A Fast and Effective Method for Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation of Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
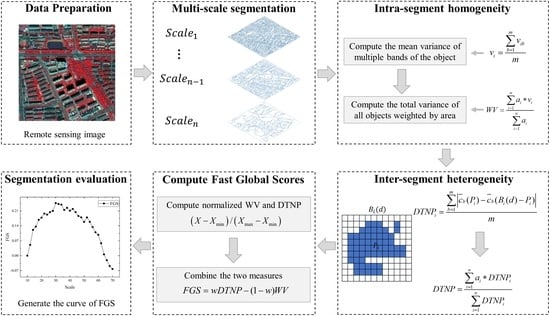
2.1. Overview
2.2. Study Area and Data
2.3. Image Segmentation
2.4. Unsupervised Evaluation Using Fast-Global Score
2.5. Accuracy Assessment Measures for the Proposed Method
2.6. Comparison with Other UE Methods and Inter-Segment Heterogeneity Measures
3. Results
3.1. Effectiveness Analysis of DTNP
3.2. Effectiveness Analysis of FGS
3.3. The Performance of FGS on Other Datasets
3.4. Computational Cost
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Van de Voorde, T.; Roberts, D.; Jiang, H.; Xu, W. Open water detection in urban environments using high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, J. An Improved Method for Road Extraction from High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Images that Enhances Boundary Information. Sensors 2020, 20, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.; Luo, J.; Zhou, Y.n.; Wang, C.; Xi, J.; Fang, J. Geo-Object-Based Land Cover Map Update for High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Images via Change Detection and Label Transfer. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.; Gao, H.; Shao, Y. An Efficient Building Extraction Method from High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on Improved Mask R-CNN. Sensors 2020, 20, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, N.; Hendrix, C.; Congalton, R.G. A comparison of urban mapping methods using high-resolution digital imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ni, L. Object-oriented classification of high resolution satellite image for better accuracy. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium Spatial Accuracy Assessement Natural Resources Environironmental Science Vol Ii: Accuracy Geomaterials, Shanghai, China, 25–27 June 2008; pp. 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.D.; Chen, D. Segmentation for Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA): A review of algorithms and challenges from remote sensing perspective. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlson, M.; Reese, H.; Ostwald, M. Tree Crown Mapping in Managed Woodlands (Parklands) of Semi-Arid West Africa Using WorldView-2 Imagery and Geographic Object Based Image Analysis. Sensors 2014, 14, 22643–22669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Xiao, P.; He, G.; Zhu, L. Segmentation quality evaluation using region-based precision and recall measures for remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, I.E.R.; Shi, W. A Random Forests classification method for urban land-use mapping integrating spatial metrics and texture analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1175–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, J.; Pocas, I.; Marcos, B.; Mucher, C.A.; Honrado, J.P. SegOptim—A new R package for optimizing object-based image analyses of high-spatial resolution remotely-sensed data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 76, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemker, R.; Salvaggio, C.; Kanan, C. Algorithms for semantic segmentation of multispectral remote sensing imagery using deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.R.; Zhang, G.F.; Wu, Z.C.; Yi, L.N. An Edge Embedded Marker-Based Watershed Algorithm for High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2781–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, L.; Soille, P. Watersheds in Digital Spaces: An Efficient Algorithm Based on Immersion Simulations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafarenko, L.; Petrou, M.; Kittler, J. Automatic watershed segmentation of randomly textured color images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, P.R.; Smith, A.M.; Hill, B.D.; Peddle, D.R.; Coburn, C.A.; Blackshaw, R.E. Hybrid segmentation—Artificial Neural Network classification of high resolution hyperspectral imagery for Site-Specific Herbicide Management in agriculture. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, Y.H.; Caspersen, J. Region merging using local spectral angle thresholds: A more accurate method for hybrid segmentation of remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Pu, H.; Song, S.R.; Du, M.Y. An adaptive scale estimating method of multiscale image segmentation based on vector edge and spectral statistics information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 6826–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Qi, Q.W.; Liu, Y. Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation Using Area-Weighted Variance and Jeffries-Matusita Distance for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Xiao, L.; Pan, D.L. Optimizing multiscale segmentation with local spectral heterogeneity measure for high resolution remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 157, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Qi, Q.W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.L.; Wang, J. Unsupervised segmentation parameter selection using the local spatial statistics for remote sensing image segmentation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 81, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fritts, J.E.; Goldman, S.A. Image segmentation evaluation: A survey of unsupervised methods. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinton, N.; Holt, A.; Scarborough, J.; Yan, L.; Gong, P. Accuracy Assessment Measures for Object-based Image Segmentation Goodness. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bian, L.; Meng, Y.H.; Wang, H.P.; Zhang, S.F.; Yang, Y.N.; Shao, X.M.; Wang, B. Discrepancy measures for selecting optimal combination of parameter values in object-based image analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 68, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, Y.H.; Weng, Q.H. An Automated Method to Parameterize Segmentation Scale by Enhancing Intrasegment Homogeneity and Intersegment Heterogeneity. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, G.M.; Camara, G.; Reis, I.A.; Bins, L.S.; Monteiro, A.M. Parameter selection for region-growing image segmentation algorithms using spatial autocorrelation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Xie, Z.X. Unsupervised image segmentation evaluation and refinement using a multi-scale approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, P.J.; He, Y.H. A multi-band approach to unsupervised scale parameter selection for multi-scale image segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Tang, Y.; Jing, L.; Li, H.; Ding, H. A Novel Unsupervised Segmentation Quality Evaluation Method for Remote Sensing Images. Sensors 2017, 17, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shapiro, L.G. Image Segmentation Techniques. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1985, 29, 100–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, X.N.; Yuan, J. Self-adaptive segmentation of satellite images based on a weighted aggregation approach. GIScience Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.D.; Nazif, A.M. Dynamic Measurement of Computer Generated Image Segmentations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1985, 7, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, C.E.; Strahler, A.H. The Factor of Scale in Remote-Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 21, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamsee, A.M.; Kamala, P.; Martha, T.R.; Kumar, K.V.; Sankar, G.J.; Amminedu, E. A Tool Assessing Optimal Multi-Scale Image Segmentation. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.J.; Shi, R.H.; Gao, W. Automatic Selection of Optimal Segmentation Scales for High-resolution Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability X, San Diego, CA, USA, 24 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Bragais, M.; Endo, I.; Magcale-Macandog, D.B.; Macandog, P.B.M. Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization Considering Within—And Between-Segment Heterogeneity at Multiple Scale Levels: Test Case for Mapping Residential Areas Using Landsat Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2015, 4, 2292–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- eCognition Software. Available online: https://geospatial.trimble.com/products-and-solutions/ecognition (accessed on 11 September 2020).
- Sun, W.; Chen, B.; Messinger, D.W. Nearest-neighbor diffusion-based pan-sharpening algorithm for spectral images. Opt. Eng. 2013, 53, 013107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ENVI Software. Available online: https://www.harris.com/solution/envi (accessed on 11 September 2020).
- Benz, U.C.; Hofmann, P.; Willhauck, G.; Lingenfelder, I.; Heynen, M. Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 58, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V. Machine Learning for Aerial Image Labeling; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]














| Test | Methods | Accuracy Assessment Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QR | OS | US | D | ||
| T1 | DTNP | 0.2875 | 0.0849 | 0.2255 | 0.1914 |
| MI | 0.5636 | 0.0281 | 0.5512 | 0.3931 | |
| BSH | 0.3275 | 0.2282 | 0.1382 | 0.2188 | |
| T2 | DTNP | 0.4236 | 0.0338 | 0.3973 | 0.2961 |
| MI | 0.4236 | 0.0338 | 0.3973 | 0.2961 | |
| BSH | 0.3383 | 0.0708 | 0.2808 | 0.2338 | |
| T3 | DTNP | 0.3491 | 0.0589 | 0.3055 | 0.2363 |
| MI | 0.3806 | 0.0579 | 0.3517 | 0.2614 | |
| BSH | 0.4927 | 0.4528 | 0.1265 | 0.3470 | |
| T4 | DTNP | 0.4204 | 0.0533 | 0.3884 | 0.2886 |
| MI | 0.4864 | 0.0508 | 0.4575 | 0.3368 | |
| BSH | 0.3013 | 0.1906 | 0.1461 | 0.2025 | |
| Test | Methods | Accuracy Assessment Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QR | OS | US | D | ||
| T1 | FGS | 0.2875 | 0.0849 | 0.2255 | 0.1914 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.2875 | 0.0849 | 0.2255 | 0.1914 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.3016 | 0.0839 | 0.2414 | 0.2012 | |
| T2 | FGS | 0.2843 | 0.2293 | 0.0856 | 0.1944 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.4242 | 0.3913 | 0.0864 | 0.2974 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.2795 | 0.1319 | 0.1702 | 0.1909 | |
| T3 | FGS | 0.3281 | 0.1744 | 0.1894 | 0.2212 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.3924 | 0.3271 | 0.1285 | 0.2697 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.3281 | 0.1744 | 0.1894 | 0.2212 | |
| T4 | FGS | 0.3237 | 0.2487 | 0.1184 | 0.2194 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.2969 | 0.1171 | 0.2073 | 0.1978 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.2915 | 0.0830 | 0.2269 | 0.1929 | |
| Test | Methods | Accuracy Assessment Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QR | OS | US | D | ||
| T5 | FGS | 0.6411 | 0.4502 | 0.3709 | 0.4589 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.6503 | 0.5059 | 0.3185 | 0.4650 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.6371 | 0.3877 | 0.4307 | 0.4564 | |
| T6 | FGS | 0.6231 | 0.3828 | 0.4091 | 0.4437 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.6231 | 0.3828 | 0.4091 | 0.4437 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.6206 | 0.4276 | 0.3622 | 0.4419 | |
| T7 | FGS | 0.6131 | 0.4192 | 0.3392 | 0.4351 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.6116 | 0.3260 | 0.4345 | 0.4348 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.6276 | 0.4715 | 0.3036 | 0.4467 | |
| T8 | FGS | 0.6491 | 0.3881 | 0.4446 | 0.4658 |
| Johnson’s method | 0.6439 | 0.4077 | 0.4181 | 0.4615 | |
| Wang’s method | 0.6465 | 0.4363 | 0.3924 | 0.4635 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Allam, M. A Fast and Effective Method for Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183005
Zhao M, Meng Q, Zhang L, Hu D, Zhang Y, Allam M. A Fast and Effective Method for Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183005
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Maofan, Qingyan Meng, Linlin Zhang, Die Hu, Ying Zhang, and Mona Allam. 2020. "A Fast and Effective Method for Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation of Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183005
APA StyleZhao, M., Meng, Q., Zhang, L., Hu, D., Zhang, Y., & Allam, M. (2020). A Fast and Effective Method for Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183005