Uncertainty of Vegetation Green-Up Date Estimated from Vegetation Indices Due to Snowmelt at Northern Middle and High Latitudes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Definition of Snow-Free Vegetation Indices
2.2. Detecting GUD from Vegetation Index (VI) Time-Series Data
2.3. Quantifying GUD Uncertainty Caused by Spring Snowmelt
3. Experimental Design
3.1. Simulation Data and Experiments
3.2. Satellite Data and Experiments
4. Results
4.1. The Simulation Experiments
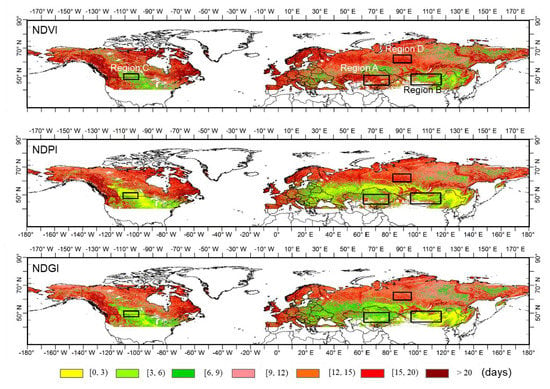
4.2. Comparisons of GUD Uncertainty at the Hemispheric Scale
4.3. Comparisons between NDVI, NDPI, and NDGI in Some Local Regions
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Hodges, J.C.F.; Gao, F.; Reed, B.C.; Huete, A. Monitoring vegetation phenology using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Vik, J.O.; Mysterud, A.; Gaillard, J.-M.; Tucker, C.J.; Stenseth, N.C. Using the satellite-derived NDVI to assess ecological responses to environmental change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.A.; Hoffman, F.; Hargrove, W.W.; Nemani, R.R. A global framework for monitoring phenological responses to climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolkovich, E.M.; Cook, B.; Allen, J.; Crimmins, T.; Betancourt, J.; Travers, S. Warming experiments underpredict plant phenological responses to climate change. Nature 2012, 485, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Scheel, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the 3rd Earth Resource Technology Satellite (ERTS) Symposium 1, College Station, TX, USA, 1 January 1974; pp. 48–62. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asam, S.; Callegari, M.; Matiu, M.; Fiore, G.; De Gregorio, L.; Jacob, A.; Menzel, A.; Zebisch, M.; Notarnicola, C. Relationship between Spatiotemporal Variations of Climate, Snow Cover and Plant Phenology over the Alps—An Earth Observation-Based Analysis. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Cao, R.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. How Does Scale Effect Influence Spring Vegetation Phenology Estimated from Satellite-Derived Vegetation Indexes? Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Kastens, J.H.; Egbert, S.L. Using USDA Crop Progress Data for the Evaluation of Greenup Onset Date Calculated from MODIS 250-Meter Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boschetti, M.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A.; Bocchi, S. Multi-year monitoring of rice crop phenology through time series analysis of MODIS images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4643–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huete, A.; Tran, N.N. Interaction of Seasonal Sun-Angle and Savanna Phenology Observed and Modelled using MODIS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.G.; Zhang, G.X.; Cong, N.; Wang, S.P.; Kong, W.D.; Piao, S.L. Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Kong, W.; Chen, A.; Piao, S. No evidence of continuously advanced green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau over the last decade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Peng, S.; Lin, X.; Chang, J. Declining snow cover may affect spring phenological trend on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2854–E2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.X.; Jönsson, A.M.; Bolmgren, K.; Langvall, O.; Eklundh, L. Disentangling remotely-sensed plant phenology and snow seasonality at northern Europe using MODIS and the plant phenology index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbart, N.; Kergoat, L.; Le Toan, T.; Lhermitte, J.; Picard, G. Determination of phenological dates in boreal regions using normalized difference water index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabanov, N.V.; Zhou, L.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B.; Tucker, C.J. Analysis of interannual changes in northern vegetation activity observed in AVHRR data from 1981 to 1994. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonsamo, A.; Chen, J.M.; Price, D.T.; Kurz, W.A.; Wu, C. Land surface phenology from optical satellite measurement and CO2 eddy covariance technique. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbart, N.; Le Toan, T.; Kergoat, L.; Fedotova, V. Remote sensing of spring phenology in boreal regions: A free of snow-effect method using NOAA-AVHRR and SPOTVGT data (1982–2004). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 101, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.H.; de Beurs, K.M. Land surface phenology of North American mountain environments using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, S.D.; Ahl, D.E.; Serbin, S.P.; Gower, S.T. Fire-induced changes in green-up and leaf maturity of the Canadian boreal forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3594–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Tang, Y.; Shi, P.; Black, T.A.; Zhu, K. A snow-free vegetation index for improved monitoring of vegetation spring green-up date in deciduous ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kobayashi, H.; Wang, C.; Shen, M.G.; Chen, J.; Matsushita, B.; Tang, Y.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Bret-Harte, S.; Zona, D.; et al. A semi-analytical snow-free vegetation index for improving estimation of plant phenology in tundra and grassland ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.R.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.X.; Eklundh, L. A physically based vegetation index for improved monitoring of plant phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, S.W.; Hoffer, R.M. Responses of spectral indices to variations in vegetation cover and soil background. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1998, 64, 915–922. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, S.; Friedl, M.A.; Tan, B.; Zhang, X.; Verma, M. Land surface phenology from MODIS: Characterization of the Collection 5 global land cover dynamics product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Tang, Y.H.; Black, T.A.; Zhu, K. A Novel Method for Removing Snow Melting-Induced Fluctuation in GIMMS NDVI3g Data for Vegetation Phenology Monitoring: A Case Study in Deciduous Forests of North America. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Liu, R.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, L.; Ge, Q. The relationship between threshold-based and inflexion-based approaches for extraction of land surface phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Werry, G.; Jansson, R.; Milbau, A. Root phenology unresponsive to earlier snowmelt despite advanced above-ground phenology in two subarctic plant communities. Funct. Ecol. 2007, 31, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchell, T. Early snowmelt decreases ablation period carbon uptake in a high elevation, subalpine forest, Niwot Ridge, Colorado, USA. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, E.E.; Bolton, D.K.; Coops, N.C.; Mityok, Z.K.; Stenhouse, G.B.; Moore, R.D. Daily estimates of Landsat fractional snow cover driven by MODIS and dynamic time-warping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsämäki, S.; Böttcher, K.; Pulliainen, J.; Luojus, K.; Cohen, J.; Takala, M.; Mattila, O.; Schwaizer, G.; Derksen, C.; Koponen, S. The accuracy of snow melt-off day derived from optical and microwave radiometer data-A study for Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.; Hall, D.; Medler, M.; Flower, A. Quantifying the early snowmelt event of 2015 in the Cascade Mountains, USA by developing and validating MODIS-based snowmelt timing maps. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.; Hall, D.K.; Medler, M.; Matthews, R.; Flower, A. Snowmelt Timing Maps Derived from MODIS for North America, 2001–2015. Oak Ridge Natl. Lab. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Johnson, P.E. Spectral mixture modeling: A new analysis of rock and soil types at the Viking Lander 1 site. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 1986, 91, 8098–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, A.M.; Hook, S.J.; Grove, C.I.; Rivera, G.G. The ASTER spectral library version 2.0. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulla-Menashe, D.; Gray, J.M.; Abercrombie, S.P.; Friedl, M.A. Hierarchical mapping of annual global land cover 2001 to present: The MODIS Collection 6 Land Cover product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cao, R.; Chen, J.; Rao, Y.; Tang, Y. Temperature sensitivity of spring vegetation phenology correlates to within-spring warming speed over the Northern Hemisphere. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.G.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. A simple method to improve the quality of NDVI time-series data by integrating spatiotemporal information with the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamon, J.; Penuelas, J.; Field, C. A narrow-waveband spectral index that tracks diurnal changes in photosynthetic efficiency. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulsig, L.; Nichol, C.J.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Landis, D.R.; Middleton, E.M.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Mammarella, I.; Levula, J.; Porcar-Castell, A. Detecting Inter-Annual Variations in the Phenology of Evergreen Conifers Using Long-Term MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Q.; Xiao, X.M.; Jiao, W.Z.; Wu, X.C.; Doughty, R.; Wang, J.; Du, L.; Zou, Z.H.; Qin, Y.W. Assessing consistency of spring phenology of snow-covered forests as estimated by vegetation indices, gross primary production, and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 275, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Matsushita, B.; Imura, H. Developing a MODIS-based index to discriminate dead fuel from photosynthetic vegetation and soil background in the Asian steppe area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 1589–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, D.; Bindraban, P. A Globally Distributed Soil Spectral Library Visible near Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectra; Soil-Plant Spectral Diagnostics Laboratory: Nairobi, Kenya, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.H.; Guo, Z.F.; Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Yao, Y.M.; Zhang, C.S.; Cui, X.H.; Cao, X. Replacing the Red Band with the Red-SWIR Band (0.74ρred+0.26ρswir) Can Reduce the Sensitivity of Vegetation Indices to Soil Background. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vargas, M.; Miura, T.; Shabanov, N.; Kato, A. An initial assessment of Suomi NPP VIIRS vegetation index EDR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 118, 12301–12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, M.G.; Tang, Y.H. An improved logistic method for detecting spring vegetation phenology in grasslands from MODIS EVI time-series data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 200, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B. Global vegetation phenology from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS): Evaluation of global patterns and comparison with in situ measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, M. The mixed pixel effect in land surface phenology: A simulation study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.Y.; Shen, M.G.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Modeling vegetation green-up dates across the Tibetan Plateau by including both seasonal and daily temperature and precipitation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, R.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, M.; Zhou, J. Uncertainty of Vegetation Green-Up Date Estimated from Vegetation Indices Due to Snowmelt at Northern Middle and High Latitudes. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010190
Cao R, Feng Y, Liu X, Shen M, Zhou J. Uncertainty of Vegetation Green-Up Date Estimated from Vegetation Indices Due to Snowmelt at Northern Middle and High Latitudes. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(1):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010190
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ruyin, Yan Feng, Xilong Liu, Miaogen Shen, and Ji Zhou. 2020. "Uncertainty of Vegetation Green-Up Date Estimated from Vegetation Indices Due to Snowmelt at Northern Middle and High Latitudes" Remote Sensing 12, no. 1: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010190
APA StyleCao, R., Feng, Y., Liu, X., Shen, M., & Zhou, J. (2020). Uncertainty of Vegetation Green-Up Date Estimated from Vegetation Indices Due to Snowmelt at Northern Middle and High Latitudes. Remote Sensing, 12(1), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010190