Precise Orbit Determination of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Using Onboard GPS and BDS Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CSES Platform Description
2.2. Data Collection and Quality Analysis
2.3. POD Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Antenna Phase Center Modelling Based on GPS Data
3.2. POD Results Based on BDS Data
3.3. POD Results Based on Combined GPS and BDS Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, X.; Zong, Q.G.; Zhang, X. Introduction to special section on the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite and initial results. Earth Planet. Phys. 2018, 2, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Zhou, B.; Magnes, W.; Lammegger, R.; Pollinger, A. High precision magnetometer for geomagnetic exploration onboard of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, G.; Bartocci, S.; Basara, L.; Battiston, R.; Burger, W.J.; Carfora, L.; Castellini, G.; Cipollone, P.; Conti, L.; Contin, A.; et al. The HEPD particle detector of the CSES satellite mission for investigating seismo-associated perturbations of the Van Allen belts. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lei, J.; Li, S.; Zeren, Z.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.; Yu, W. The Electric Field Detector (EFD) onboard the ZH-1 satellite and first observational results. Earth Planet. Phys. 2018, 2, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.B.; Zeng, L.; Zhan, F.; Wang, Z.G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.C.; Ji, Z.Q.; Wang, P.F.; Liu, Z.W.; et al. The electromagnetic wave experiment for CSES mission: Search coil magnetometer. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, A.; Piero, D.; Sun, Y. The technology of space plasma in-situ measurement on the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, J.; Shen, X.; Wan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Analysis of GNSS radio occultation data from satellite ZH-01. Earth Planet. Phys. 2018, 2, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ou, M.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, F.; Yu, X.; Zhen, W. Preliminary observation results of the Coherent Beacon System onboard the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite-1. Earth Planet. Phys. 2018, 2, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Ries, J.C.; Davis, G.W.; Eanes, R.J.; Schutz, B.E.; Shum, C.K.; Watkins, M.M.; Marshall, J.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Putney, B.H.; et al. Precision orbit determination for TOPEX/POSEIDON. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1994, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Kroes, R. In-flight performance analysis of the CHAMP BlackJack GPS Receiver. GPS Solut. 2003, 7, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertiger, W.; Bar-Sever, Y.; Bettadpur, S.; Dunn, C.; Haines, B.; Kruizinga, G.; Kuang, D.; Nandi, S.; Romans, L.; Watkins, M.; et al. GRACE: Millimeters and Microns in Orbit. Jet Propuls. Lab. 2020. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2014/10373 (accessed on 24 September 2002).
- Jäggi, A.; Hugentobler, U.; Bock, H.; Beutler, G. Precise orbit determination for GRACE using undifferenced or doubly differenced GPS data. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, D.; Ju, B.; Yao, J.; Duan, X.; Yi, D. Basic performance of BeiDou-2 navigation satellite system used in LEO satellites precise orbit determination. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Shi, C.; Jiang, K.; Guo, X.; Dai, X.; Meng, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, G.; Liao, M. Precise orbit determination of the Fengyun-3C satellite using onboard GPS and BDS observations. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, C.; Lu, C.; Zhu, J.; Ding, H. Orbit determination using real tracking data from FY3C-GNOS. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberius, C.; Kenselaar, F. Variance component estimation and precise GPS positioning: Case study. J. Surv. Eng. 2003, 129, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Piergiorgio, P.; Dai, J. The state-of-the-art of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite mission. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Yang, G.; Liao, M.; Ma, H.; Liu, J. Enhanced orbit determination for BeiDou satellites with FengYun-3C onboard GNSS data. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Ge, M. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2017, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förste, C.; Bruinsma, S.L.; Shako, R.; Marty, J.C.; Flechtner, F.; Abrikosov, O.; Dahle, C.; Lemoine, J.M.; Neumayer, K.H.; Biancale, R.; et al. EIGEN-6—A New Combined Global Gravity Field Model Including GOCE Data from the Collaboration of GFZ-Potsdam and GRGS-Toulouse; EGU2011-3242-2, EGU General Assembly; General Assembly European Geosciences Union: Vienna, Austria, 2011; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.; Luthcke, S. Modeling radiation forces acting on TOPEX/Poseidon for precision orbit determination. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1994, 31, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Standish, E.M. JPL Planetary and Lunar Ephemerides, DE405/LE405; JPL Interoffice Memorandum 312.F-98-048; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions 2010, Technical Report; IERS Convention Center: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Biancale, R.; Ill, M.; Barlier, F. Improvement of the empirical thermospheric model DTM: DTM94–a comparative review of various temporal variations and prospects in space geodesy applications. J. Geod. 1998, 72, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambis, D. Monitoring Earth orientation using space-geodetic techniques: State-of-the-art and prospective. J. Geod. 2004, 78, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Tapley, B.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.; Nagel, P.; Pastor, R. Precise orbit determination for the GRACE mission using only GPS data. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.R. Jason-1 Precision Orbit Determination Using GPS Combined with SLR and DORIS Tracking Data. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dow, J.; Neilan, R.; Rizos, C. The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sat. Type | A (cm) | C (cm) | R (cm) | 3D (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEO | 175.4 | 311.1 | 27.2 | 378.5 |
| IGSO | 7.2 | 15.0 | 4.6 | 17.7 |
| MEO | 8.7 | 7.5 | 2.8 | 12.1 |
| Item | Contents |
|---|---|
| Reference frame | J2000.0 |
| Gravity model | EIGEN-6C. Static part of EIGEN-6C up to degree and order 120; temporal part of EIGEN-6C up to degree and order 50 [21] |
| N-body | JPL DE405 [23] |
| Solid earth tide | IERS Conventions 2010 [24] |
| Pole tide | IERS Conventions 2010 [24] |
| Ocean tide | FES2004 [25] |
| Solar radiation Pressure | Box-wing |
| Attitude | Nominal |
| Atmospheric drag | DTM94 [26]. Piecewise constant drag coefficients estimated |
| Empirical forces | Piecewise periodical terms in along-track, cross-track and radial direction (a priori sigma 10 nm/s2) |
| Basic observables | Un-differenced BDS B1/B2 and GPS L1/L2 ionosphere-free linear combination of code (a priori sigma 10 m) and phase (a priori sigma 1 cm) |
| GPS orbits and clocks | IGS final products |
| BDS orbits and clocks | Recomputed products/GFZ products |
| Sampling rate | 30 s |
| GPS antenna phase center | PCOs and PCVs from IGS |
| BDS antenna phase center | Only PCO from IGS MGEX |
| CSES PCO | Corrected using default values, estimated Z component based on GPS-only POD |
| CSES PCV | PCV map modeling based on the phase residuals of GPS-only POD |
| Earth rotation parameters | IERS C04 [27] |
| Relativistic effects | IERS Conventions 2010 [24] |
| Ambiguities | Float value for each ambiguity pass |
| Receiver clock | One per epoch as process noise |
| Drag coefficient | One per 360 min for both GPS and BDS |
| Empirical accelerations | GPS: One per 90 min for GPS BDS: One per 360 min for BDS |
| Cutoff elevation | 10° |
| Solutions | Residuals (mm) | Full 6-h Overlap (cm) | Central 5-h Overlap (cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | C | R | 3D | A | C | R | 3D | ||
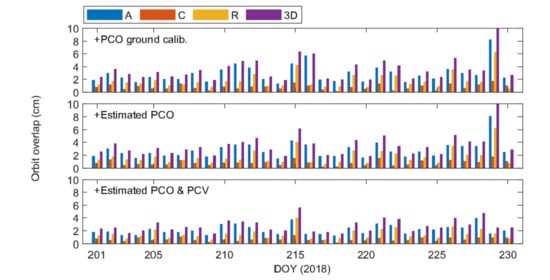
| +PCO ground calib. | 5.63 | 2.94 | 0.85 | 1.83 | 3.65 | 1.93 | 0.63 | 0.92 | 2.28 |
| +Estimated PCO | 5.61 | 2.86 | 0.87 | 1.81 | 3.56 | 1.81 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 2.17 |
| +Estimated PCO&PCV | 4.11 | 2.18 | 0.72 | 1.50 | 2.80 | 1.51 | 0.52 | 0.81 | 1.86 |
| PANDA (mm) | GFZ (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With GEOs | W/o GEOs | With GEOs | W/o GEOs | |
| GEO | 17.8 | / | 33.7 | / |
| IGSO | 9.7 | 3.0 | 14.8 | 3.2 |
| MEO | 8.9 | 3.2 | 16.3 | 3.5 |
| GNSS Products | Methods | With GEOs (cm) | Without GEOs (cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | C | R | 3D | A | C | R | 3D | ||
| PANDA | Full 6-h overlap | 37.49 | 18.76 | 14.56 | 45.43 | 19.80 | 8.02 | 8.25 | 23.68 |
| Central 5-h overlap | 31.72 | 17.15 | 13.50 | 39.54 | 17.77 | 7.4 | 7.89 | 21.50 | |
| Comparison w/o Helmert trans. | 31.62 | 14.12 | 12.58 | 37.24 | 14.50 | 5.25 | 6.06 | 16.75 | |
| Comparison with Helmert trans. | 25.60 | 14.73 | 10.90 | 31.75 | 12.56 | 5.10 | 5.78 | 14.83 | |
| GFZ | Full 6-h overlap | 69.14 | 35.2 | 26.6 | 83.91 | 21.62 | 8.78 | 8.95 | 25.83 |
| Central 5-h overlap | 63.16 | 32.57 | 24.76 | 77.2 | 19.31 | 8.07 | 8.56 | 23.39 | |
| Comparison w/o Helmert trans. | 51.46 | 31.76 | 19.78 | 64.11 | 15.27 | 5.55 | 6.35 | 17.68 | |
| Comparison with Helmert trans. | 44.14 | 26.40 | 18.48 | 55.07 | 13.25 | 5.50 | 6.10 | 15.72 | |
| Residuals (mm) | Full 6-h Overlap (cm) | Central 5-h Overlap (cm) | Orbit Comparison (cm) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | BDS IGSO | BDS MEO | A | C | R | 3D | A | C | R | 3D | A | C | R | 3D |
| 4.2 | 8.9 | 8.2 | 2.15 | 0.63 | 1.46 | 2.73 | 1.48 | 0.44 | 0.78 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 1.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qing, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, X.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S. Precise Orbit Determination of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Using Onboard GPS and BDS Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193234
Qing Y, Lin J, Liu Y, Dai X, Lou Y, Gu S. Precise Orbit Determination of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Using Onboard GPS and BDS Observations. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193234
Chicago/Turabian StyleQing, Yun, Jian Lin, Yang Liu, Xiaolei Dai, Yidong Lou, and Shengfeng Gu. 2020. "Precise Orbit Determination of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Using Onboard GPS and BDS Observations" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193234
APA StyleQing, Y., Lin, J., Liu, Y., Dai, X., Lou, Y., & Gu, S. (2020). Precise Orbit Determination of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Using Onboard GPS and BDS Observations. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193234