Impact of Cyclonic Ocean Eddies on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response to Typhoon Soudelor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Typhoon Track and Intensity
2.1.2. Satellite Observation of Sea Surface Temperature
2.1.3. Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Height Anomaly and Surface Current
2.1.4. Argo Observations
2.1.5. Numerical Model Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Eddy Center Detection
2.2.2. Calculation of Heat Content Change
2.2.3. Heat Transport by Horizontal Advection
3. Observed Upper Ocean Responses to Super Typhoon Soudelor
3.1. Sea Surface Cooling
3.2. Subsurface Warming
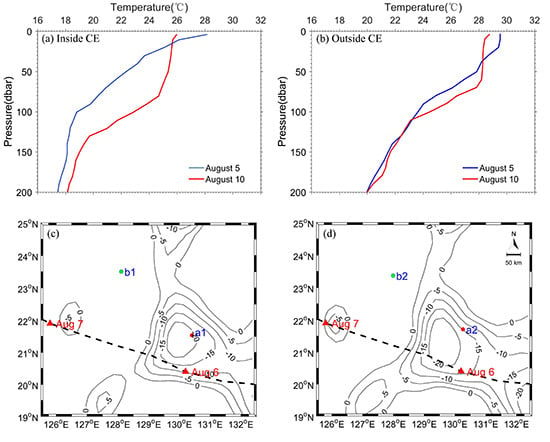
3.3. Impact of the Cyclonic Eddy on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response
4. The Horizontal Heat Advection Induced by Eddy Movement
4.1. Verification of HYCOM Data
4.2. Heat Transport by Horizontal Advection
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Price, J.F.; Sanford, T.B.; Forristall, G.Z. Forced stage response to a moving hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper ocean response to a Hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, C.C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Hu, C.; Zhen, Z.; Liang, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.K. New evidence for enhanced ocean primary production triggered by tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.D.; Leben, R.R.; Balasubramanian, S. Hurricane-forced upwelling and chlorophyll a, enhancement within cold-core cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 18610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, E.A.; Sanford, T.B.; Niiler, P.P.; Terrill, E.J. Cold wake of Hurricane Frances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 15609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Ho, C.R.; Kuo, N.J. Importance of pre-existing oceanic conditions to upper ocean response induced by Super Typhoon Hai-Tang. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Ho, C.R.; Zheng, Q.A.; Lo, Y.T.; Kuo, N.J.; Gopalakrishnan, G. Effects of preexisting cyclonic eddies on upper ocean responses to category 5 typhoons in the western north pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Ho, C.R.; Zheng, Q.A.; Kuo, N.J.; Lo, Y.T. Satellite observation and model simulation of upper ocean biophysical response to Super Typhoon Nakri. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.K.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.H.; Ding, T.; Zhou, B. Upper ocean response to typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 6520–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, R.H.; Chen, D.K.; Liu, X.H.; He, H.L.; Tang, Y.M.; Ke, D.X.; Shen, Z.Q.; Li, J.D.; Xie, J.C.; et al. Net modulation of upper ocean thermal structure by Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 7154–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Sun, Y. Estimate of ocean mixed layer deepening after a typhoon passage over the south china sea by using satellite data. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.Y.; Huang, L.; Devlin, A.T.; Lin, H. Quantification of typhoon-induced phytoplankton blooms using satellite multi-sensor data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cione, J.J.; Uhlhorn, E.W. Sea surface temperature variability in hurricanes: Implications with respect to intensity change. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.K.; Lei, X.T.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.H.; Han, G.J.; Zhou, L. Upper ocean response and feedback mechanisms to typhoon (in Chinese). Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Lin, S.; Jiang, X.M. Influence of tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific. In Recent Developments in Tropical Cyclone Dynamics, Prediction and Detection; Anthony, L., Ed.; InTech: Croatia, Austria, 2016; pp. 3–24. ISBN 978-953-51-2703-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ooyama, K. Numerical simulation of the life cycle of tropical cyclones. J. Atmos. Sci. 1969, 26, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.L.; Wu, C.R.; Oey, L.Y. Typhoon Kai-Tak: An ocean’s perfect storm. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, T.B.; Price, J.F.; Girton, J.B. Upper-ocean response to Hurricane Frances (2004) observed by profiling EM-APEX floats. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K. Contribution of tropical cyclones to meridional heat transport by the oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 14771–14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriver, R.L.; Huber, M. Observational evidence for an ocean heat pump induced by tropical cyclones. Nature 2007, 447, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriver, R.L. Observational evidence supports the role of tropical cyclones in regulating climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15173–15174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, A.; Meehl, G.A. Effect of the Atlantic hurricanes on the oceanic meridional overturning circulation and heat transport. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 03702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.D.; Joshi, M.; Jain, I.; Ravichandran, M. Response of subsurface waters in the eastern Arabian Sea to tropical cyclones. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, J. Understanding surface and subsurface temperature changes induced by tropical cyclones in the Kuroshio. Ocean Dyn. 2015, 65, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kwon, Y.; Price, J.F. Argo array observation of ocean heat content changes induced by tropical cyclones in the north Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Yang, Y.J.; Xian, T. Ocean responses to Typhoon Namtheun explored with Argo floats and multiplatform satellites. Atmos. Ocean 2012, 50, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissa, N.K.; Satyanarayana, A.N.V.; Kumar, B.P. Response of upper ocean during passage of MALA cyclone utilizing Argo data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 14, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, L.; Johnson, N.C.; Ling, Z. Observed three-dimensional structure of ocean cooling induced by Pacific tropical cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7632–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Sun, L.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Y.J. The responses of cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies to typhoon forcing: The vertical temperature-salinity structure changes associated with the horizontal convergence /divergence. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 4974–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, L.K.; Goni, G.J.; Black, P.G. Effects of a warm oceanic feature on Hurricane Opal. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Wu, C.C.; Emanuel, K.A.; Lee, I.H.; Wu, C.R.; Pun, I.F. The interaction of Supertyphoon Maemi (2003) with a warm ocean eddy. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 2635–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, G.; Shang, X.D. Response of a pre-existing cyclonic ocean eddy to a typhoon. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, Y.J.; Xian, T.; Lu, Z.M.; Fu, Y.F. Strong enhancement of chlorophyll a concentration by a weak typhoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 404, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chelton, D.B.; Gaube, P.; Schlax, M.G.; Early, J.J.; Samelson, R.M. The influence of nonlinear mesoscale eddies on near-surface oceanic chlorophyll. Science 2011, 334, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGillicuddy, D.J. Eddies masquerade as planetary waves. Science 2011, 334, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; McWilliams, J.C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D. Global heat and salt transports by eddy movement. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, H. Dynamically derived tropical cyclone intensity changes over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentemann, C.L. Near real time global optimum interpolated microwave SSTs: Applications to hurricane intensity forecasting. In Proceedings of the 26th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, Miami, FL, USA, 2–7 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M. Improved global sea surface temperature analyses using optimum interpolation. J. Clim. 1994, 7, 929–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H. Global Ocean Argo Scatter Data Set (V2.1) (1996/01-2017/05) User Manual; China Argo Real-time Data Center: Hangzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chassignet, E.P.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Smedstad, O.M.; Halliwell, G.R.; Hogan, P.J.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Baraille, R.; Bleck, R. The HYCOM (HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model) data assimilative system. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 65, 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.H.; Li, C.Y. Upper ocean response to the passage of two sequential typhoons. Deep Sea Res. 2018, 132, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isern-Fontanet, J.; Garcíaladona, E.; Font, J. Identification of marine eddies from altimetric maps. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isern-Fontanet, J.; Garcíaladona, E.; Font, J. Vortices of the Mediterranean Sea: An altimetric Perspective. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigneau, A.; Eldin, G.; Dewitte, B. Eddy activity in the four major upwelling systems from satellite altimetry (1992–2007). Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 83, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigneau, A.; Texier, M.L.; Eldin, G.; Grados, C.; Pizarro, O. Vertical structure of mesoscale eddies in the eastern South Pacific Ocean: A composite analysis from altimetry and Argo profiling floats. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kara, A.B.; Rochford, P.A.; Hurlburt, H.E. An optimal definition for ocean mixed layer depth. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 16803–16821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlhorn, E.W.; Shay, L.K. Loop current mixed layer energy response to hurricane Lili (2002), Part II: Idealized Numerical Simulations. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1173–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jiang, G.Q.; Liu, X. Parameterization of typhoon-induced ocean cooling using temperature equation and machine learning algorithms: An example of typhoon Soulik (2013). Ocean Dyn. 2017, 67, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Heat Content Change | Near-Surface HCC (GJ/m2) | Subsurface HCC (GJ/m2) | Total HCC (GJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| This study (inside the CE) | −0.08 | 1.73 | 1.65 |
| This study (outside the CE) | −0.12 | 0.39 | 0.27 |
| Park et al. [25] | −0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | −0.02 ± 0.07 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Fan, K. Impact of Cyclonic Ocean Eddies on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response to Typhoon Soudelor. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080938
Ning J, Xu Q, Zhang H, Wang T, Fan K. Impact of Cyclonic Ocean Eddies on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response to Typhoon Soudelor. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(8):938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080938
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Jue, Qing Xu, Han Zhang, Tao Wang, and Kaiguo Fan. 2019. "Impact of Cyclonic Ocean Eddies on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response to Typhoon Soudelor" Remote Sensing 11, no. 8: 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080938
APA StyleNing, J., Xu, Q., Zhang, H., Wang, T., & Fan, K. (2019). Impact of Cyclonic Ocean Eddies on Upper Ocean Thermodynamic Response to Typhoon Soudelor. Remote Sensing, 11(8), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080938