Non-Tidal Mass Variations in the IGS Second Reprocessing Campaign: Interpretations and Noise Analysis from GRACE and Geophysical Models
Abstract
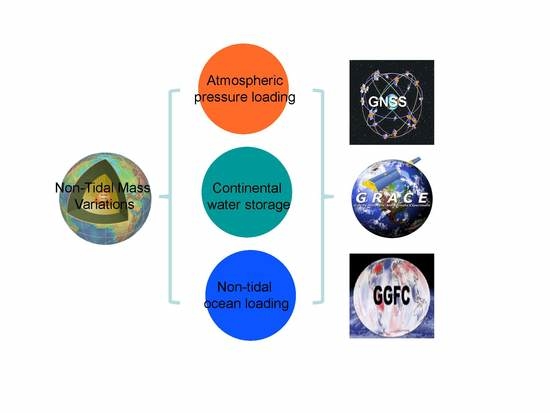
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. GNSS Time Series
2.2. GRACE Data
2.3. Surface Loading Datasets
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Consistency Analysis between GNSS, GRACE and GGFC
3.1.1. Similarity of Annual Harmonic Signals
3.1.2. Quantitative Evaluation with Correlation Coefficient and WRMS Reduction
3.1.3. Sampling Effects on the Comparisons
3.1.4. Remaining Disagreements between GNSS and GRACE or GGFC
3.2. Noise Analysis
3.3. Revisiting GRACE-Derived Non-Tidal DeformationWith GNSS Station PositionTime Series
3.3.1. Horizontal Deformations Variations
3.3.2. Degree-1 SHC Effects on the GNSS/GRACE Results
4. Discussions
4.1. Comparison to Previous Work
4.2. Thermal ExpansionEffects
4.3. Leakage ErrorsAnalysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altamimi, Z.; Rebischung, P.; Métivier, L.; Collilieux, X. ITRF2014: A new release of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 6109–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Van Dam, T.; Wdowinski, S. Observing and understanding the earth system variations from space geodesy. J. Geodyn. 2013, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dam, T.; Wahr, J.; Chao, Y.; Leuliette, E. Predictions of crustal deformation and of geoid and sea-level variability caused by oceanic and atmospheric loading. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 129, 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Klos, A.; Gruszczynska, M.; Bos, M.S.; Boy, J.P.; Bogusz, J. Estimates of vertical velocity errors for IGS ITRF2014 stations by applying the improved singular spectrum analysis method and environmental loading models. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 1823–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, J.; Klos, A. On the significance of periodic signals in noise analysis of GPS station coordinates time series. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collilieux, X.; Van Dam, T.; Ray, J.; Coulot, D.; Métivier, L.; Altamimi, Z. Strategies to mitigate aliasing of loading signals while estimating GPS frame parameters. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.; Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; Van Dam, T. Anomalous harmonics in the spectra of GPS position estimates. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Mohammadloo, T.H.; Argus, D.F. Multivariate analysis of GPS position time series of JPL second reprocessing campaign. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Deng, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H. Effects on noise properties of GPS time series caused by higher-order ionospheric corrections. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, N.T.; Stewart, M.P. Aliased tidal signatures in continuous GPS height time series. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rebischung, P.; Altamimi, Z.; Ray, J.; Garayt, B. The IGS contribution to ITRF2014. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Cheng, M.K.; Miyazaki, S. Anatomy of apparent seasonal variations from GPS-derived site position time series. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ETG-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanard, K.; Fleitout, L.; Calais, E.; Rebischung, P.; Avouac, J.P. Toward a global horizontal and vertical elastic load deformation model derived from GRACE and GNSS station position time series. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 3225–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C. Elastic deformation of the Australian continent induced by seasonal water cycles and the 2010–2011 La Niña determined using GPS and GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2763–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannel, B.; Dobslaw, H.; Dill, R.; Glaser, S.; Balidakis, K.; Thomas, M.; Schuh, H. Correcting surface loading at the observation level: Impact on global GNSS and VLBI station networks. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggenbuck, O.; Thaller, D.; Engelhardt, G.; Franke, S.; Dach, R.; Steigenberger, P. Loading-Induced Deformation Due to Atmosphere, Ocean and Hydrology: Model Comparisons and the Impact on Global SLR, VLBI and GNSS Solutions. In International Association of Geodesy Symposia; REFAG, 2014; Van Dam, T., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 146. [Google Scholar]
- Nordman, M.; Virtanen, H.; Nyberg, S.; Mäkinen, J. Non-tidal loading by the Baltic Sea: Comparison of modeled deformation with GNSS time series. GeoResJ 2015, 7, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.L.; Elosegui, P.; Mitrovica, J.X.; Tamisea, M.E. Climate-driven deformation of the solid earth from GRACE and GPS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L24605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Freymueller, J. Seasonal and long-term vertical deformation in the Nepal Himalaya constrained by GPS and GRACE measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, B3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Fan, D.; You, W.; Su, Y. Seasonal crustal vertical deformation induced by environmental mass loading in mainland China derived from GPS, GRACE and surface loading models. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, T.; Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; Ray, J. Topographically induced height errors in predicted atmospheric loading effects. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, T.; Wahr, J.; Milly, P.C.D.; Shmakin, A.B.; Blewitt, G.; Lavallée, D.; Larson, K.M. Crustal displacements due to continental water loading. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Chen, W.; Yuan, L. Crustal vertical deformation response to different spatial scales of GRACE and GCMs surface loading. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 204, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Zou, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y. Vertical Displacements Driven by Groundwater Storage Changes in the North China Plain Detected by GPS Observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesmer, V.; Steigenberger, P.; van Dam, T.; Mayer-Gürr, T. Vertical deformations from homogeneously processed GRACE and global GPS long-term series. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Fan, D.; You, W. Comparison of observed and modeled seasonal crustal vertical displacements derived from multi-institution GPS and GRACE solutions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7219–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothacher, M.; Angermann, D.; Artz, T.; Bosch, W.; Drewes, H.; Gerstl, M.; Kelm, R.; König, D.; König, R.; Meisel, B.; et al. GGOS-D: Homogeneous reprocessing and rigorous combination of space geodetic observations. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 679–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Van Dam, T.; Ding, W. Comparative analysis of different environmental loading methods and their impacts on the GPS height time series. J. Geod. 2014, 87, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, T.; Wahr, J.; Lavallée, D. A comparison of annual vertical crustal displacements from GPS and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) over Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B03404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Deng, L.; Wang, K.; Zhou, B. Quantitative analysis of geophysical sources of common mode component in CMONOC GPS coordinate time series. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 2896–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.D.P.; Penna, N.T. Non-tidal ocean loading effects on geodetic GPS heights. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L09314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Ma, Y. Assessment of second- and third-order ionospheric effects on regional networks: Case study in china with longer CMONOC GPS coordinate time series. J. Geod. 2016, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.A.; Watson, C.S. Long GPS coordinate time series: Multipath and geometry effects. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B04403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J.; Hugentobler, U.; Steigenberger, P.; Lutz, S. Impact of Earth radiation pressure on GPS position estimates. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Li, Z.; Wei, N.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H. GPS-derived geocenter motion from the IGS second reprocessing campaign. Earth Planets Space 2019, 71, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völksen, C. Reprocessing of a regional GPS network in Europe. In Observing Our Changing Earth: Proceedings of the 2007 IAG General Assembly, Perugia, Italy, 2–13 July 2007; Sideris, M.G., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Maciuk, K. The Study of Seasonal Changes of Permanent Stations Coordinates based on Weekly EPN Solutions. Artif. Satell. 2016, 51, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dousa, J.; Vaclavovic, P.; Elias, M. Tropospheric products of the second GOP European GNSS reprocessing (1996–2014). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3589–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L09607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusche, J.; Schrama, E. Surface mass redistribution inversion from global GPS deformation and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) gravity data. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettadpur, S. UTCSR Level-2 Processing Standards Document for Product Release 0006; GRACE 327-742; Center for Space Research, The University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.L.; Wilson, C.R.; Tapley, B.D.; Grand, S. GRACE detects coseismic and postseismic deformation from the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Post-processing removal of correlated errors in GRACE data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Riva, R.; Ditmar, P. Optimizing estimates of annual variations and trends in geocenter motion and J2 from a combination of GRACE data and geophysical models. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 8352–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flechtner, F. GRACE AOD1B Product Description Document (Rev. 2.1); GRACE 327-750 (GR-GFZ-AOD-0001); GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam: Potsdam, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, T.; Wahr, J. Displacements of the Earth’s surface due to atmospheric loading: Effects on Gravity and Baseline Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Lee, T.; Fukumori, I. Mechanisms controlling the interannual variation of mixed layer temperature averaged over the Nio-3 region. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3822–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregoning, P.; Watson, C. Atmospheric effects and spurious signals in GPS analyses. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, B09403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Dong, D.; Fang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, N.; Zhou, F. Contributions of thermoelastic deformation to seasonal variations in GPS station position. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. Terrestrial water storage response to the 2012 drought estimated from the vertical position anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6145–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C. Seasonal clockwise gyration and tilt of the Australian continent chasing the center of mass of the Earth’s system from GPS and GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 7666–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Freymueller, J.T.; Ding, K.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q. Evaluating seasonal loading models and their impact on global and regional reference frame alignment. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 1337–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.D.P. The effect of coloured noise on the uncertainties of rates estimated from geodetic time series. J. Geod. 2003, 76, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, J. Estimating rate uncertainty with maximum likelihood: Differences between power-law and flicker-random-walk models. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Bos, M.S.; Montillet, J.P.; Fernandes, R.M.S. Investigation of the noise properties at low frequencies in long GNSS time series. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Argus, D.F.; Freymueller, J.T.; Heflin, M.B. Horizontal motion in elastic response to seasonal loading of rain water in the Amazon Basin and monsoon water in Southeast Asia observed by GPS and inferred from GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 6048–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, M. Contributions of thermal expansion of monuments and nearby bedrock to observed GPS height changes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fand, M.; Dong, D.; Hager, B.H. Displacements due to surface temperature variation on a uniform elastic sphere with its centre of mass stationary. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Landerer, F.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.; Watkins, M.M. Quantifying and reducing leakage errors in the JPL RL05M GRACE mascon solution. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7490–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Data Type | Annual Amplitudes (mm) | Annual Phase (°) |
|---|---|---|
| GNSS | 3.5 | 196.2 |
| GGFC | 2.6 | 176.6 |
| GRACE | 2.7 | 187.4 |
| GNSS corrected by GGFC | 1.7 | 192.9 |
| GNSS corrected by GRACE | 2.2 | 207.6 |
| Data Types | WRMS% > 0 | WRMS% < 0 | −20% < WRMS% < 0 | WRMS% < −20% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS corrected by GGFC | Number of stations | 49 | 137 | 52 | 85 |
| Mean value of WRMS | 47.6% | −24.6% | −10.2% | −33.4% | |
| GNSS corrected by GRACE | Number of stations | 38 | 148 | 87 | 61 |
| Mean value of WRMS | 9.7% | −17.9% | −10.8% | −28.1% |
| Index | Monthly Solutions | Weekly Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Annual amplitudes and phases | 2.6 mm/176.9° | 2.6 mm/167.5° |
| Stations with WRMS reduction | 74% | 73% |
| Mean values of WRMS variations | −5.6% | −5.4% |
| Correlation coefficients | 0.45 | 0.44 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, L.; Chen, H.; Ma, A.; Chen, Q. Non-Tidal Mass Variations in the IGS Second Reprocessing Campaign: Interpretations and Noise Analysis from GRACE and Geophysical Models. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152477
Deng L, Chen H, Ma A, Chen Q. Non-Tidal Mass Variations in the IGS Second Reprocessing Campaign: Interpretations and Noise Analysis from GRACE and Geophysical Models. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(15):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152477
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Liansheng, Hua Chen, Ailong Ma, and Qusen Chen. 2020. "Non-Tidal Mass Variations in the IGS Second Reprocessing Campaign: Interpretations and Noise Analysis from GRACE and Geophysical Models" Remote Sensing 12, no. 15: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152477
APA StyleDeng, L., Chen, H., Ma, A., & Chen, Q. (2020). Non-Tidal Mass Variations in the IGS Second Reprocessing Campaign: Interpretations and Noise Analysis from GRACE and Geophysical Models. Remote Sensing, 12(15), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152477