Spatiotemporal Variations of City-Level Carbon Emissions in China during 2000–2017 Using Nighttime Light Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methods
3.1. Integration of Two Nighttime Light Data
3.2. Estimation of Carbon Emission
3.3. Evaluation of Spatiotemporal Variations of Carbon Emissions
4. Results and Discussion
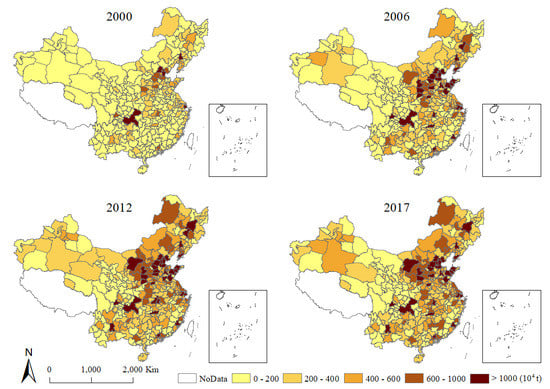
4.1. Spatial Distribution of Carbon Emissions
4.2. Regional Disparity of Carbon Emissions
4.3. Spatial Autocorrelation of Carbon Emissions
4.4. Uncertainties in the Results
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Baninla, Y.; Zhang, S.; Stenseth, N.C.; Hessen, D.O.; Tian, H.; Obersteiner, M.; Chen, D. Drivers of change in China’s energy-related CO2 emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 117, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, B. Exploring the spatial effect of urbanization on multi-sectoral CO2 emissions in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gruber, N.; Brunner, D. Spatiotemporal patterns of the fossil-fuel CO2 signal in central Europe: Results from a high-resolution atmospheric transport model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 14145–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke-Sather, A.; Qu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y. Carbon inequality at the sub-national scale: A case study of provincial-level inequality in CO2 emissions in China 1997–2007. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Shang, Y. Multiscale analysis on spatiotemporal dynamics of energy consumption CO2 emissions in China: Utilizing the integrated of DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light datasets. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 703, 134394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X. China’s city-level energy-related CO2 emissions: Spatiotemporal patterns and driving forces. Appl. Energy 2017, 200, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Shan, J.; Singh, R.P.; Wu, Y.; Pan, J.; Wang, Y.; Lichtfouse, E. High spatio-temporal heterogeneity of carbon footprints in the Zhejiang Province, China, from 2005 to 2015: Implications for climate change policies. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ou, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Jiao, L.; Liu, Y. Estimating spatiotemporal variations of city-level energy-related CO2 emissions: An improved disaggregating model based on vegetation adjusted nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ji, G.; Yue, Y.; Lai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Zheng, W. Spatio-temporal dynamics of urban residential CO2 emissions and their driving forces in China using the integrated two nighttime light datasets. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal variations of CO2 emissions and their impact factors in China: A comparative analysis between the provincial and prefectural levels. Appl. Energy 2019, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, N.; Jakob, M.; Mouratiadou, I. Decomposing inequality in CO2 emissions: The role of primary energy carriers and economic sectors. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 100, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Li, G.; Feng, K. CO2, economic growth, and energy consumption in China’s provinces: Investigating the spatiotemporal and econometric characteristics of China’s CO2 emissions. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Guan, X.; Pang, B.; Ma, H. Urbanisation, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A panel data analysis of China’s provinces. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Streets, D.G.; Xu, Y.; Du, M.; Lin, J. Spatiotemporal dynamics of CO2 emissions from central heating supply in the North China Plain over 2012–2016 due to natural gas usage. Appl. Energy 2019, 241, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F. Mapping spatiotemporal variations of CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions using nighttime light data in Guangdong Province. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 2019, 110, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Y.; Gao, L.; Zuo, J. How national policies facilitate low carbon city development: A China study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Mao, X.; Cao, L. Carbon dioxide emissions from cities in China based on high resolution emission gridded data. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 15, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R.; Rayner, P.J.; Paget, M. Regional variations in spatial structure of nightlights, population density and fossil-fuel CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4756–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, F. Spatialization of electricity consumption of China using saturation-corrected DMSP-OLS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.R.; Sajjad, H.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ting, Y.; Pandey, P.C.; Rani, M.; Kumar, P. Modeling of Electric Demand for Sustainable Energy and Management in India Using Spatio-Temporal DMSP-OLS Night-Time Data. Environ. Manag. 2017, 61, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiński, T. Modeling electricity consumption using nighttime light images and artificial neural networks. Energy 2019, 179, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, W. Modeling population density based on nighttime light images and land use data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keola, S.; Andersson, M.; Hall, O. Monitoring Economic Development from Space: Using Nighttime Light and Land Cover Data to Measure Economic Growth. World Dev. 2015, 66, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Fu, X.; Yan, L. Comparison between the Suomi-NPP Day-Night Band and DMSP-OLS for Correlating Socio-Economic Variables at the Provincial Level in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Niu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J. Assessing the Distribution of Heavy Industrial Heat Sources in India between 2012 and 2018. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Modeling and mapping total freight traffic in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Spatiotemporally enhancing time-series DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery for assessing large-scale urban dynamics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.; Muller, J.-P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time Imagery as a Tool for Global Mapping of Socioeconomic Parameters and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Ambio 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, P.J.; Raupach, M.R.; Paget, M.; Peylin, P.; Koffi, E. A new global gridded data set of CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion: Methodology and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, X. Aligning Pixel Values of DMSP and VIIRS Nighttime Light Images to Evaluate Urban Dynamics. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS night-time light images to evaluate city light dynamics of Syria’s major human settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Weng, Q.; Wang, K. Developing a new cross-sensor calibration model for DMSP-OLS and Suomi-NPP VIIRS night-light imageries. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 153, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, X. Re-examining environmental Kuznets curve for China’s city-level carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Spat. Stat. 2017, 21, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Version 4 DMSP-OLS Nighttime Lights Time Series. Available online: https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp/downloadV4composites.html (accessed on 9 November 2019).
- The Chinese Academy of Sciences. Version of the Earth Luminous Data Set (codenamed “Flint”) Provides Annual Data Download Service. Available online: https://www.jianshu.com/p/5fde55a4d267 (accessed on 9 November 2019).
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, Q. The Uncertainty of Nighttime Light Data in Estimating Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China: A Comparison between DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, M.; Yang, H.; Ge, W. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, J.P.; Tan, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z. Modeling China’s prefecture-level economy using VIIRS imagery and spatial methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Anderson, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C. Using Nighttime Satellite Imagery as a Proxy Measure of Human Well-Being. Sustainbility 2013, 5, 4988–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the Estimators for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Lin, C.-F.; Chu, C.-S.J. Unit root tests in panel data: Asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J. Econ. 2002, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltagi, B.H.; Chang, Y.-J. Testing for random individual effects using recursive residuals. Econ. Rev. 1996, 15, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, T.; Levin, N.; Possingham, H.P.; Levy, Y.; Rocchini, D.; Richardson, A.J.; Kark, S. Can satellite-based night lights be used for conservation? The case of nesting sea turtles in the Mediterranean. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 159, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Wu, F. Analyzing the impact factors of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: What can spatial panel regressions tell us. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S. Urban energy use and carbon emissions from cities in China and policy implications. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 4208–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Shao, S.; Guan, D. An emissions-socioeconomic inventory of Chinese cities. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paez, A.; Wheeler, D. Geographically Weighted Regression. Int. Encycl. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 28, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanorte, A.; Danese, M.; Lasaponara, R.; Murgante, B. Multiscale mapping of burn area and severity using multisensor satellite data and spatial autocorrelation analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geo-Inf. 2013, 20, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.P. The Interpretation of Statistical Maps. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1948, 10, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J. Are the temporal variation and spatial variation of ambient SO2 concentrations determined by different factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Davis, S.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Guan, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Hubacek, K. Outsourcing CO2 within China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11654–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, T.; Du, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mi, Z.; Guan, D.; Zuo, J. Carbon transfer within China: Insights from production fragmentation. Energy Econ. 2020, 86, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Wang, B. Comparative analysis of regional carbon emissions accounting methods in China: Production-based versus consumption-based principles. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Crawford-Brown, D.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Liu, J. A low-carbon road map for China. Nature 2013, 500, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Hubacek, K.; Sun, L.; Liu, Z. Consumption-based CO2 accounting of China’s megacities: The case of Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai and Chongqing. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 47, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, G.; Wiedmann, T.; Wang, Y.; Geschke, A.; Shi, L. Supply-side carbon accounting and mitigation analysis for Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Data Source | DMSP-OLS | NPP-VIIRS |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial resolution | 0.008333° (30 arc-seconds) | 0.004167° (15 arc-seconds) |
| Radiometric resolution | 6-bit | 14-bit |
| Overpass time | 19:30 | 01:30 |
| On-board calibration | No | Yes |
| DN range | 0–63 | 0–255 |
| Temporal sequence | 2000–2013 annual composites | 2012–2017 annual composites |
| City | Actual DMSP-OLS | Earlier Model | Proposed Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated DMSP-OLS | RE (%) | Simulated DMSP-OLS | RE (%) | ||
| Beijing | 295,151 | 182,634 | −38.62 | 291,495 | −1.24 |
| Tianjin | 263,157 | 197,382 | −26.15 | 261,843 | −0.50 |
| Shanghai | 252,233 | 144,852 | −42.61 | 247,273 | −1.97 |
| Chongqing | 208,011 | 249,348 | 14.98 | 212,461 | 2.14 |
| Suzhou | 272,465 | 181,829 | −33.81 | 269,128 | −1.22 |
| Fuyang | 54,572 | 77,287 | 36.61 | 55,429 | 1.57 |
| Xiamen | 51,250 | 31,666 | −38.59 | 50,521 | −1.42 |
| Heze | 91,337 | 122,301 | 31.26 | 91,286 | −0.06 |
| Shangqiu | 71,604 | 102,934 | 38.11 | 73,017 | 1.97 |
| Zhoukou | 65,964 | 94,697 | 34.77 | 68,841 | 4.36 |
| Shenzhen | 113,702 | 55,092 | −51.56 | 111,414 | −2.01 |
| Yaan | 9425 | 13,795 | 40.22 | 9638 | 2.26 |
| MARE | - | - | 16 | - | 4.95 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wu, Y.; Schlink, U.; Singh, R.P. Spatiotemporal Variations of City-Level Carbon Emissions in China during 2000–2017 Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182916
Sun Y, Zheng S, Wu Y, Schlink U, Singh RP. Spatiotemporal Variations of City-Level Carbon Emissions in China during 2000–2017 Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182916
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yu, Sheng Zheng, Yuzhe Wu, Uwe Schlink, and Ramesh P. Singh. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Variations of City-Level Carbon Emissions in China during 2000–2017 Using Nighttime Light Data" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182916
APA StyleSun, Y., Zheng, S., Wu, Y., Schlink, U., & Singh, R. P. (2020). Spatiotemporal Variations of City-Level Carbon Emissions in China during 2000–2017 Using Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182916