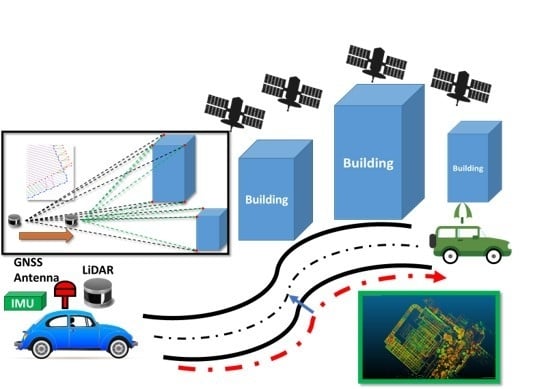
Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. INS/GNSS with Land Vehicle Motion Constraints
2.2. Feature-Based 3D LiDAR SLAM (LiDAR Odometry and Mapping)
2.2.1. Feature Extraction
2.2.2. LiDAR Odometry
2.2.3. LiDAR Mapping
2.3. Integrated Navigation Structure for Automated Vehicles
2.3.1. Fault Detection and Exclusion
2.3.2. SLAM-PVA EKF Model
2.3.3. Error Model for 3D LiDAR SLAM Measurements
2.3.4. Refreshing Map
2.3.5. Integrity Assessment
3. Field Testing
3.1. Configuration Description
3.2. Scenario Description
3.2.1. Scenario 1: GNSS-Hostile Region
3.2.2. Scenario 2: Highway Area
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Scenario 1: GNSS-Hostile Region
4.2. Scenario 2: Highway Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Liu, L.; Qiu, T.; Ren, Z.; Hu, J.; Ti, F. Driver’s intention identification and risk evaluation at intersections in the internet of vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handte, M.; Foell, S.; Wagner, S.; Kortuem, G.; Marrón, P.J. An internet-of-things enabled connected navigation system for urban bus riders. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Cheng, N.; Zhang, N.; Shen, X.; Mark, J.W. Connected vehicles: Solutions and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuutti, S.; Fallah, S.; Katsaros, K.; Dianati, M.; Mccullough, F.; Mouzakitis, A. A survey of the state-of-the-art localization techniques and their potentials for autonomous vehicle applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J. Aided Navigation: Gps with High Rate Sensors; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X. Gps Stochastic Modelling: Signal. Quality Measures and Arma Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Nassar, S.; El-Sheimy, N. Two-filter smoothing for accurate ins/gps land-vehicle navigation in urban centers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 4256–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Wu, W.; Hu, X.; Shen, L. Ins/gps integration: Global observability analysis. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 58, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagle, N.; Broumandan, A.; Lachapelle, G. Multiantenna gnss and inertial sensors/odometer coupling for robust vehicular navigation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4816–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yao, M.; Ma, H.; Jia, W. Improving accuracy of the vehicle attitude estimation for low-cost ins/gps integration aided by the gps-measured course angle. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 14, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.-W.; Chang, H.-W.; Li, Y.-H.; Tsai, G.-J.; Tseng, C.-L.; Tien, Y.-C.; Hsu, P.-C. Assessment for ins/gnss/odometer/barometer integration in loosely-coupled and tightly-coupled scheme in a gnss-degraded environment. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 3057–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, P. Gnss solutions: Multipath vs. Nlos signals. How does non-line-of-sight reception differ from multipath interference. Inside GNSS Mag. 2013, 8, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, P.D.; Jiang, Z.; Rudi, M.; Strode, P. A portfolio approach to nlos and multipath mitigation in dense urban areas. In Proceedings of the 26th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2013), The Institute of Navigation, Nashville, TN, USA, 16–19 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, E.-H. Estimation Techniques for Low-Cost Inertial Navigation. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Tightly Coupled Mems Ins/Gps Integration with Ins Aided Receiver Tracking Loops. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, P. Mems-Based Integrated Navigation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Julier, S.J.; Durrant-Whyte, H.F. On the role of process models in autonomous land vehicle navigation systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2003, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Petovello, M.; Cannon, M.E. Integration of steering angle sensor with global positioning system and micro-electro-mechanical systems inertial measurement unit for vehicular positioning. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2008, 12, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.G.; Hwang, P.Y. Introduction to Random Signals and Applied Kalman Filtering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, S.-W.; van Graas, F.; de Haag, M.U. Positioning with two satellites and known receiver clock, barometric pressure and radar elevation. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, X.; Tang, W.; Zhang, W. A fusion strategy for reliable vehicle positioning utilizing rfid and in-vehicle sensors. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Yang, J.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. A pervasive integration platform of low-cost mems sensors and wireless signals for indoor localization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 5, 4616–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivet, D.; Gérossier, F.; Checchin, P.; Trassoudaine, L.; Chapuis, R. Mobile ground-based radar sensor for localization and mapping: An evaluation of two approaches. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, M.; Koechling, J.; Stanley, B.; Zhang, B. Localizing ground penetrating radar: A step toward robust autonomous ground vehicle localization. J. Field Robot. 2016, 33, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Folkesson, J. Vehicle localization with low cost radar sensors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gothenburg, Sweden, 19–22 June 2016; pp. 864–870. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Orb-slam2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taketomi, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Ikeda, S. Visual slam algorithms: A survey from 2010 to 2016. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 2017, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvišić, I.; Ćesić, J.; Marković, I.; Petrović, I. Soft-slam: Computationally efficient stereo visual simultaneous localization and mapping for autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles. J. Field Robot. 2018, 35, 578–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakne, P.; O’Keefe, K. Tightly-coupled gnss/vision using a sky-pointing camera for vehicle navigation in urban areas. Sensors 2018, 18, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holz, D.; Ichim, A.E.; Tombari, F.; Rusu, R.B.; Behnke, S. Registration with the point cloud library: A modular framework for aligning in 3-d. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. Low-drift and real-time lidar odometry and mapping. Auton. Robot. 2017, 41, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S.; Burgard, W.; Fox, D. Probabilistic Robotics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kaartinen, H.; Kukko, A.; Zhu, L.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Hyyppä, J. An integrated gnss/ins/lidar-slam positioning method for highly accurate forest stem mapping. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hening, S.; Ippolito, C.A.; Krishnakumar, K.S.; Stepanyan, V.; Teodorescu, M. 3D lidar slam integration with gps/ins for uavs in urban gps-degraded environments. In Aiaa Information Systems-AIAA Infotech@ Aerospace; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Grapevine, TX, USA, 2017; p. 0448. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.-W.; Tsai, G.-J.; Chang, H.-W.; Joly, C.; EI-Sheimy, N. Seamless navigation and mapping using an ins/gnss/grid-based slam semi-tightly coupled integration scheme. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, J.; Montemerlo, M.; Thrun, S. Map-based precision vehicle localization in urban environments. In Robotics: Science and Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, A.Y.; Wolf, D.F. Feature detection for vehicle localization in urban environments using a multilayer lidar. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 17, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. 3D is here: Point cloud library (pcl). In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gebre-Egziabher, D.; Gleason, S. Gnss Applications and Methods; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.-W.; Tsai, G.-J.; Chu, H.-J.; El-Sheimy, N. Performance enhancement of ins/gnss/refreshed-slam integration for acceptable lane-level navigation accuracy. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 2463–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GmbH. i.N. Inav-rqh-0018. Available online: https://www.imar-navigation.de/downloads/nav_rqh_0018_en.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
















| iNAV-RQH | ||
| Accelerometer | Gyroscope | |
| Bias Instability | 15 | 0.002° |
| Random Walk Noise | 8 | 0.0018° |
| PwrPak7D-E1 (Epson G320N) | ||
| Accelerometer | Gyroscope | |
| Bias Instability | 100 | 3.5° |
| Random Walk Noise | 0.5 | 0.1° |
| INS/RTK/Odometer | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | North (meter) | East (meter) | Height (meter) | North Velocity (m/s) | East Velocity (m/s) | Vertical Velocity (m/s) | Heading (degree) |
| Mean | −1.072 | −1.276 | 1.698 | −0.011 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.281 |
| STD | 2.268 | 2.739 | 2.246 | 0.057 | 0.052 | 0.120 | 0.151 |
| RMSE | 2.509 | 3.021 | 2.815 | 0.059 | 0.052 | 0.120 | 0.314 |
| Max. | 9.747 | 8.389 | 7.531 | 0.348 | 0.277 | 1.392 | 0.567 |
| INS/RTK/3D LiDAR-SLAM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | North (meter) | East (meter) | Height (meter) | North Velocity (m/s) | East Velocity (m/s) | Vertical Velocity (m/s) | Heading (degree) |
| Mean | −0.088 | −0.252 | 0.198 | 0.001 | 0.001 | −0.002 | 0.256 |
| STD | 0.678 | 0.836 | 0.591 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.118 | 0.121 |
| RMSE | 0.684 | 0.873 | 0.623 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.118 | 0.283 |
| Max. | 3.184 | 3.507 | 2.906 | 0.223 | 0.337 | −0.002 | 0.564 |
| Improvement | 73% | 71% | 77% | 52% | 17% | 2% | 10% |
| INS/RTK/Odometer | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | North (meter) | East (meter) | Height (meter) | North Velocity (m/s) | East Velocity (m/s) | Vertical Velocity (m/s) | Heading (degree) |
| Mean | 0.105 | 2.387 | 1.083 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.167 |
| STD | 1.505 | 5.192 | 1.315 | 0.038 | 0.060 | 0.235 | 0.294 |
| RMSE | 1.509 | 5.714 | 1.703 | 0.038 | 0.060 | 0.235 | 0.338 |
| Max. | 6.780 | 21.426 | 4.638 | 0.272 | 0.341 | 2.179 | 0.617 |
| INS/RTK/3D LiDAR-SLAM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | North (meter) | East (meter) | Height (meter) | North Velocity (m/s) | East Velocity (m/s) | Vertical Velocity (m/s) | Heading (degree) |
| Mean | 0.146 | 0.328 | 0.537 | 0.001 | 0.001 | −0.001 | 0.152 |
| STD | 0.916 | 1.247 | 0.716 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.214 | 0.276 |
| RMSE | 0.927 | 1.289 | 0.895 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.214 | 0.315 |
| Max. | 5.597 | 6.999 | 3.626 | 0.223 | 0.337 | 2.164 | 0.538 |
| Improvement | 39% | 77% | 47% | 26% | 28% | 9% | 7% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiang, K.-W.; Tsai, G.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101564
Chiang K-W, Tsai G-J, Li Y-H, Li Y, El-Sheimy N. Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101564
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiang, Kai-Wei, Guang-Je Tsai, Yu-Hua Li, You Li, and Naser El-Sheimy. 2020. "Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101564
APA StyleChiang, K. -W., Tsai, G. -J., Li, Y. -H., Li, Y., & El-Sheimy, N. (2020). Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101564