Estimation of Surface Concentrations of Black Carbon from Long-Term Measurements at Aeronet Sites over Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Periods
2.2. AERONET Sun-Sky Radiometer
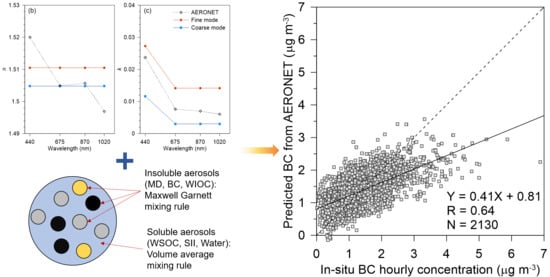
2.3. Separation of the Refractive Index (RI) into Real and Imaginary Parts for Fine- and Coarse-Mode Aerosols
2.4. Determination of the Volume Fractions for Chemical Components in Fine Mode
2.5. In-Situ BC Measurements and Meteorological Data
3. Results
3.1. Estimated Column Concentration of Chemical Components of Fine Mode Aerosol at AERONET Sites
3.2. Monthly Variation in the Columnar BC Concentration Estimated from AERONET
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison between Columnar BC Concentration Estimated from AERONET and In-Situ BC Concentrations
4.2. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) Model for Predicting Surface BC Concentration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samset, B.H.; Myhre, G.; Herber, A.; Kondo, Y.; Li, S.M.; Moteki, N.; Koike, M.; Oshima, N.; Schwarz, J.P.; Balkanski, Y.; et al. Modelled black carbon radiative forcing and atmospheric lifetime in AeroCom Phase II constrained by aircraft observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12465–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.; Forster, P.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.; Flanner, M.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Hua, J.; Mu, Z.; Peng, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, R.; Kan, H. Differentiating the associations of black carbon and fine particle with daily mortality in a Chinese city. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.R.; Jerrett, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Burnett, R.T.; Stone, V.; Derwent, R.; Atkinson, R.W.; Cohen, A.; Shonkoff, S.B.; Krewski, D.; et al. Public health benefits of strategies to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions: Health implications of short-lived greenhouse pollutants. Lancet 2009, 374, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suglia, S.F.; Gryparis, A.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, R.J. Association between Traffic-Related Black Carbon Exposure and Lung Function among Urban Women. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.H.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; van Bree, L.; ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson Richard, W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Black Carbon as an Additional Indicator of the Adverse Health Effects of Airborne Particles Compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; Ghissassi, F.E.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. The carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution. The Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Dentener, F.; van Aardenne, J.A.; Monni, S.; Doering, U.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Pagliari, V.; et al. Gridded emissions of air pollutants for the period 1970–2012 within EDGAR v4.3.2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1987–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F.; Pan, X.; Li, J.; Ge, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, H. Estimation of atmospheric aging time of black carbon particles in the polluted atmosphere over central-eastern China using microphysical process analysis in regional chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grythe, H.; Kristiansen, N.I.; Groot Zwaaftink, C.D.; Eckhardt, S.; Ström, J.; Tunved, P.; Krejci, R.; Stohl, A. A new aerosol wet removal scheme for the Lagrangian particle model FLEXPART v10. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1447–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winiger, P.; Andersson, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; Gustafsson, Ö. The sources of atmospheric black carbon at a European gateway to the Arctic. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kanaya, Y.; Park, S.M.; Matsuki, A.; Sadanaga, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Uno, I.; Pan, X.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.; et al. Regional variability in black carbon and carbon monoxide ratio from long-term observations over East Asia: Assessment of representativeness for black carbon (BC) and carbon monoxide (CO) emission inventories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanaya, Y.; Pan, X.; Miyakawa, T.; Komazaki, Y.; Taketani, F.; Uno, I.; Kondo, Y. Long-term observations of black carbon mass concentrations at Fukue Island, western Japan, during 2009–2015: Constraining wet removal rates and emission strengths from East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10689–10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S.; Holben, B.N. Identification of columnar aerosol types under high aerosol optical depth conditions for a single AERONET site in Korea. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, P.B.; Kacenelenbogen, M.; Livingston, J.M.; Hasekamp, O.P.; Burton, S.P.; Schuster, G.L.; Johnson, M.S.; Knobelspiesse, K.D.; Redemann, J.; Ramachandran, S. A multiparameter aerosol classification method and its application to retrievals from spaceborne polarimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9838–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Sinyuk, A.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Thompson, A.M.; Schafer, J.S. An analysis of AERONET aerosol absorption properties and classifications representative of aerosol source regions. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.E.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, M.; Yoon, S.C.; Lee, S. Carbonaceous aerosol AAE inferred from in-situ aerosol measurements at the Gosan ABC super site, and the implications for brown carbon aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6173–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahadur, R.; Praveen, P.S.; Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V. Solar absorption by elemental and brown carbon determined from spectral observations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17366–17371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-W.; Cho, C.; Rupakheti, M. Estimating contributions of black and brown carbon to solar absorption from aethalometer and AERONET measurements in the highly polluted Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, M.; Lim, S.; Fang, W.; Gustafsson, Ö.; Andersson, A.; Park, R.J.; Sheridan, P.J. Observation-based estimates of the mass absorption cross-section of black and brown carbon and their contribution to aerosol light absorption in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Arola, A.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N. Remote sensing of soot carbon—Part 2: Understanding the absorption Ångström exponent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1587–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazorla, A.; Bahadur, R.; Suski, K.J.; Cahill, J.F.; Chand, D.; Schmid, B.; Ramanathan, V.; Prather, K.A. Relating aerosol absorption due to soot, organic carbon, and dust to emission sources determined from in-situ chemical measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9337–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lack, D.A.; Cappa, C.D. Impact of brown and clear carbon on light absorption enhancement, single scatter albedo and absorption wavelength dependence of black carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4207–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arola, A.; Schuster, G.; Myhre, G.; Kazadzis, S.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, S. Inferring absorbing organic carbon content from AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Singh, R.P.; Holben, B.N. Retrieval of black carbon and specific absorption over Kanpur city, northern India during 2001–2003 using AERONET data. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Clothiaux, E.E. Inferring black carbon content and specific absorption from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) aerosol retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, A.; Schuster, G.L.; Pitkänen, M.R.A.; Dubovik, O.; Kokkola, H.; Lindfors, A.V.; Mielonen, T.; Raatikainen, T.; Romakkaniemi, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; et al. Direct radiative effect by brown carbon over the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12731–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, K.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Aerosol physical and chemical properties retrieved from ground-based remote sensing measurements during heavy haze days in Beijing winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10171–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Li, L. Estimate of aerosol absorbing components of black carbon, brown carbon, and dust from ground-based remote sensing data of sun-sky radiometers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Li, K.; Xu, H. Study on influence of different mixing rules on the aerosol components retrieval from ground-based remote sensing measurements. Atmos. Res. 2014, 145–146, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.S.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, K.T.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, X.F.; et al. Estimation of atmospheric aerosol composition from ground-based remote sensing measurements of Sun-sky radiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S. Estimation of columnar concentrations of absorbing and scattering fine-mode aerosol components using AERONET data. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 13628–13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xie, Y. Estimation of atmospheric columnar organic matter (OM) mass concentration from remote sensing measurements of aerosol spectral refractive indices. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 179, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Arola, A. Remote sensing of soot carbon—Part 1: Distinguishing different absorbing aerosol species. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1565–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Saadi, J.; Szykman, J.; Pierce, R.B.; Kittaka, C.; Neil, D.; Chu, D.A.; Remer, L.; Gumley, L.; Prins, E.; Weinstock, L. Improving national air quality forecasts with satellite aerosol observations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Che, H.-Z.; Gong, S.-L.; An, X.; Cao, C.-X.; Guang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, X.-C.; et al. Correlation between PM concentrations and aerosol optical depth in eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5876–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global estimates of ambient fine particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: Development and application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2. 5 mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Ferrare, R.; Szykman, J.; Lewis, J.; Scarino, A.; Hains, J.; Burton, S.; Chen, G.; Tsai, T.; Hostetler, C.; et al. Regional characteristics of the relationship between columnar AOD and surface PM2.5: Application of lidar aerosol extinction profiles over Baltimore–Washington Corridor during DISCOVER-AQ. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote sensing of particulate pollution from space: Have we reached the promised land? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, M.; Apituley, A.; Timmermans, R.M.A.; Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; de Leeuw, G. Exploring the relation between aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 at Cabauw, the Netherlands. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: Multiple regression approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Puttaswamy, S.J.; et al. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the Southeastern United States using MAIAC AOD retrievals and a two-stage model. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Si, M.; Li, W.; Wu, J. A multidimensional comparison between MODIS and VIIRS AOD in estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over a heavily polluted region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Jeong, U.; Kim, W.; Holben, B.N.; Kim, S.W.; Song, C.H.; Lim, J.H. Estimation of PM10 concentrations over Seoul using multiple empirical models with AERONET and MODIS data collected during the DRAGON-Asia campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-M.; Yoon, J.; Moon, K.-J.; Kim, D.-R.; Koo, J.-H.; Choi, M.; Kim, K.N.; Lee, Y.G. Empirical estimation and diurnal patterns of surface PM2.5 concentration in Seoul using GOCI AOD. Korean J. Remote. Sens. 2018, 34, 451–463. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Li, Z.; Kim, J.; Koo, J.H.; Go, S.; Irie, H.; Labow, G.; et al. Comparisons of spectral aerosol single scattering albedo in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Cayetano, M.G.; Batmunkh, T.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, J. Spectral optical properties of long-range transport Asian dust and pollution aerosols over Northeast Asia in 2007 and 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5391–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.H.; Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S. Classification of diurnal patterns of particulate inorganic ions downwind of metropolitan Seoul. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8917–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.B.; Chatenet, B.; Gomes, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tsay, S.C.; et al. Columnar aerosol optical properties at AERONET sites in central eastern Asia and aerosol transport to the tropical mid-Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D06202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Yoon, S.-C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-Y. Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over east Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR, and AERONET Sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Won, J.-G.; Winker, D.M.; Yoon, S.-C.; Dubovik, O.; McCormick, M.P. Development of global aerosol models using cluster analysis of Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D10S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kanaya, Y.; Takigawa, M.; Zhu, C.; Park, S.M.; Matsuki, A.; Sadanaga, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Pan, X.; Pisso, I. Investigation of the wet removal rate of black carbon in East Asia: Validation of a below- and in-cloud wet removal scheme in FLEXPART v10.4. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, A.J.; Lee, T.; Park, T.; Choi, J.; Seo, S.J.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Fog composition at Baengnyeong Island in the eastern Yellow Sea: Detecting markers of aqueous atmospheric oxidations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.; Choi, J.; Lee, G.; Ahn, J.; Park, J.S.; Atwood, S.A.; Schurman, M.; Choi, Y.; Chung, Y.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Characterization of aerosol composition, concentrations, and sources at Baengnyeong Island, Korea using an aerosol mass spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebert, B.J.; Bates, T.; Russell, P.B.; Shi, G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kawamura, K.; Carmichael, G.; Nakajima, T. An overview of ACE-Asia: Strategies for quantifying the relationships between Asian aerosols and their climatic impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, T.; Yoon, S.-C.; Ramanathan, V.; Shi, G.-Y.; Takemura, T.; Higurashi, A.; Takamura, T.; Aoki, K.; Sohn, B.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; et al. Overview of the Atmospheric Brown Cloud East Asian Regional Experiment 2005 and a study of the aerosol direct radiative forcing in east Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V.; Ramanathan, V.; Feng, Y.; Yoon, S.C.; Kim, S.W.; Carmichael, G.R.; Schauer, J.J. Warming influenced by the ratio of black carbon to sulphate and the black-carbon source. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanré, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Arola, A.; Ferrare, R.A.; Hostetler, C.A.; Crumeyrolle, S.N.; Berkoff, T.A.; Welton, E.J.; Lolli, S.; et al. Observations of rapid aerosol optical depth enhancements in the vicinity of polluted cumulus clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11633–11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinyuk, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Giles, D.M.; Slutsker, I.; Korkin, S.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Sorokin, M.; Lyapustin, A. The AERONET Version 3 aerosol retrieval algorithm, associated uncertainties and comparisons to Version 2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.S.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Thornhill, K.L.; Anderson, B.E.; Sinyuk, A.; Giles, D.M.; Winstead, E.L.; Ziemba, L.D.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; et al. Intercomparison of aerosol single-scattering albedo derived from AERONET surface radiometers and LARGE in situ aircraft profiles during the 2011 DRAGON-MD and DISCOVER-AQ experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 7439–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, E.; Ogren, J.A.; Kinne, S.; Samset, B. Comparison of AOD, AAOD and column single scattering albedo from AERONET retrievals and in situ profiling measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6041–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Beelen, A.; Roelofs, G.; Hasekamp, O.; Henzing, J.; Röckmann, T. Estimation of aerosol water and chemical composition from AERONET Sun–sky radiometer measurements at Cabauw, the Netherlands. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5969–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuesta, J.; Flamant, P.H.; Flamant, C. Synergetic technique combining elastic backscatter lidar data and sunphotometer AERONET inversion for retrieval by layer of aerosol optical and microphysical properties. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 4598–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Qie, L.; Che, H.; Xu, H. Estimation of aerosol complex refractive indices for both fine and coarse modes simultaneously based on AERONET remote sensing products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J. Algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B: Fortran subroutines for large-scale bound-constrained optimization. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1997, 23, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Ajtai, T.; Kandler, K.; Lieke, K.; Linke, C.; Müller, T.; Schnaiter, M.; Vragel, M. Complex refractive indices of Saharan dust samples at visible and near UV wavelengths: A laboratory study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2491–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesins, G.; Chylek, P.; Lohmann, U. A study of internal and external mixing scenarios and its effect on aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, AAC-5-1–AAC-5-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light Absorption by Carbonaceous Particles: An Investigative Review. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Noone, K. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: From air pollution to climate change. Phys. Today 1998, 51, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmüller, K.; Steil, B.; Brühl, C.; Tost, H.; Lelieveld, J. Sensitivity of aerosol radiative effects to different mixing assumptions in the AEROPT 1.0 submodel of the EMAC atmospheric-chemistry–climate model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 2503–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J.; Zhu, C. A Limited Memory Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1995, 16, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, K. Improved inversion of aerosol components in the atmospheric column from remote sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Komazaki, Y.; Pochanart, P.; Liu, Y.; Akimoto, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. Mass concentrations of black carbon measured by four instruments in the middle of Central East China in June 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 7637–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanaya, Y.; Taketani, F.; Komazaki, Y.; Liu, X.; Kondo, Y.; Sahu, L.K.; Irie, H.; Takashima, H. Comparison of Black Carbon Mass Concentrations Observed by Multi-Angle Absorption Photometer (MAAP) and Continuous Soot-Monitoring System (COSMOS) on Fukue Island and in Tokyo, Japan. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Lee, M.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S.; Kang, K. Ionic and carbonaceous compositions of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 at Gosan ABC Superstation and their ratios as source signature. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2007–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyakawa, T.; Oshima, N.; Taketani, F.; Komazaki, Y.; Yoshino, A.; Takami, A.; Kondo, Y.; Kanaya, Y. Alteration of the size distributions and mixing states of black carbon through transport in the boundary layer in east Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5851–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogren, J.A.; Wendell, J.; Andrews, E.; Sheridan, P.J. Continuous light absorption photometer for long-term studies. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4805–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Draxler, R.; Stunder, B.; Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Taylor, A. HYSPLIT4 User’s Guide Version 4-Last Revision: February 2018. HYSPLIT Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.arl.noaa.gov/wp_arl/wp-content/uploads/documents/reports/hysplit_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2020).
- Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Miyakawa, T.; Weber, R.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Worsnop, D.R. Oxygenated and water-soluble organic aerosols in Tokyo. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S.; Segal Rozenhaimer, M.; Redemann, J.; LeBlanc, S.E.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.; Park, T.; Schwarz, J.P.; Lamb, K.D.; et al. Temporal and spatial variations of aerosol optical properties over the Korean peninsula during KORUS-AQ. Atmos. Environ. 2020, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.S.; Son, S.-C. Relationship between carbonaceous components and aerosol light absorption during winter at an urban site of Gwangju, Korea. Atmos. Res. 2017, 185, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Cho, S.Y. Tracking sources and behaviors of water-soluble organic carbon in fine particulate matter measured at an urban site in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, C.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yi, S.M.; Kim, Y.P. Concentrations and Characteristics of Carbonaceous Compounds in PM10 over Seoul : Measurement between 2006 and 2007. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 31, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batmunkh, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Cayetano, M.G.; Jung, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.C.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Chang, L.S.; et al. Time-Resolved Measurements of PM2.5 Carbonaceous Aerosols at Gosan, Korea. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis, 1980 Onward. Part I: System Description and Data Assimilation Evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, H.; Oh, S. Quantitative determination of the biomass-burning contribution to atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols in Daejeon, Korea, during the rice-harvest period. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Zhuanshi, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, G.U. Chemical Composition of Post-Harvest Biomass Burning Aerosols in Gwangju, Korea. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bo, Y.; Xie, S. Estimating emissions from crop residue open burning in China based on statistics and MODIS fire products. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, B.; Tang, Z.; Wu, H.; Xie, L. Characteristics of MERRA-2 black carbon variation in east China during 2000–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S. Assessment of the clear-sky bias issue using continuous PM10 data from two AERONET sites in Korea. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 53, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Gupta, P. Satellite Remote Sensing of Particulate Matter Air Quality: The Cloud-Cover Problem. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liu, D.; Zhao, D.; Hu, K.; Tian, P.; Zhou, W.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Sheng, J.; et al. Size-Related Physical Properties of Black Carbon in the Lower Atmosphere over Beijing and Europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11112–11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Zhao, D.; He, C.; Huang, M.; He, H.; Tian, P.; Liu, Q.; Bi, K.; Yu, C.; Pitt, J.; et al. Observed Interactions Between Black Carbon and Hydrometeor During Wet Scavenging in Mixed-Phase Clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 8453–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghim, Y.S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Bae, C.H.; Park, J.; Shin, H.J. Model Performance Evaluation and Bias Correction Effect Analysis for Forecasting PM2.5 Concentrations. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 33, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Park, R.J.; Ho, C.-H. Estimates of ground-level aerosol mass concentrations using a chemical transport model with Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aerosol observations over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.I.; Noh, Y.; Shin, D.H.; Shin, S.K.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, C.H. Estimation of surface-level PM concentration from satellite observation taking into account the aerosol vertical profiles and hygroscopicity. Chemosphere 2016, 143, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Location | AERONET Site Name | Land Use | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul | Yonsei_University | Urban | 2011.03–2018.12 |
| Yongin | Hankuk_UFS | Rural | 2015.01–2018.12 |
| Anmyon | Anmyon | Rural | 2014.03–2017.04 |
| Baengnyeong | Baengnyeong | Background | 2010.08–2016.08 |
| Gosan | Gosan_SNU | Background | 2012.03–2015.12 |
| n | K | Density | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 440 nm | 675 nm | 870−1020 nm | (g cm−3) | |||
| BC | 1.95 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 1.8 | [77] |
| WSOC a | 1.53 | 0.0232 | 0.0032 | 0.001 | 1.2 | [24] |
| WIOC | 1.53 | 0.063 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 1.2 | [25,78] |
| SII b | 1.53 | 10−7 | 10−7 | 10−7 | 1.76 | [79] |
| MD | 1.57 | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 2.3 | [29] |
| Water | 1.33 | 1.96 × 10−9 | 1.96 × 10−9 | 1.96 × 10−9 | 1 | [76] |
| Study Sites | Column Concentration a | In-Situ Concentration b | R | Period | Instrument | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul, Korea | 1.40 | 1.36 | 0.39 | 2011.03–2018.12 | Sunset OC/EC | This study |
| Yongin, Korea | 1.33 | 0.87 | 0.18 | 2015.01–2018.12 | MAAP | |
| Anmyon, Korea | 0.99 | 1.05 | 0.35 | 2014.03–2017.04 | AE31 | |
| Baengnyeong, Korea | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.48 | 2010.08–2016.08 | Sunset OC/EC | |
| Gosan, Korea | 0.76 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 2012.03–2015.12 | CLAP | |
| Yongin, Korea | 2.33 | 1.08 | 0.78 | 2012.3–2012.5 | MAAP | [32] |
| Beijing, China | 4.24 | - | 0.73 | 2014.10–2015.1 (2014.10.15–2014.11.13) | AE31 | [33] |
| 3.70 | 1.44 | 0.79 | 2014.10.16–2015.1.29 | AE31 | [31] | |
| 6.84 | 4.33 | 0.80 | 2012.10.11–2012-10.31 | AE51 | [29] | |
| - | - | 0.77 | 2012.2.11–2.29 | AE51 | [28] | |
| Cabauw, the Netherlands | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.37 | 2008.5.1–2008.5.15 | MAAP | [71] |
| In-Situ Concentration (µg m−3) | Column Concentration (mg cm−2) | R | a | b | N | In-Situ Concentration (µg m−3) | Column Concentration (mg cm−2) | R | a | b | N | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Season | (b) Wind direction | ||||||||||||
| Spring | 1.40 ± 0.85 | 1.20 ± 0.84 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.61 | 1018 | North | 1.17 ± 0.71 | 1.10 ± 0.88 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.63 | 636 |
| Summer | 1.04 ± 0.60 | 0.97 ± 0.73 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 422 | East | 1.38 ± 0.86 | 0.92 ± 0.70 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.51 | 402 |
| Fall | 1.47 ± 0.90 | 1.05 ± 0.88 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 578 | West | 1.37 ± 0.84 | 1.26 ± 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 637 |
| Winter | 1.72 ± 1.09 | 1.49 ± 1.09 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 112 | South | 1.62 ± 0.99 | 1.17 ± 0.72 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 455 |
| (c) Wind speed (m s−1) | (d) Relative humidity (%) | ||||||||||||
| 0–1 | 1.77 ± 0.98 | 1.18 ± 0.76 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.60 | 215 | 10–20 | 1.17 ± 0.60 | 1.53 ± 0.82 | −0.23 | −0.32 | 1.24 | 40 |
| 1–1.5 | 1.69 ± 0.90 | 1.29 ± 0.88 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.68 | 302 | 20–30 | 1.17 ± 0.72 | 1.40 ± 0.83 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.72 | 159 |
| 1.5–2 | 1.51 ± 0.93 | 1.15 ± 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.61 | 238 | 30–40 | 1.24 ± 0.72 | 1.27 ± 0.83 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.58 | 236 |
| 2–3 | 1.39 ± 0.86 | 1.26 ± 1.03 | 0.43 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 400 | 40–50 | 1.46 ± 0.95 | 1.26 ± 1.05 | 0.44 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 256 |
| 3–4 | 1.24 ± 0.71 | 1.10 ± 0.85 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.56 | 332 | 50–60 | 1.43 ± 0.86 | 1.12 ± 0.86 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.58 | 319 |
| 4–5 | 1.11 ± 0.69 | 1.00 ± 0.73 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.63 | 306 | 60–70 | 1.44 ± 0.90 | 1.00 ± 0.77 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 311 |
| 5–6 | 1.07 ± 0.68 | 0.94 ± 0.76 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 164 | 70–80 | 1.40 ± 0.86 | 1.05 ± 0.76 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 284 |
| 6–15 | 1.00 ± 0.73 | 0.90 ± 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 173 | 80–90 | 1.33 ± 0.95 | 0.99 ± 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 160 |
| (e) PBLH (km) | (f) Temperature (°K) | ||||||||||||
| 0.2–0.3 | 1.40 ± 0.85 | 0.97 ± 0.73 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.57 | 365 | 263–273 | 1.61 ± 0.85 | 1.50 ± 1.02 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 30 |
| 0.3–0.4 | 1.57 ± 0.95 | 1.02 ± 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 399 | 273–278 | 1.65 ± 0.91 | 1.22 ± 0.88 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 167 |
| 0.4–0.6 | 1.40 ± 0.87 | 1.05 ± 0.78 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 503 | 278–283 | 1.48 ± 0.90 | 1.04 ± 0.73 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 324 |
| 0.6–0.8 | 1.33 ± 0.84 | 1.17 ± 0.90 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 326 | 283–288 | 1.46 ± 0.95 | 1.09 ± 0.78 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.65 | 444 |
| 0.8–1 | 1.19 ± 0.73 | 1.19 ± 0.94 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 231 | 288–293 | 1.33 ± 0.84 | 1.10 ± 0.88 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 466 |
| 1–1.5 | 1.17 ± 0.79 | 1.47 ± 1.07 | 0.51 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 257 | 293–298 | 1.22 ± 0.76 | 1.20 ± 0.97 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 403 |
| 1.5–2 | 1.12 ± 0.59 | 1.59 ± 0.89 | −0.14 | −0.21 | 1.14 | 44 | 298–303 | 1.16 ± 0.69 | 1.10 ± 0.76 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.71 | 266 |
| 2–2.5 | 1.23 ± 0.70 | 1.21 ± 0.60 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.18 | 5 | 303–313 | 0.99 ± 0.46 | 1.37 ± 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 29 |
| Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|
| (a) Continuous variables | ||
| Intercept | −9.533 *** | |
| BCcolumn (mg m−2) | 0.330 *** | |
| Temperature (°K) | 0.022 *** | |
| RH (%) | 0.050 *** | |
| PBLH (km) | −0.162 ** | |
| Wind speed (m s−1) | −0.041 *** | |
| (b) Categorical variables | ||
| Wind direction | East | - |
| North | 0.025 | |
| South | 0.085 | |
| West | 0.043 | |
| Season | Jan | - |
| Feb | 0.15 | |
| Mar | −0.212 | |
| Apr | −0.311 * | |
| May | −0.574 *** | |
| Jun | −1.067 *** | |
| Jul | −1.275 *** | |
| Aug | −1.126 *** | |
| Sep | −0.935 *** | |
| Oct | −0.404 ** | |
| Nov | −0.07 | |
| Dec | 0.042 | |
| Land-use | Background | - |
| Rural | 0.262 *** | |
| Urban | 0.750 *** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Park, S.-M.; Song, I.-h. Estimation of Surface Concentrations of Black Carbon from Long-Term Measurements at Aeronet Sites over Korea. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233904
Choi Y, Ghim YS, Zhang Y, Park S-M, Song I-h. Estimation of Surface Concentrations of Black Carbon from Long-Term Measurements at Aeronet Sites over Korea. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(23):3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233904
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yongjoo, Young Sung Ghim, Ying Zhang, Seung-Myung Park, and In-ho Song. 2020. "Estimation of Surface Concentrations of Black Carbon from Long-Term Measurements at Aeronet Sites over Korea" Remote Sensing 12, no. 23: 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233904
APA StyleChoi, Y., Ghim, Y. S., Zhang, Y., Park, S. -M., & Song, I. -h. (2020). Estimation of Surface Concentrations of Black Carbon from Long-Term Measurements at Aeronet Sites over Korea. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233904