Identification of Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield within Ecological Red Line Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Method
2.3.1. RUSLE Model
2.3.2. InVEST Model
2.3.3. Geographical Detector
3. Results
3.1. Simulation and Pattern Analysis of Soil Erosion and Water Yield in Beijing and ERL Areas
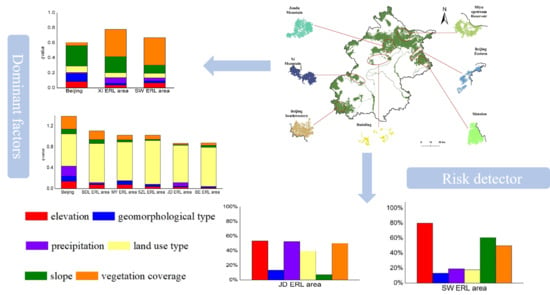
3.2. Quantitative Attribution of Single Factor Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield in ERL Areas
3.3. Identification of Interactions Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield in ERL Areas
3.4. Distribution of High Soil Erosion Risk Areas and High Water Yield Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Su, C.; Forsius, M. Linking ecosystem processes and ecosystem services. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.M.; Fu, B.J.; Hu, H.T.; Sun, G. A method to identify the variable ecosystem services relationship across time: A case study on Yanhe Basin. China. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Semmens, D.J.; Waage, S.; Winthrop, R. A comparative assessment of decision-support tools for ecosystem services quantification and valuation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, E27–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, N.; Corbera, E. Payments for ecosystem services as commodity fetishism. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Pan, Y.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, Y.L. Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Guo, B. Multicriteria decision analysis for monitoring ecosystem service function of the Three-River Headwaters region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.B.; Liang, W.; Miao, C.Y. Hydrogeomorphic Ecosystem Responses to Natural and Anthropogenic Changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Yue, Y.; Qi, X. How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: An analysis of vegetation carbon sequestration in the karst area of northwest Guangxi, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5307–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, W.; Sun, T. Effects of Freshwater Releases on the Delivery of Ecosystem Services in Coastal Wetlands of the Yellow River Delta Using an Improved Input-State-Output Approach. Wetlands 2015, 36, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsch, M.; Lasch-Born, P.; Kollas, C.; Suckow, F.; Reyer, C.P.O. Balancing trade-offs between ecosystem services in Germany’s forests under climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egoh, B.N.; Reyers, B.; Rouget, M.; Richardson, D.M. Identifying priority areas for ecosystem service management in South African grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Han, S. Ecosystem service status and changes of degraded natural reserves—A study from the Changbai Mountain Natural Reserve, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 20, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, X. Ecosystem Services Valuation of Lakeside Wetland Park beside Chaohu Lake in China. Water 2016, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysingha, N.S.; Singh, M.; Sehgal, V.K.; Khanna, M.; Pathak, H.; Jayakody, P.; Srinivasan, R. Assessment of water yield and evapotranspiration over 1985 to 2010 in the Gomti River basin in India using the SWAT model. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, T.; Ju, C.; He, C. Effect of reforestation on annual water yield in a large watershed in northeast China. J. For. Res. 2015, 26, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K. Mapping spatio-temporal dynamics of the cover and management factor (C-factor) for grasslands in Switzerland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovic, V.; Jaksic, D.; Jaramaz, D.; Kokovic, N.; Cakmak, D.; Mitrovic, M.; Pavlovic, P. Spatio-temporal analysis of land use/land cover change and its effects on soil erosion (Case study in the Oplenac wine-producing area, Serbia). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, H. Temporal analysis on quantitative attribution of karst soil erosion: A case study of a peak-cluster depression basin in Southwest China. Catena 2019, 172, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.; Fu, B. Understanding the impacts of climate and landuse change on water yield. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.M.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. How China will protect one-quarter of its land. Nature 2019, 569, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, J.; Hou, P.; Cao, W.; Yang, M.; Cai, M.Y.; Li, J. Ecosystem assessment and protection effectiveness of a tropical rainforest region in Hainan Island, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.S.; Sun, G.Y.; Dang, L.J. Identifying Ecological Red Lines: A Case Study of the Coast in Liaoning Province. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9461–9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Delu, P. Zoning of Hangzhou Bay ecological red line using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2017, 139, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G.; Barnett, J. China’s ambitious ecological red lines. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. GIS Based Measurement and Regulatory Zoning of Urban Ecological Vulnerability. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Yang, G.; Tan, Y. Identifying ecological red lines in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: A regional approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Mccool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agricultural Handbook: No. 703; United States. Dept. of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Williams, J.R.; Jones, C.A.; Kiniry, J.R.; Spanel, D.A. The EPIC crop growth-model. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldus, H.M.J.; Boodt, M.D.; Gabriels, D. An approximation of the rainfall factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In Assessment of Erosion; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1980; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Moore, D.; He, P.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Extension of a GIS procedure for calculating the RUSLE equation LS factor. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised slope steepness factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised slope length factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; DING, S.; SHI, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of Applying USLE and Geographical Information System IDRISI to Predict Soil Erosion in Small Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shi, M.; Jiang, Q.O. Influence of land use /cover change on soil erosion in Chaobai River Basin. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 17, 121–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, J. Effects of landscape patterns on soil erosion processes in a mountain-basin system in the North China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 1567–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, D. Estimating Soil Erosion in North China Plain Based on RS/GIS and RUSLE. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 32, 214–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.R.; Chan, K.M.A.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M.; et al. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Xu, C. Determinants and identification of the northern boundary of China’s tropical zone. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xia, S. Identifying the Impacts of Social, Economic, and Environmental Factors on Population Aging in the Yangtze River Delta Using the Geographical Detector Technique. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Luo, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, L.; Tian, L.; Chen, G. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Spatial Differentiation of Urban Black and Odorous Waters in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Christakos, G.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lv, X. The association between heavy metal soil pollution and stomach cancer: A case study in Hangzhou City, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geographica Sinica 2017, 72, 116–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ren, D.; Zhu, J. Geographical Detector-Based Risk Assessment of the Under-Five Mortality in the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Fan, M. Soil Erosion Simulation in Mountain Areas of Beijing Based on InVEST Model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 17, 9–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, A.; Duan, S. Calculation on soil erosion in Beijing City based on GIS. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 9, 24–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Shangguan, Z.P. Effect of ryegrasses on soil runoff and sediment control. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.Q.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y. Responses of the water-yield ecosystem service to climate and land use change in Sancha River Basin, China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 101, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, W. Monitoring and Evaluation of Soil Erosion in Western Mountain of Beijing Based on RS and GIS. J. Cap. Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 30, 83–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, G.; Wen, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations of Water Yield and Water Quality Purification Service Functions in Guanting Reservoir Basin based on InVEST Model. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 406–414. [Google Scholar]




| Data | Sources | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| DEM | Google Earth | 9 m |
| Watershed | Beijing Municipal Ecological Environment Bureau | |
| Geomorphological Type | Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform (http://www.resdc.cn) | 1:1,000,000 |
| Landsat 8 OLI images (2015, 2018) | USGS (https://glovis.usgs.gov/) | 30 m |
| GF-1 images (2015, 2018) | China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application (http://www.cresda.com/CN/) | 8 m |
| Meteorological (2015, 2018) | National Meteorological Information Center of China (http://data.cma.cn/) | Monthly |
| Mechanical Composition | Cold and Arid Regions Sciences Data Center at Lanzhou (http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn/) | 1 km |
| Soil Depth | Soil Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://soil.geodata.cn) | 1 km |
| Land Use Type | Paddy Field | Dry Land | Garden Plot | Grassland | Forest | Waste Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Bare Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p Value | 0.35 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Description | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Weaken, nonlinear | |
| Weaken, single factor nonlinear | |
| Enhance, double factors | |
| Independent | |
| Enhance, nonlinear |
| Beijing | Xi ERL Area | SW ERL Area | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant interaction1 | vegetation coverage ∩ slope | vegetation coverage ∩ slope | vegetation coverage ∩ slope |
| q value | 0.579 | 0.682 | 0.586 |
| Dominant interaction2 | vegetation coverage ∩ geomorphological type | vegetation coverage ∩ precipitation | vegetation coverage ∩ precipitation |
| q value | 0.325 | 0.463 | 0.440 |
| Dominant interaction3 | slope ∩ geomorphological type | slope ∩ precipitation | vegetation coverage ∩ land use type |
| q value | 0.303 | 0.446 | 0.437 |
| Beijing | BDL ERL Area | MY ERL Area | SZL ERL Area | JD ERL Area | BE ERL Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant interaction1 | LU ∩ precipitation | LU ∩ VC | LU ∩ elevation | LU ∩ slope | LU ∩ precipitation | LU ∩ GT |
| q value | 0.792 | 0.848 | 0.804 | 0.856 | 0.811 | 0.779 |
| Dominant interaction2 | LU ∩ elevation | LU ∩ slope | LU ∩ GT | LU ∩ elevation | LU ∩ elevation | LU ∩ slope |
| q value | 0.654 | 0.834 | 0.791 | 0.855 | 0.739 | 0.778 |
| Dominant interaction3 | LU ∩ GT | LU ∩ GT | LU ∩ slope | LU ∩ VC | LU ∩ slope | LU ∩ elevation |
| q value | 0.634 | 0.788 | 0.770 | 0.851 | 0.735 | 0.768 |
| Beijing | Xi ERL Area | SW ERL Area | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation (m) | 1783–2007 | 229–451 | 7–229 |
| Geomorphological type | High relief mountain | Plain | Platform |
| Precipitation (mm) | 507–530 | 530–553 | 576–599 |
| Land use type | Unused land | Unused land | Unused land |
| Slope (°) | >35 | >35 | >35 |
| Vegetation coverage | 0.3–0.4 | 0.5–0.6 | 0.4–0.5 |
| Beijing | BDL ERL Area | MY ERL Area | SZL ERL Area | JD ERL Area | BE ERL Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation (m) | 7–229 | 229–451 | 7–229 | 673–895 | 229–451 | 7–229 |
| Geomorphological type | Plain | Plain | Hill | Hill | High relief mountain | Plain |
| Precipitation (mm) | 668–691 | 645–668 | 576–599 | 622–645 | 645–668 | 553–576 |
| Land use type | Unused land | Low coverage grassland | Construction land | Construction land | Construction land | Construction land |
| Slope (°) | 0–5 | >35 | 0–5 | 30–35 | >35 | 5–10 |
| Vegetation coverage | 0.1–0.2 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.3–0.4 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.4–0.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, L. Identification of Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield within Ecological Red Line Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030399
Gao J, Jiang Y, Wang H, Zuo L. Identification of Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield within Ecological Red Line Areas. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(3):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030399
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jiangbo, Yuan Jiang, Huan Wang, and Liyuan Zuo. 2020. "Identification of Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield within Ecological Red Line Areas" Remote Sensing 12, no. 3: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030399
APA StyleGao, J., Jiang, Y., Wang, H., & Zuo, L. (2020). Identification of Dominant Factors Affecting Soil Erosion and Water Yield within Ecological Red Line Areas. Remote Sensing, 12(3), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030399