Performance of a Radar Mosaic Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm Based on a New Data Quality Index for the Chinese Polarimetric Radars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polarimetric Radar Data Analysis
2.1.1. Beam Blockage Situation of Polarimetric Radars
2.1.2. Data and Quality Control Method
2.1.3. Analysis of Polarimetric Radars Data Consistency
2.2. The Key Methods in Polarimetric Radar Mosaic QPE Algorithm
2.2.1. BB Correction
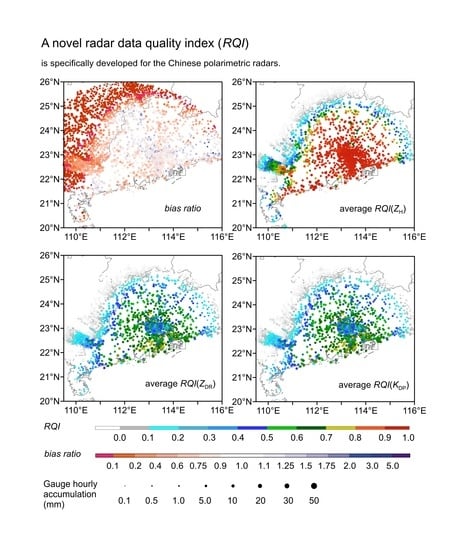
2.2.2. Radar Data Quality Index and Polarimetric Radar Mosaic Algorithm
2.2.3. Polarimetric Radar Mosaic QPE Algorithm
3. Results
3.1. Performances of BB Correction
3.2. Results of the Polarimetric Radar Data Mosaic
3.3. Results of Polarimetric Radar Mosaic QPE
3.4. Sensitivity Tests about the Precipitation Types
4. Discussion
4.1. AVPD under BB
4.2. The Relationship between QPE Accuracy and RQI
5. Conclusions
- After BB correction, the values of ZH, ZDR, and KDP in BB become closer to those under BB than before. However, the BB correction performance of KDP is not as good as that of ZH and ZDR. Only the corrected ZH and ZDR are used to estimate precipitation in the BBA. Precipitation is overestimated even when using polarimetric parameters in the BBA prior to BB correction. BB correction in this new radar mosaic QPE algorithm obviously mitigates the overestimation of rainfall in the BBA.
- The new polarimetric radar mosaic QPE algorithm based on RQI can combine the different radars’ advantages to improve QPE performances in the blocked area and the area far from the radars, thereby obtaining more accurate and wider range of mosaic data and QPE products. The new algorithm also performs better than the single radar QPE algorithm in the area close to the two radars. Within 180 km of the radars, the RMSE and NE decrease by at least 5.29% and 5.59%, respectively. The near real-time statistics of evaluated indicators show that there is a near real-time improvement when the radar mosaic QPE algorithm is applied. It is important for the operational application of this new algorithm.
- The sensitivity tests with the changing percentage of stratiform and convective precipitation show that NE and NB are basically stable when this percentage changes. The new polarimetric radar mosaic QPE algorithm can perform well and stably for any type of precipitation occurred in warm seasons.
- There is good correlation between QPE accuracy and the RQI of ZH (ZDR and KDP). An effective QPE area can be defined with an RQI of ZH lager than 0.9, resulting in a small bias (NB = −2.84%) for rainfall events in this study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; ISBN 1139429469. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Tan, H.; Cifelli, R. Rainfall estimation from ground radar and TRMM Precipitation Radar using hybrid deep neural networks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10669–10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Cocks, S.; Zhang, P.; Ryzhkov, A.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B. A Dual-polarization Radar Synthetic QPE for Operations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Y.; Kirstetter, P.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Xue, X. Evaluation of a method to enhance real-time, ground radar-based rainfall estimates using climatological profiles of reflectivity from space. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Gourley, J.J. Constructing Three-Dimensional Multiple-Radar Reflectivity Mosaics: Examples of Convective Storms and Stratiform Rain Echoes. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Vasiloff, S.; Kaney, B.; Arthur, A.; Cooten, S.V.; Kelleher, K.; Kitzmiller, D.; Ding, F.; et al. National mosaic and multi-sensor QPE (NMQ) system: Description, results, and future plans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1321–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, H. Technique for generating hybrid reflectivity field based on 3D mosaicked reflectivity of weather radar network. Act. Meteor. Sin. 2008, 66, 470–473. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liang, J.; Li, C. Radar quantitative precipitation estimation techniques and effect evaluation. J. Trop. Meteor. 2012, 28, 77–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, C. Operational application and evaluation of the quantitative precipitation estimates algorithm based on the multi–radar mosaic. Act. Meteor. Sin. 2014, 72, 731–748. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Kou, L.; Li, N. Mitigating Spatial Discontinuity of Multi-Radar QPE Based on GPM/KuPR. Hydrology 2018, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Martinaitis, S.; et al. Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) Quantitative Precipitation Estimation: Initial Operating Capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wen, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.H. Evaluation of the Polarimetric-Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimates of an Extremely Heavy Rainfall Event and Nine Common Rainfall Events in Guangzhou. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.T.; Chandrasekar, V. Algorithm for estimation of the specific differential phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2565–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioli, J.; Schneebeli, M.; Berne, A. Accuracy of phase-based algorithms for the estimation of the specific differential phase shift using simulated polarimetric weather radar data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, K.; Giangrande, S.E. A hybrid method to estimate specific differential phase and rainfall with linear programming and physics constraints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, L.; Wei, M.; Xi, B.; Yu, M. Statistics–based optimization of the polarimetric radar Hydrometeor Classification Algorithm and its application for a squall line in South China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 296–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryde, J.W. The Attenuation and Radar Echoes Produced at Centimeter Wavelengths by Various Meteorological Phenomena. In Meteorological Factors in Radio Wave Propagation, London, U.K.; The Physical Society: London, UK, 1946; pp. 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.M.; Bemis, A.C. A Quantitative Study of the `Bright Band’ in Radar Precipitation Echoes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1950, 7, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wexler, R.; Atlas, D.; Mason, B.J. Factors influencing radar-echo intensities in the melting layer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1956, 82, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, R.M.; Atlas, D. Doppler fall speed and particle growth in stratiform precipitation. In Proceedings of the 10th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Washington, DC, USA, 22–25 April 1963; American Meteorological Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1963; pp. 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Langston, C.; Howard, K. Brightband Identification Based on Vertical Profiles of Reflectivity from the WSR-88D. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1859–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, J.J.; Calvert, C.M. Automated Detection of the Bright Band Using WSR-88D Data. Wea. Forecast. 2003, 18, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y. A Real-Time Algorithm for the Correction of Brightband Effects in Radar-Derived QPE. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J. Correction of Radar QPE Errors Associated with Low and Partially Observed Brightband Layers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Cluckie, I.D.; Han, D. Correction of the bright band using dual-polarisation radar. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2005, 6, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reino, K.; Laura, C.A.; Jason, S. Estimation of Melting Layer Altitudes from Dual- Polarization Weather Radar Observations. In Proceedings of the Eighth European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mario, M.; Nicoletta, R.; Elisa, A.; Eugenio, G.; Luca, B. Investigation of weather radar quantitative precipitation estimation methodologies in complex orography. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, K.; Hagen, M.; Einfalt, T. A Quality Control Concept for Radar Reflectivity, Polarimetric Parameters, and Doppler Velocity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 865–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vulpiani, G.; Montopoli, M.; Passeri, L.D.; Gioia, A.G.; Giordano, P.; Marzano, F.S. On the Use of Dual-Polarized C-Band Radar for Operational Rainfall Retrieval in Mountainous Areas. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2012, 51, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabary, P. The New French Operational Radar Rainfall Product. Part I: Methodology. Wea. Forecast. 2010, 22, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J. A Physically Based Two-Dimensional Seamless Reflectivity Mosaic for Radar QPE in the MRMS System. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y. Preliminary analysis of data quality of Guangzhou S-band polarimetric weather radar. J. Trop. Meteor. 2018, 34, 59–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bech, J.; Codina, B.; Lorente, J.; Bebbington, D. The sensitivity of single polarization weather radar beam blockage correction to variability in the vertical refractivity gradient. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y. Radial interference echo identification algorithm based on fuzzy logic for weather radar. Act. Meteor. Sin. 2020, 78, 116–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wei, F.; Chandrasekar, V. Radar-based quantitative precipitation estimation for the identification of debris flow occurrence over earthquake-affected regions in Sichuan, China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 18, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Cao, Q. VPR correction of bright band effects in radar QPEs using polarimetric radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 3627–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B. Radar Quality Index (RQI)—A combined measure for beam blockage and VPR effects in a national network. In Proceedings of the Symposium Weather Radar and Hydrology, Exeter, UK, 18–21 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. Data Quality Analysis, Hydrometeor Classification and Mosaic Application of Polarimetric Radars in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Flaming, Z.L.; Hu, J.; Qi, Y. Evaluation and uncertainty estimation of NOAA/NSSL next-generation National Mosaic QPE (Q2) over the continental United States. J. Hydrometeor. 2013, 14, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


















| Parameter Type | Setting |
|---|---|
| The antenna diameter (m) | 8.54 |
| The antenna gain (dB) | 45.31 |
| The beam width (°) | <0.98 |
| The first side lobe (dB) | <−30 |
| The wave length (cm) | 10.3 |
| The operating mode | simultaneous horizontal and |
| vertical transmission and reception | |
| The minimum detectable power (dBm) | −117.8 |
| The volume scan mode | VCP21 (9 tilts) |
| The range resolution (km) | 0.25 |
| # | Date (UTC) | Total Time (h) | No. of Valued Gauges | Mean Gauge Accumulation (mm) | Max Gauge Accumulation (mm) | Precipitation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 May 2016 | 12 | 730 | 19.04 | 118.5 | squall line |
| 2 | 9–10 May 2016 | 34 | 905 | 34.68 | 222.8 | convective |
| 3 | 15 May 2016 | 10 | 963 | 14.19 | 67.1 | squall line |
| 4 | 19–21 May 2016 | 43 | 1001 | 55.77 | 416.6 | stratocumulus |
| 5 | 27–28 May 2016 | 24 | 991 | 30.48 | 177.2 | squall line |
| 6 | 4–5 June 2016 | 24 | 935 | 29.20 | 109.4 | stratocumulus |
| 7 | 9 June 2016 | 8 | 269 | 9.56 | 80.2 | stratocumulus |
| 8 | 11–14 June 2016 | 86 | 1007 | 44.57 | 211.4 | stratocumulus |
| 9 | 15 June 2016 | 6 | 719 | 11.99 | 79 | squall line |
| Method | Based on Raw Data in BB | Based on Corrected Data in BB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | NE (%) | NB (%) | CC | NE (%) | NB (%) | |
| R1(ZH) | 0.39 | 41.66 | 37.55 | 0.80 | 11.79 | −1.24 |
| R2(ZH) | 0.39 | 40.42 | 36.42 | 0.80 | 11.50 | −1.22 |
| R1(KDP) | 0.15 | 100.2 | 73.30 | 0.26 | 60.28 | 16.96 |
| R2(KDP) | 0.15 | 97.52 | 71.14 | 0.26 | 59.02 | 16.41 |
| R(ZH,ZDR) | 0.52 | 38.38 | 31.06 | 0.87 | 13.81 | 1.53 |
| R(KDP,ZDR) | 0.16 | 93.39 | 66.61 | 0.26 | 59.30 | 16.17 |
| Method | CC | RMSE (mm) | NE (%) | NB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radar mosaic QPE | 0.86 | 3.76 | 39.72 | −5.89 |
| Guangzhou Radar QPE | 0.85 | 3.97 | 42.07 | −2.06 |
| Yangjiang Radar QPE | 0.65 | 5.88 | 64.26 | −29.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wen, H. Performance of a Radar Mosaic Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm Based on a New Data Quality Index for the Chinese Polarimetric Radars. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213557
Zhang Y, Liu L, Wen H. Performance of a Radar Mosaic Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm Based on a New Data Quality Index for the Chinese Polarimetric Radars. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(21):3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213557
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Liping Liu, and Hao Wen. 2020. "Performance of a Radar Mosaic Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm Based on a New Data Quality Index for the Chinese Polarimetric Radars" Remote Sensing 12, no. 21: 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213557
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, L., & Wen, H. (2020). Performance of a Radar Mosaic Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Algorithm Based on a New Data Quality Index for the Chinese Polarimetric Radars. Remote Sensing, 12(21), 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213557