed. The combination of the real-time Wi-Fi FTM ranging model and the multi-sensor estimation method effectively improves the accuracy and stability of final dead reckoning.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Positioning Method Based on Wi-Fi FTM
2.2. Multi-Pattern-Based Dead Reckoning via Multiple Sensors
2.2.1. Multi-Pattern-Based Step Detection and Step-Length Estimation
2.2.2. Location Update
2.3. Challenges of Indoor Positioning for Pedestrians
3. Ranging Model of Wi-Fi FTM
3.1. Model of Clock Deviation Error
3.2. Model of NLOS and Multipath Propagation
4. Integrated Localization Based on Wi-Fi FTM and PDR
4.1. System Model Based on Unscented Kalman filter
4.2. Data Fusion via Unscented Kalman filter
- (1)
- Getting sigma point set based on the previous location and the corresponding weight:where is the dimension of the state value, is the corresponding number of sigma point set, and is the proportional parameter which is used to scale of the weight. is the state covariance matrix at the current moment t.
- (2)
- Further prediction of sigma point sets, :
- (3)
- Weighting sigma point set, getting predicted value and covariance matrix.
- (4)
- Getting the sigma point set again using UT transform based on the predicted state value.
- (5)
- Further prediction of observation based on 2n + 1 sigma point sets of prediction, .where and are calculated in .
- (6)
- Weighting sigma point sets, getting predicted observation value, and corresponding covariance matrix.where is the covariance matrix calculated by and , and is the covariance matrix calculated by and .
- (7)
- Calculating the Kalman gain.
- (8)
- System status and covariance updating.
5. Experimental Results of DRWMs
5.1. Evaluation of Multi-Pattern-Based Dead Reckoning
5.2. Experiment Results of Wi-Fi FTM-Based Ranging Model
5.3. Experiment Results of DRWMs Algorithm
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahfouz, M.R.; Zhang, C.; Merkl, B.C.; Kuhn, M.J.; Fathy, A.E. Investigation of high-accuracy indoor 3-d positioning using UWB technology. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Yang, D.; Chen, Z.; Tan, G. 3d ble indoor localization based on denoising autoencoder. IEEE Access 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shao, H. Wifi-based indoor positioning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, Z.; Long, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, F.; Jiang, Z.L.; Chen, Z. High-speed indoor navigation system based on visible light and mobile phone. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chen, R.; El-Sheimy, N. Multi-Sensor Multi-Floor 3D Localization with Robust Floor Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76689–76699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintalapudi, K.; Padmanabha Iyer, A.; Padmanabhan, V.N. Indoor localization without the pain. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Chicago, IL, USA, 20–24 September 2010; pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Gao, M.; Ni, L.M. On distinguishing the multiple radio paths in RSS-based ranging. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 2201–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.; Liu, C.; Hu, S.; Li, S. High resolution TOA estimation based on compressed sensing. Wirel. Personal Commun. 2015, 84, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.F.; Wu, W.R.; Liu, Y.T. High-resolution AoA estimation for hybrid antenna arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2955–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xiao, J.; Yi, Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, X.; Ni, L.M. CSI-based indoor localization. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2013, 24, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Lan, H.; Li, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. PDR/INS/WiFi integration based on handheld devices for indoor pedestrian navigation. Micromachines 2015, 6, 793–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chan, S.H.G. Wi-Fi fingerprint-based indoor positioning: Recent advances and comparisons. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 466–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEE Standard for Information Technology–Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems Local and Metropolitan Area Networks–Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. IEEE Std 802.11-2016 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.11-2012). 2016, pp. 1–3534. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7786995 (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Ibrahim, M.; Liu, H.; Jawahar, M.; Nguyen, V.; Gruteser, M.; Howard, R.; Bai, F. Verification: Accuracy Evaluation of WiFi Fine Time Measurements on an Open Platform. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, New Delhi, India, 29 October–2 November 2018; pp. 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, I.; Yu, K. Indoor TOA error measurement, modeling, and analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.T.; Tsui, W.Y.; So, H.C.; Ching, P.C. Time-of-arrival based localization under NLOS conditions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2006, 55, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wen, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, R.; Zhao, H. Pedestrian dead-reckoning indoor localization based on OS-ELM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 6116–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shen, R.; Fu, L.; Tian, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, X. iBILL: Using iBeacon and inertial sensors for accurate indoor localization in large open areas. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14589–14599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, P.K.; Zihajehzadeh, S.; Kang, B.S.; Park, E.J. Robust biomechanical model-based 3-D indoor localization and tracking method using UWB and IMU. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.; Piché, R. A survey of selected indoor positioning methods for smartphones. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1347–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Zhan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wu, Y.; Feng, R. A Precise Dead Reckoning Algorithm Based on Bluetooth and Multiple Sensors. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Tightly-coupled integration of WiFi and MEMS sensors on handheld devices for indoor pedestrian navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Gu, T.; Tao, X.; Ye, H.; Lu, J. A reliability-augmented particle filter for magnetic fingerprinting based indoor localization on smartphone. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2016, 15, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, R.M.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.J.; Garcia-Haro, J. Improving RSSI-based path-loss models accuracy for critical infrastructures: A smart grid substation case-study. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, G.; Gallagher, T.; Li, B.; Dempster, A.G.; Rizos, C. Differences in RSSI readings made by different Wi-Fi chipsets: A limitation of WLAN localization. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference Localization GNSS (ICL-GNSS 2011), Tampere, Finland, 29–30 June 2011; pp. 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Boano, C.A.; Wennerström, H.; Zúñiga, M.A.; Brown, J.; Keppitiyagama, C.; Oppermann, F.J.; Roedig, U.; Nordén, L.Å.; Voigt, T.; Römer, K. Hot Packets: A Systematic Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature on Low Power Wireless Transceivers. In Proceedings of the Extrem. Conference Commun. Association of Computing Machinery, Thorsmork, Iceland, 24–30 August 2013; pp. 7–12. Available online: http://soda.swedishict.se/5619/1/camera-ready.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Liu, H.; Darabi, H.; Banerjee, P.; Liu, J. Survey of wireless indoor positioning techniques and systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. Part C 2007, 37, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Trappe, W.; Zhang, Y.; Nath, B. Robust statistical methods for securing wireless localization in sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN 2005), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25–27 April 2005; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Lan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Niu, X.; El-Sheimy, N. A hybrid WiFi/magnetic matching/PDR approach for indoor navigation with smartphone sensors. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y. Pedestrian dead reckoning for MARG navigation using a smartphone. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Proc. 2014, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, J.; Batzer, U.; Seitz, J.; Patino-Studencka, L.; Boronat, J.G. Comparison and evaluation of acceleration based step length estimators for handheld devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, S.; Bassompierre, C.; Godin, C.; Lesecq, S.; Barraud, A. Calibration methods for inertial and magnetic sensors. Sens. Actuators: A Phys. 2009, 156, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Molisch, A.F.; Salmi, J. Accurate passive location estimation using TOA measurements. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Najar, M. Frequency domain joint TOA and DOA estimation in IR-UWB. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Razul, S.G.; Lin, Z.; See, C.M. Target tracking in mixed LOS/NLOS environments based on individual measurement estimation and LOS detection. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.R.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, J. ACES: Adaptive clock estimation and synchronization using Kalman filtering. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–17 September 2008; pp. 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, S.; Kuang, Y.; Åström, K. TOA sensor network self-calibration for receiver and transmitter spaces with difference in dimension. Signal Proc. 2015, 107, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Ansari, N. NLOS error mitigation for TOA-based localization via convex relaxation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 4119–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Salmi, J.; Lohan, E.S. Analysis of kurtosis-based LOS/NLOS identification using indoor MIMO channel measurement. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 2871–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Piché, R.; Kuusniemi, H.; Chen, R. Adaptive mobile tracking in unknown non-line-of-sight conditions with application to digital TV networks. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Proc. 2014, 2014, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Ali-Löytty, S.; Piché, R.; Wu, L. Mobile tracking in mixed line-of-sight/non-line-of-sight conditions: Algorithm and theoretical lower bound. Wirel. Personal Commun. 2012, 65, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Renaudin, V.; Aoustin, Y.; Le-Carpentier, E.; Robert, T. Walking gait step length asymmetry induced by handheld device. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, L.; Liu, D.; Zou, D.; Choy, R.L.F.; Chen, Y.; He, Z. Optimal heading estimation based multidimensional particle filter for pedestrian indoor positioning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49705–49720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Toh, H.S.; Soh, W.S.; Wong, W.C. A robust dead-reckoning pedestrian tracking system with low cost sensors. In Proceedings of the Pervasive Computing and Communications, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, G. NLOS error mitigation for TOA-based source localization with unknown transmission time. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3605–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shi, W.; Chen, W. Comparison of unscented and extended Kalman filters with application in vehicle navigation. J. Navig. 2017, 70, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shi, W.; Chen, W. Correlational inference-based adaptive unscented Kalman filter with application in GNSS/IMU-integrated navigation. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Walking Pattern | True Steps | Detected Steps | Misclassification Steps | Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | 100 | 98 | 2 (Not detected) | 2% |
| Backward | 100 | 95 | 4 (Forward), 1(Not detected) | 5% |
| Left Lateral | 100 | 92 | 5 (Forward), 3(Not detected) | 8% |
| Right Lateral | 100 | 93 | 4 (Forward), 3(Not detected) | 7% |
| Walking Pattern | True Distance/m | Detected Distance/m | Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | 50 | 48.62 | 2.76% |
| Backward | 50 | 48.34 | 3.32% |
| Left Lateral | 50 | 47.58 | 4.84% |
| Right Lateral | 50 | 47.91 | 4.18% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Guo, G.; Ye, F.; Liu, Z. A Robust Dead Reckoning Algorithm Based on Wi-Fi FTM and Multiple Sensors. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050504
Yu Y, Chen R, Chen L, Guo G, Ye F, Liu Z. A Robust Dead Reckoning Algorithm Based on Wi-Fi FTM and Multiple Sensors. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(5):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050504
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yue, Ruizhi Chen, Liang Chen, Guangyi Guo, Feng Ye, and Zuoya Liu. 2019. "A Robust Dead Reckoning Algorithm Based on Wi-Fi FTM and Multiple Sensors" Remote Sensing 11, no. 5: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050504
APA StyleYu, Y., Chen, R., Chen, L., Guo, G., Ye, F., & Liu, Z. (2019). A Robust Dead Reckoning Algorithm Based on Wi-Fi FTM and Multiple Sensors. Remote Sensing, 11(5), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050504