Adaptive Blending Method of Radar-Based and Numerical Weather Prediction QPFs for Urban Flood Forecasting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Study Area
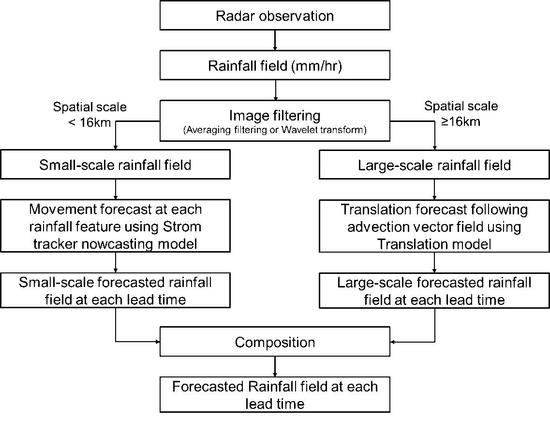
2.1.1. Radar-Based QPFs
2.1.2. Numerical Weather Prediction Models
2.1.3. Study Area
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Adaptive Blending Using the Harmony Search Algorithm
2.2.2. Hydrologic and Hydraulic Models for Urban Flood Forecasting Using Various QPFs
3. Results
3.1. Real-Time Blending and Analysis of QPF Accuracy
3.2. Analysis of Real-Time Urban Runoff Forecasting Using QPFs
3.3. Analysis of Real-time Urban Inundation Forecasting Using QPFs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daley, R. Atmospheric Data Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- Golding, B.W. Long lead time flood warnings: Reality or fantasy? Meteorol. Appl. 2009, 16, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, B.W. Nimrod: A system for generating automated very short range forecasts. Meteorol. Appl. 1998, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, C.E.; Hardaker, P.J.; Collier, C.G.; Haggett, C.M. GANDOLF: A system for generating automated nowcasts of convective precipitation. Meteorol. Appl. 2000, 7, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.K.; Lai, E.S.T. RAPIDS—Operational Blending of Nowcast and NWP QPF. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Quantitative Precipitation Forecasting and Hydrology, Boulder, CO, USA, 4–8 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bowler, N.E.; Pierce, C.E.; Seed, A.W. STEPS: A probabilistic precipitation forecasting scheme which merges an extrapolation nowcast with downscaled NWP. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 2127–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, W.K.; Yeung, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, M.X. Towards the blending of NWP with nowcast: Operation experience in B08FDP. In Proceedings of the World Weather Research Program Symposium on Nowcasting, Whistler, BC, Canada, 30 August–4 Sepetember 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Vasic, S.; Kilambi, A.; Turner, B.; Zawadzki, I. Precipitation forecast skill of numerical weather prediction models and radar nowcasts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L14801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; Seed, A. Use of radar rainfall estimates to evaluate mesoscale model forecasts of convective rainfall. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Hydrological Applications of Weather Radar, Melbourne, Australia, 2–4 February 2004; pp. 271–273. [Google Scholar]
- Kilambi, A.; Zawadzki, I. An evaluation of ensembles based upon MAPLE precipitation nowcasts and NWP precipitation forecasts. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Albuquerque, Mexico, 24–29 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.; Xu, M. Experiments in blending radar echo extrapolation and NWP for nowcasting convective storms. In Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 September 2006; pp. 519–522. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.; Mueller, C.; Weygandt, S.; Ahijevych, D.; Rehak, N.; Megenhardt, D. Fusion observation- and model-based probability forecasts for the short term prediction of convection. In Proceedings of the 12th Conference on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteorology, Atlanta, Georgia, 30 January–2 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Golding, B.W. Quantitative precipitation forecasting in the UK. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 286–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atencia, A.; Rigo, T.; Sairouni, A.; More, J.; Bech, J.; Vilacara, E.; Cunillera, J.; Llasat, M.C.; Garrote, L. Improving QPF by blending techniques at the Meteorological Service of Catalonia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.S. Development of radar-based quantitative precipitation forecasting using spatial-scale decomposition method for urban flood management. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 50, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Laroche, S.; Zawadzki, I. A variational analysis method for the retrieval of three-dimensional wind field from single Doppler radar data. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 53, 2664–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U.; Zawadzki, I. Scale dependence of the predictability of precipitation from continental radar images. Part I: Description of the methodology. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 2859–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U.; Zawadzki, I.; Turner, B. Predictability of precipitation from continental radar images. Part IV: Limits to prediction. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2092–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Lee, H.C.; Ha, J.C.; Lee, Y.H. Development of a nowcasting system combined variational echo tracking and radar-AWS rainrate composition. Conference of Korean Meteorological Society, Busan, Korea, 26 October 2011; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.M.; Kay, J.K.; Lee, S.W. Development and evaluation of the High Resolution Limited Area Ensemble Prediction System in the Korea Meteorological Administration Atmosphere. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 25, 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. Development of the Advanced Storm-Scale Analysis and Prediction System; Technical Report, Korea, NIMR-TN-2014-023; National Institute of Meteorological Sciences: Seogwipo-si, Korea, 2014. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.S.; Lee, B.J. Effects of using high-density rain gauge networks and weather radar data on urban hydrological analyses. Water 2017, 9, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.J. Application of the urban flooding forecasting by the flood nomograph. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2014, 14, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.I.; Kim, J.S. Reducing the Risk of Floods in Urban Areas with Combined Inland-River System. CUNY Academic Works. 2014. Available online: http://academicworks.cuny.edu/cc_conf_hic/370 (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Geem, Z.W.; Kim, J.H.; Loganathan, G.V. A new heuristic optimization algorithm: Harmony search. Simulation 2001, 76, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, L.; Ostfeld, A. Optimal cost design of water distribution networks using harmony search. Eng. Optim. 2007, 39, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geem, Z.W. State-of-the-art in the structure of harmony search algorithm. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2010, 270, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geem, Z.W. Parameter Estimation of the Nonlinear Muskingum Model Using Parameter-Setting-Free Harmony Search. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.C.; Heaney, J.P.; Nix, S.J.; Dickinson, R.E.; Polmann, D.J. Storm Water Management Model User’s Manual Version III; EPA-600/2-84-109a; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1984; p. 504.
- Huber, W.C.; Dickinson, R.E. Storm Water Management Model, Version 4: Users Manual; US Environmental Protection Agency, 600/3-88/001a; Environmental Research Laboratory, EPA: Athens, Greece, 1988.
- Lee, B.J.; Yoon, S.S. Development of grid based inundation analysis model (GIAM). J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 50, 181–190. [Google Scholar]















| CT | AWS | MAPLE | KONOS | SCDM | UM | ASAPS | BLENDED | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | |
| 15:00 | 0.63 | 0.32 | −0.71 | −0.30 | 0.49 | −84.67 | −0.20 | 0.49 | −83.37 | 0.59 | 0.37 | −42.60 | −0.56 | −0.55 | −76.51 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.36 | −62.89 |
| 15:30 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 1.42 | 0.40 | 0.48 | −64.70 | 0.44 | 0.47 | −60.77 | 0.42 | 0.44 | −54.20 | −0.58 | −0.58 | −76.15 | 0.14 | 0.51 | −19.11 | 0.40 | 0.38 | −34.79 |
| 15:50 | 0.80 | 0.22 | 2.78 | 0.42 | 0.41 | −8.52 | 0.52 | 0.36 | 14.55 | 0.55 | 0.35 | −0.89 | 0.37 | −0.36 | −0.83 | 0.21 | 0.47 | 11.66 | 0.48 | 0.33 | −2.07 |
| CT | AWS | MAPLE | KONOS | SCDM | UM | ASAPS | BLENDED | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | |
| 21:00 | 0.76 | 0.34 | −6.67 | 0.40 | 0.67 | −65.03 | 0.30 | 0.61 | −65.03 | 0.47 | 0.65 | −65.02 | −0.57 | 0.79 | −12.51 | 0.68 | 0.79 | 35.08 | 0.01 | 0.50 | −27.08 |
| 21:30 | 0.82 | 0.32 | 2.41 | 0.49 | 0.56 | −55.54 | 0.60 | 0.48 | −53.44 | 0.62 | 0.51 | −54.00 | −0.61 | 0.90 | −10.05 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 38.05 | 0.83 | 0.31 | −15.79 |
| 22:00 | 0.87 | 0.28 | −7.64 | 0.98 | 0.35 | −45.44 | 0.87 | 0.32 | −43.79 | 0.98 | 0.37 | −47.18 | −0.06 | 0.88 | −10.56 | −0.12 | 1.02 | 15.38 | 0.51 | 0.60 | −14.00 |
| CT | AWS | MAPLE | KONOS | SCDM | UM | ASAPS | BLENDED | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | r | RMSE | REPD | |
| 9:20 | 0.94 | 0.22 | −2.00 | 0.81 | 0.53 | −59.39 | 0.89 | 0.55 | −63.22 | 0.83 | 0.48 | −61.67 | 0.89 | 0.58 | −67.11 | 0.89 | 0.33 | −24.50 | 0.92 | 0.26 | −15.83 |
| 9:30 | 0.93 | 0.24 | 5.78 | 0.85 | 0.48 | −50.50 | 0.83 | 0.46 | −34.89 | 0.90 | 0.51 | −51.50 | 0.93 | 0.51 | −52.66 | 0.91 | 0.30 | −28.39 | 0.94 | 0.24 | −19.11 |
| 9:40 | 0.92 | 0.25 | 0.44 | 0.92 | 0.47 | −53.78 | 0.83 | 0.43 | −30.11 | 0.92 | 0.54 | −55.11 | 0.93 | 0.46 | −51.39 | 0.93 | 0.27 | −25.56 | 0.95 | 0.20 | −8.67 |
| Criteria | AWS | MAPLE | KONOS | SCDM | UM | ASAPS | BLENDED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Depth (m) | 6.70 | 4.49 | 5.81 | 6.45 | 6.10 | 6.05 | 6.36 |
| Inundated area over 20 cm (m2) | 11,376 | 144 | 2376 | 7596 | 5148 | 4068 | 9180 |
| Inundated area over 40 cm (m2) | 11,268 | 72 | 1512 | 5328 | 3600 | 3888 | 6588 |
| Inundated area over 60 cm (m2) | 9036 | 36 | 360 | 3600 | 4248 | 3240 | 3600 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.-S. Adaptive Blending Method of Radar-Based and Numerical Weather Prediction QPFs for Urban Flood Forecasting. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11060642
Yoon S-S. Adaptive Blending Method of Radar-Based and Numerical Weather Prediction QPFs for Urban Flood Forecasting. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(6):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11060642
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Seong-Sim. 2019. "Adaptive Blending Method of Radar-Based and Numerical Weather Prediction QPFs for Urban Flood Forecasting" Remote Sensing 11, no. 6: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11060642
APA StyleYoon, S. -S. (2019). Adaptive Blending Method of Radar-Based and Numerical Weather Prediction QPFs for Urban Flood Forecasting. Remote Sensing, 11(6), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11060642