Remotely Sensed Mid-Channel Bar Dynamics in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
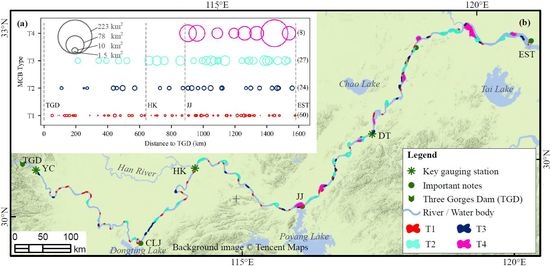
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Landsat Images
2.2.2. High Spatial Resolution (HSR) Images
2.2.3. Gauged Datasets
2.3. Producing MCBs
2.3.1. Extracting MCBs with Landsat Images
2.3.2. Calculating MCBs’ Attributions
2.4. Processing Validation Data
2.5. Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Understanding of the Extracted MCBs
3.1.1. Accuracy of Extracted MCBs Data
3.1.2. General Overview of MCBs
3.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of MCBs
3.2.1. Longitudinal Distribution
3.2.2. Temporal Dynamics of MCBs
4. Discussion
4.1. Scale Effects on the Temporal Dynamics
4.2. Potential Effects of TGD Operation
4.3. Limitation and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freyer, J.B.; Jefferson, A.J. An exception to island loss in the engineered upper Mississippi River: History of land growth in Pool 6 and implications for restoration. Anthropocene 2013, 2, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.S.; Lacombe, G.; Arias, M.E.; Dang, T.D.; Piman, T. Hydropower dams of the Mekong River basin: a review of their hydrological impacts. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J. Potentially massive greenhouse-gas sources in proposed tropical dams. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liermann, C.R.; Nilsson, C.; Robertson, J.; Ng, R.Y. Implications of dam obstruction for global freshwater fish diversity. Bioscience 2012, 62, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, S.; Moog, O. Dams: Ecological impacts and management. In Riverine Ecosystem Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Adami, L.; Bertoldi, W.; Zolezzi, G. Multidecadal dynamics of alternate bars in the Alpine Rhine River. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 8938–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterkamp, W.R. Processes of fluvial island formation, with examples from Plum Creek, Colorado and Snake River, Idaho. Wetlands 1998, 18, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J. Mid-channel bar growth and its relationship to local flow strength and direction. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, J.M. The significance of mid-channel bars in an active meandering river. Sedimentology 1986, 33, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintenberger, C.L.; Rodrigues, S.; Claude, N.; Juge, P.; Breheret, J.G.; Villar, M. Dynamics of nonmigrating mid-channel bar and superimposed dunes in a sandy-gravelly river (Loire River, France). Geomorphology 2015, 248, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X. Evolution of mid-channel bars in a braided river and complex response to reservoir construction: An example from the middle Hanjiang River, China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1997, 22, 953–965. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.Y.; Mei, X.F.; Dai, Z.J.; Wang, J.; Wei, W. Evolution of the mid-channel bars in the middle and lower reaches of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River from 1989 to 2014 based on the Landsat satellite images: Impact of the Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacchi, E.; Steiger, J.; Corenblit, D.; Monaghan, M.T.; Planty-Tabacchi, A.-M. Implications of biological and physical diversity for resilience and resistance patterns within Highly Dynamic River Systems. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 71, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonkin, J.D.; Merritt, D.M.; Olden, J.D.; Reynolds, L.V.; Lytle, D.A. Flow regime alteration degrades ecological networks in riparian ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooke, J.M.; Yorke, L. Channel bar dynamics on multi-decadal timescales in an active meandering river. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 1910–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Assessing Morphodynamics of the Lower Mississippi River from 1985 to 2015 with Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.Q.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y.Y.; Yu, M.Q. Interacting effects of multiple factors on the morphological evolution of the meandering reaches downstream the Three Gorges Dam. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, N.C.; Erwin, S.O.; Schmidt, J.C. Spatial and temporal patterns in channel change on the Snake River downstream from Jackson Lake dam, Wyoming. Geomorphology 2013, 200, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E. Complex response of river channel morphology subsequent to reservoir construction. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1979, 3, 329–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, W.D. Downstream geomorphic impacts of large dams: The case of Glenbawn Dam, NSW. Appl. Geogr. 1985, 5, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, W.L. Downstream hydrologic and geomorphic effects of large dams on American rivers. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provansal, M.; Dufour, S.; Sabatier, F.; Anthony, E.J.; Raccasi, G.; Robresco, S. The geomorphic evolution and sediment balance of the lower Rhône River (southern France) over the last 130 years: Hydropower dams versus other control factors. Geomorphology 2014, 219, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, Z.J.; Mei, X.F.; Lou, Y.Y.; Wei, W.; Ge, Z.P. Immediately downstream effects of Three Gorges Dam on channel sandbars morphodynamics between Yichang-Chenglingji Reach of the Changjiang River, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, J.T. Impacts of large dams on downstream fluvial sedimentation: An example of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) on the Changjiang (Yangtze River). J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yin, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. China’s ecological rehabilitation: Unprecedented efforts, dramatic impacts, and requisite policies. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Ouchi, K. Analysis of bar morphology using multi-temporal and multi-sensor satellite images: Example from the Han Estuary, Korea. Mar. Geol. 2012, 311, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.W.; Xu, Y.J.; Cheng, H.Q.; Wang, B.; Xu, W.; Wu, S.H. Riverbed erosion of the final 565 kilometers of the Yangtze River (Changjiang) following construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Rep.-UK 2018, 8, 11917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, D.; Yang, H. Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on flow regime in the middle and lower Yangtze River. Quatern. Int. 2013, 304, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baki, A.B.M.; Gan, T.Y. Riverbank migration and island dynamics of the braided Jamuna River of the Ganges-Brahmaputra basin using multi-temporal Landsat images. Quatern. Int. 2012, 263, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Chen, S.; Yu, J. River islands’ change and impacting factors in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River based on remote sensing. Quatern. Int. 2013, 304, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raška, P.; Dolejš, M.; Hofmanová, M. Effects of damming on long-term development of fluvial islands, Elbe River (N Czechia). River research and applications. 2017, 33, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.P. Dam Regulations Effects on Sand Bar Migration on the Missouri River: Southeastern South Dakota. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Montana, Missoula, MT, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, T.; Balogh, M. Characteristics of point-bar development under the influence of a dam: Case study on the Dráva River at Sigetec, Croatia. J. Environ. Geogr. 2015, 8, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piégay, H.; Grant, G.; Nakamura, F.; Trustrum, N. Braided river management: from assessment of river behaviour to improved sustainable development. In Braided Rivers: Process, Deposits, Ecology and Management; Smith, G.H.S., Best, J.L., Bristow, C.S., Petts, G.E., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA. USA, 2006; pp. 257–275. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Tan, G.; Shu, C.; Han, Q. Morphodynamic adjustments in the Yichang–Chenglingji Reach of the Middle Yangtze River since the operation of the Three Gorges Project. CATENA 2019, 172, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Milliman, J.D.; Li, P.; Xu, K. 50,000 dams later: Erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 75, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, Y.J. Decadal-Scale Riverbed Deformation and Sand Budget of the Last 500 km of the Mississippi River: Insights Into Natural and River Engineering Effects on a Large Alluvial River. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 874–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, L. Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, K.H.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Luo, X.X. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Tam, C.; Chen, X. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Feng, G.; Kutler, J.; Teng-Kui, L. A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for North America, 1990-2000. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Guide. Landsat 4-7 Surface Reflectance (LEDAPS) Product; Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VG, USA, 2018.
- Product Guide. Landsat 8 Surface Reflectance Code (LASRC) Product; Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VG, USA, 2018.
- Young, N.E.; Anderson, R.S.; Chignell, S.M.; Vorster, A.G.; Lawrence, R.; Evangelista, P.H. A survival guide to Landsat preprocessing. Ecology 2017, 98, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, D.G.; Church, M. Bed-material transport estimated from channel morphodynamics: Chilliwack River, British Columbia. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms. 2000, 25, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Gleason, C.J.; Wada, Y. Downstream Yangtze River levels impacted by Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpoorter, C.; Kutser, T.; Seekell, D.A.; Tranvik, L.J. A global inventory of lakes based on high-resolution satellite imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6396–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated water extraction index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Wylie, B. Analysis of dynamic thresholds for the normalized difference water index. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2009, 75, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, B.; Shen, Q.; Ye, H.P.; Wang, S.L.; Lu, Z.Y. A simple automated dynamic threshold extraction method for the classification of large water bodies from landsat-8 OLI water index images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 3429–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESRI. ArcGIS desktop: Release 10.3; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yan, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. An accident data–based approach for congestion risk assessment of inland waterways: A Yangtze River case. P. I. Mech. Eng. O-J. Ris. 2014, 228, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, G.C. Tests of equality between sets of coefficients in two linear regressions. Econometrica 1960, 28, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.S. Change-point problems: bibliography and review. J. Stat. Theory Pract. 2010, 4, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.Y.; Landry, C.E. River restoration and hedonic property value analyses: Guidance for effective benefit transfer. Water Resour. Econ. 2017, 17, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2013. Available online: https://repo.bppt.go.id/cran/web/packages/dplR/vignettes/intro-dplR.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- Asaeda, T.; Rashid, M.H. The impacts of sediment released from dams on downstream sediment bar vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterkamp, W.R.; Hupp, C.R. Fluvial processes and vegetation - Glimpses of the past, the present, and perhaps the future. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilvear, D.; Willby, N. Channel dynamics and geomorphic variability as controls on gravel bar vegetation; River Tummel, Scotland. River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K. The human role in changing river channels. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Cai, X. Remotely sensed analysis of channel bar morphodynamics in the middle Yangtze River in response to a major monsoon flood in 2002. Remote Sens. BASEL 2018, 10, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Van Gelder, P.; Gao, J. Linking Three Gorges Dam and downstream hydrological regimes along the Yangtze River, China. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Rhoads, B.L.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, X. Impacts of large dams on the complexity of suspended sediment dynamics in the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Yin, D.; Finlayson, B.L.; Wei, T.; Li, M.; Yuan, W.; Yang, S.; Dai, Z.; Gao, S.; Chen, Z. Will river erosion below the Three Gorges Dam stop in the middle Yangtze? J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cai, X.B.; Wang, X.L.; Yan, R.R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, X.R. Remotely Sensed Trajectory Analysis of Channel Migration in Lower Jingjiang Reach during the Period of 1983–2013. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16241–16256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.H.; Yin, D.W.; Finlayson, B.; Chen, Z.Y. Assessing the potential for change in the middle Yangtze River channel following impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 2012, 147, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changjiang Water Resources Commission. Changjiang Sediment Bulletin; Changjiang Water Resources Commission: Wuhan, China, 2003–2017. Available online: http://www.cjw.gov.cn/zwzc/bmgb/ (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- Lai, X.J.; Jiang, J.H.; Yang, G.S.; Lu, X.X. Should the Three Gorges Dam be blamed for the extremely low water levels in the middle-lower Yangtze River? Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, N.; Suciu, D. Answering queries from statistics and probabilistic views. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Trondheim, Norway, 30 August–4 September 2005; pp. 805–816. [Google Scholar]
- Planet Team. Planet Application Program Interface: In Space for Life on Earth. San Francisco, CA, USA. Available online: https://www.planet.com (accessed on 26 January 2020).














| HSR Images in Google Earth | Landsat Images | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Acquisition Date | Sensor | Path | Row | Acquisition Date |
| DigitalGlobe | 2010-12-02 | Landsat 5 | 119 | 038 | 2010-12-01 |
| CNES Airbus | 2013-12-10 | Landsat 8 | 119 | 038 | 2013-12-11 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2003-01-04 | Landsat 5 | 120 | 038 | 2003-01-07 |
| CNES Airbus | 2013-11-15 | Landsat 8 | 120 | 038 | 2013-11-20 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2014-11-18 | Landsat 8 | 120 | 038 | 2014-11-16 |
| CNES Airbus | 2017-12-12 | Landsat 8 | 120 | 038 | 2017-12-11 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2008-12-10 | Landsat 5 | 121 | 039 | 2008-12-08 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2015-02-13 | Landsat 8 | 121 | 039 | 2015-02-08 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2017-12-19 | Landsat 8 | 121 | 039 | 2017-12-21 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2017-12-26 | Landsat 8 | 122 | 039 | 2017-12-21 |
| CNES Airbus | 2018-01-11 | Landsat 8 | 122 | 039 | 2018-01-11 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2004-02-13 | Landsat 5 | 123 | 039 | 2004-02-14 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2006-12-19 | Landsat 5 | 123 | 039 | 2006-12-17 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2017-02-16 | Landsat 8 | 123 | 039 | 2017-02-13 |
| CNES Airbus | 2015-01-01 | Landsat 8 | 124 | 039 | 2014-12-31 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2016-12-05 | Landsat 8 | 124 | 039 | 2016-12-08 |
| CNES Airbus | 2017-01-22 | Landsat 8 | 124 | 039 | 2017-01-16 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2017-12-24 | Landsat 8 | 124 | 039 | 2017-12-17 |
| DigitalGlobe | 2018-01-09 | Landsat 8 | 124 | 039 | 2018-01-09 |
| Type | Explanation | Area range (km2) | Proportion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | |||
| T1 | Small size | 0.02 a | 2 | 50% |
| T2 | Middle size | 2 | 7 | 25% |
| T3 | Large size | 7 | 33 | 20% |
| T4 | Extra-large size | 33 | 223 b | 5% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Shao, G.; Wu, S. Remotely Sensed Mid-Channel Bar Dynamics in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030409
Wen Z, Yang H, Zhang C, Shao G, Wu S. Remotely Sensed Mid-Channel Bar Dynamics in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(3):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030409
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Zhaofei, Hong Yang, Ce Zhang, Guofan Shao, and Shengjun Wu. 2020. "Remotely Sensed Mid-Channel Bar Dynamics in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam, China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 3: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030409
APA StyleWen, Z., Yang, H., Zhang, C., Shao, G., & Wu, S. (2020). Remotely Sensed Mid-Channel Bar Dynamics in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Remote Sensing, 12(3), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030409