Uncertainty Analysis for Topographic Correction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Link of Topographic Correction
2.1.1. Core Formulas
2.1.2. Data Link
2.2. Uncertainty Propagation
2.2.1. General Concepts
2.2.2. Uncertainty Sources
2.2.3. Uncertainties Introduced by Input Quantities
2.2.4. Total Combined Standard Uncertainty
2.2.5. Expanded Uncertainty
3. Exemplar Experiment
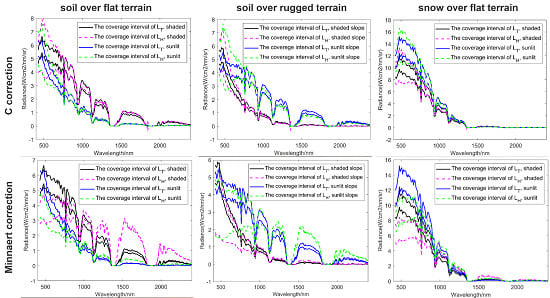
3.1. Experimental Area and Data Set
3.2. Uncertainty Analysis
3.2.1. Estimation of Uncertainty Sources
3.2.2. Uncertainties of Input Quantities
3.2.3. Uncertainty Components of the Total Combined Uncertainty
3.2.4. Uncertainty of the Corrected Radiance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BIPM; IEC; IFCC; ILAC; ISO; IUPAC; IUPAP; OIML. Evaluation of Measurement Data-Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement. Available online: http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/documents/jcgm/JCGM_100_2008_E.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Fox, N. A Guide to Expression of Uncertainty of Measurements. Available online: http://qa4eo.org/docs/QA4EO-QAEO-GEN-DQK-006_v4.0.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Fidelity and Uncertainty in Climate Data Records from Earth Observations. Available online: http://www.fiduceo.eu/ (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Woolliams, E.; Hueni, A.; Gorrono, J. Intermediate Uncertainty Analysis for Earth Observation (Instrument Calibration): NPL Training Course Textbook. Available online: http://www.emceoc.org/documents/uaeo-int-trg-course.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Chrien, T.G.; Green, R.O.; Eastwood, M.L. Accuracy of the spectral and radiometric laboratory calibration of the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Orlando, FL, USA, 1 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, M.; Makarau, A.; Segl, K.; Richter, R. Estimating the influence of spectral and radiometric calibration uncertainties on EnMAP data products-examples for ground reflectance retrieval and vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Basel 2015, 7, 10689–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W. Measurement chain of influence quantities and uncertainty of radiometric calibration for imaging spectrometer. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2006, 14, 822–828. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Zhao, H.; Li, H. Uncertainty propagation algorithm from the radiometric calibration to the restored earth observation radiance. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 9442–9449. [Google Scholar]
- Honkavaara, E.; Markelin, L.; Hakala, T.; Peltoniemi, J. The metrology of directional, spectral reflectance factor measurements based on area format imaging by UAVs. Photogramm. Fernerkun. 2014, 2014, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Xue, Q.; Zhao, H. Uncertainty analysis for surface reflectance retrieved from hyperspectral remote sensing image using empirical line method. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 23–26 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Teillet, P.M.; Guindon, B.; Goodenough, D.G. On the slope-aspect correction of multispectral scanner data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1982, 8, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, P.; Itten, K.I.; Kellenberger, T.; Sandmeier, S. Radiometric corrections of topographically induced effects on Landsat TM data in an alpine environment. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 1993, 48, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincini, M.; Reeder, D.; Frazzi, E. An empirical topographic normalization method for forest TM data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, W. Variable empirical coefficient algorithm for removal of topographic effects on remotely sensed data from rugged terrain. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Civco, D.L. Topographic normalization of Landsat thematic mapper digital imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. Sens. 1989, 55, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Baraldi, A.; Gironda, M.; Simonetti, D. Operational two-stage stratified topographic correction of spaceborne multispectral imagery employing an automatic spectral-rule-based decision-tree preliminary classifier. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2010, 48, 112–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Water Resource and Hydrological Processes Studies on the Urumqi River Basin, Tianshan, China by Means of Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, D.; Gillespie, A. Topographic normalization of Landsat TM images of forest based on subpixel sun-canopy-sensor geometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proy, C.; Tanre, D.; Deschamps, P.Y. Evaluation of topographic effects in remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 30, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, S.; Itten, K.I. A physically-based model to correct atmospheric and illumination effects in optical satellite data of rugged terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1997, 35, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soenen, S.A.; Peddle, D.R.; Coburn, C.A. SCS+C: A modified sun-canopy-sensor topographic correction in forested terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2005, 43, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Lin, T.L.; Ranson, K.L. The Lambertian assumption and Landsat data. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. S. 1980, 46, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Vincini, M.; Reeder, D.; Frazzi, E. Seasonal Landsat TM data topographic dependence in rugged deciduous forest areas. In Proceedings of the Analysis of Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images-the First International Workshop on Multitemp, Trento, Italy, 13–14 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, X. Analysis of errors of derived slope and aspect related to DEM data properties. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.K. Hill shading and the reflectance map. Proc. IEEE 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Vocabulary of Metrology—Basic and General Concepts and Associated Terms (VIM 3rd edition). Available online: https://www.bipm.org/utils/common/documents/jcgm/JCGM_200_2012.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Sun, R.H. Applied Mathematical Statistics, 3rd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M.P.; Colby, J.D. Anisotropic reflectance correction of SPOT-3 HRV imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.P.; Shroder, J.F., Jr.; Colby, J.D. Remote sensing and geomorphometry for studying relief production in high mountains. Geomorphology 2003, 55, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model Version 2- Summary of Validation Results. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/documents/220/Summary_GDEM2_validation_report_final.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Nolin, A.W.; Liang, S. Progress in bidirectional reflectance modeling and applications for surface particulate media: Snow and soils. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 307–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Correction Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C correction | 5% | 62.47% | 20.25% | 5.50% |
| Minnaert correction | 3.02% |
| Number | Coordinates | Slope (rad) | Aspect (rad) | Terrain | Cover Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (76, 182) | 0.0555 | 0.2268 | flat, shaded | soil |
| 2 | (258, 214) | 0.0395 | 4.3906 | flat, sunlit | soil |
| 3 | (283, 236) | 0.3923 | 1.4090 | rugged, shaded | soil |
| 4 | (210, 258) | 0.04396 | 3.6607 | rugged, sunlit | soil |
| 5 | (303, 90) | 0.0458 | 0.2450 | flat, shaded | snow |
| 6 | (173, 288) | 0.0314 | 2.3562 | flat, sunlit | snow |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Jia, G.; Schaepman, M.E.; Zhao, H. Uncertainty Analysis for Topographic Correction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040705
Ma Z, Jia G, Schaepman ME, Zhao H. Uncertainty Analysis for Topographic Correction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040705
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhaoning, Guorui Jia, Michael E. Schaepman, and Huijie Zhao. 2020. "Uncertainty Analysis for Topographic Correction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040705
APA StyleMa, Z., Jia, G., Schaepman, M. E., & Zhao, H. (2020). Uncertainty Analysis for Topographic Correction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040705