Insect Mass Estimation Based on Radar Cross Section Parameters and Support Vector Regression Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Datasets
2.2. Support Vector Regression
2.3. Feature Extraction
3. Results
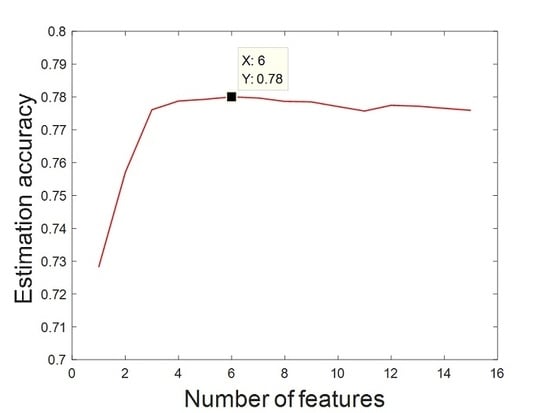
3.1. Mass Estimation Based on SVR
3.2. Comparison with Traditional Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holland, R.A.; Wikelski, M.; Wilcove, D.S. How and why do insects migrate. Science 2006, 313, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, J.R.; Reynolds, D.R.; Farrow, R.A. The migration of Nilaparvata lugens (Stal) (Delphacidae) and other Hemiptera associated with rice during the dry season in the Philippines: A study using radar, visual observations, aerial netting and ground trapping. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1987, 77, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Q.; Zhao, X.C.; Wu, X.F.; Wu, B.; Wu, K.M.; Cheng, D.F.; Guo, Y.Y. Autumn Migration of Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Over the Bohai Sea in Northern China. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.M.; Guo, Y.Y.; Head, G. Resistance Monitoring of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Bt Insecticidal Protein During 2001–2014 in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.Q.; Gould, F.; Huang, Y.X.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Wu, K.M. Modeling the Population Dynamics of Cotton Bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Over a Wide Area in Northern China. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altizer, S.; Bartel, R.; Han, B.A. Animal migration and infectious disease risk. Science 2011, 331, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, S.; Hoye, B.J. Migratory animals couple biodiversity and ecosystem functioning worldwide. Science 2014, 344, 1242552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Lim, K.S.; Horvitz, N.; Clark, S.J.; Reynolds, D.R.; Sapir, N.; Chapman, J.W. Mass seasonal bioflows of high-flying insect migrants. Science 2016, 354, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, J.W.; Drake, V.A.; Reynolds, D.R. Recent insights from radar studies of insect flight. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, J.W.; Reynolds, D.R.; Smith, A.D. Vertical-looking radar: A new tool for monitoring high-altitude insect migration. BioScience 2003, 53, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, K.; Hu, C.; Wang, R.; Sui, Y.; Mao, H.F.; Li, H.Y. Deep-learning-based extraction of the animal migration patterns from weather radar images. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 140304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, G.W. Radar observations of insect flight. Proc. Symp. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1976, 7, 157–197. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, J.W.; Smith, A.D.; Woiwood, I.P.; Reynolds, D.R.; Riley, J.R. Development of Vertical-Looking Radar Technology for Monitoring Insect Migration. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 35, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, V.A.; Chapman, J.W.; Lim, K.S.; Reynolds, D.R.; Riley, J.R.; Smith, A.D. Ventral-aspect radar cross sections and polarization patterns of insects at X band and their relation to size and form. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5022–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, T.J.; Drake, V.A. Monitoring insect migration with radar: The ventral-aspect polarization pattern and its potential for target identification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 3957–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, V.A. Distinguishing target classes in observations from vertically pointing entomological radars. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3811–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R.; Reynolds, D.R. Radar-based Studies of the Migratory Flight of Grasshoppers in the Middle Niger Area of Mali. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1979, 204, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Kong, S.Y.; Wang, R.; Long, T.; Fu, X.W. Identification of Migratory Insects from their Morphological Features using a Decision-Tree Support Vector Machine and its Application to Radar Entomology. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldhous, A.C. An Investigation of the Polarisation Dependence of Insect Radar cross Sections at Constant Aspect. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield Institute Technology, Cranfield, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, S.E.; Aldhous, A.C. Insect ventral radar cross section polarisation dependence measurements for radar entomology. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2006, 153, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Li, W.D.; Wang, R.; Long, T.; Liu, C.J.; Drake, V.A. Insect Biological Parameter Estimation Based on the Invariant Target Parameters of the Scattering Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6212–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, C.; Liu, C.J.; Kong, S.Y.; Lang, T.J. Migratory Insect Multifrequency Radar Cross Sections for Morphological Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 3450–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V.N. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brereton, R.G.; Lloyd, G.R. Support vector machines for classification and regression. Analyst 2010, 135, 230–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasolli, E.; Melgani, F.; Alajlan, N.; Bazi, Y. Active learning methods for biophysical parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4071–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieder, M.; Leitaoão, P.J.; Suess, S.; Senf, C.; Hostert, P. Estimating Fractional Shrub Cover Using Simulated EnMAP Data: A Comparison of Three Machine Learning Regression Techniques. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3427–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasan, V.; Javad, S.; Kamran, A.; Hadi, F.; Hamed, N.; Tien, P.; Dieu, B. Improving accuracy estimation of forest aboveground biomass based on incorporation of ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-2A imagery and machine learning: A case study of the hyrcanian forest area (Iran). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, D.; Srimanta, P.; Patranbis, D.C. Support vector regression. Neural Inf. Process. 2007, 11, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, W.W.; Vaughn, C.R.; Harris, R.; Loper, G.M. Insect radar cross-sections for aerial density measurements and target classification. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1993, 36, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Tai, D. Evaluation of mutual information, genetic algorithm and SVR for feature selection in QSAR regression. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.; Gao, W.; Li, J. Computational identification of antigenicity-associated sites in the hemagglutinin protein of A/H1N1 seasonal influenza virus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. Libsvm: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, C.; Fu, X.W.; Long, T.; Zeng, T. Micro-doppler measurement of insect wing-beat frequencies with W-band coherent radar. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Species Number | Species | Quantity | Mass (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) | 31 | 67.8–199.2 |
| 2 | Loxostege sticticalis (Linnaeus) | 19 | 26–101.5 |
| 3 | Mythimna separata (Walker) | 15 | 103.7–234.8 |
| 4 | Ascotis selenaria (Schiffermuller et Denis) | 13 | 40.9–172.3 |
| 5 | Agrotis ypsilon (Rottemberg) | 13 | 134.8–401.3 |
| 6 | Psilogramma menephron (Gramer) | 11 | 314.6–964 |
| 7 | Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenée) | 11 | 26.5–47.3 |
| 8 | Holotrichia convexopyga (Moser) | 9 | 301.3–735.4 |
| 9 | Diaphania quadrimaculalis (Bremer et Grey) | 7 | 25.6–80.1 |
| 10 | Agrotis putris (Linnaeus) | 6 | 40.1–102.8 |
| 11 | Semiothisa cinerearia (Bremer et Grey) | 5 | 77.3–96.4 |
| 12 | Theretra japonica (Orza) | 4 | 294.9–387.7 |
| 13 | Deilephila elpenor (Linnaeus) | 4 | 456.1–722.6 |
| 14 | Macdunnoughia crassisigna (Warren) | 4 | 60.6–85 |
| 15 | Diaphania indica (Saunders) | 4 | 30.8–52 |
| 16 | Percnia luridaria nominoneura (Prout) | 3 | 57.5–116 |
| 17 | Reticulitermes chinensis (Snyder) | 3 | 35.5–44.7 |
| 18 | Emmelia trabealis (Scopoli) | 2 | 25.8–34.7 |
| 19 | Stilprotia salicis (Linnaeus) | 2 | 131.9–298.5 |
| 20 | Melicleptria scutosa (Schiffermüller) | 2 | 57.6–94 |
| 21 | Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner) | 1 | 37.8 |
| Dataset | Quantity | Mass (mg) | Measurement Range (GHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D | 156 | 9–4120 | 9.4 or 10 |
| L | 39 | 1.83–80.1 | 9.4 |
| M | 12 | 33–1094.1 | 10 |
| K | 169 | 25.6–964 | 8.25–11.75 |
| No. | Feature | No. | Feature | No. | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 11 | |||
| 2 | 7 | 12 | |||
| 3 | 8 | 13 | |||
| 4 | 9 | 14 | |||
| 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Method | MRE | |
|---|---|---|
| Aldhous et al. (1989) | 29.03% | |
| Chapman et al. (2002) | 33.91% | |
| Drake et al. (2017) | 24.50% | |
| Hu et al. (2019) | 27.24% | |
| 27.43% | ||
| SVR | 22.00% | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Kong, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L. Insect Mass Estimation Based on Radar Cross Section Parameters and Support Vector Regression Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111903
Hu C, Kong S, Wang R, Zhang F, Wang L. Insect Mass Estimation Based on Radar Cross Section Parameters and Support Vector Regression Algorithm. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(11):1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111903
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Cheng, Shaoyang Kong, Rui Wang, Fan Zhang, and Lianjun Wang. 2020. "Insect Mass Estimation Based on Radar Cross Section Parameters and Support Vector Regression Algorithm" Remote Sensing 12, no. 11: 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111903
APA StyleHu, C., Kong, S., Wang, R., Zhang, F., & Wang, L. (2020). Insect Mass Estimation Based on Radar Cross Section Parameters and Support Vector Regression Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 12(11), 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111903