Retrieval and Calculation of Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes by a Coherent Doppler Lidar and a Sun Photometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instruments and Methodology
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Wind Field Retrieval by a CDL
2.2.2. Aerosol Optical Properties Retrieval by a CDL and a Sun Photometer
2.2.3. Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes Retrieval by a CDL and a Sun Photometer
3. Experiment and Measurements
3.1. Experiment
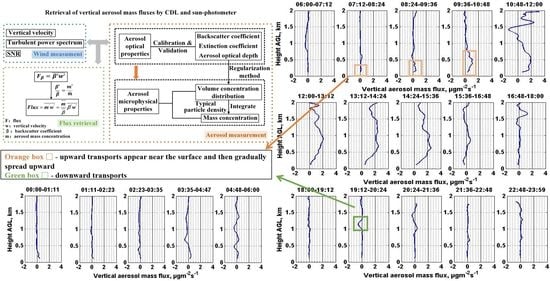
3.2. A Measurement Case of a 24-h Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes Observation
3.3. Error Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- By analyzing the variation processes of the vertical velocity, the aerosol backscatter coefficients at 1550 nm, and the vertical aerosol mass fluxes of 13 April 2020, it is found that, from 10:48 LST to 18:00 LST, the upward transport and the vertical mixture of aerosol are obvious in the PBL which may be caused by the radiation heating of near-surface and the enhanced vertical convection. During this time period, the aerosol backscatter coefficients tend to be constant with height in the PBL. Additionally, most of the aerosol mass fluxes values are positive which means that the upward transport process is in progress at the same period. In the other time periods, the vertical aerosol mass fluxes at all heights are nearly close to zero which means that the atmosphere is relatively stable and that there are few obvious vertical transport processes. The values of the integrated vertical aerosol mass fluxes of the whole PBL are positive from 07:12 LST to 15:36 LST approximately, while close to zero during the other time periods. During 07:12–15:36 LST, the values of the integrated vertical aerosol mass fluxes increase and reach the maximum of about 260 at 14:24 LST, and then decrease gradually.
- (2)
- A downward process of aerosol particles is observed at about 1200 m during 19:12–22:48 LST. Furthermore, during 19:12–20:24 LST, the aerosol mass flux values of the corresponding height are negative, which indicates that an ongoing downward transport process exists.
- (3)
- The vertically averaged mean mass concentration between 120 m and about 2000 m varies in the range of 15 to 30 , with the minimum value of 15.4 and the maximum value of 27.4 . It stabilizes before 06:00 LST and goes through two processes (firstly decreases and then increases).
- (4)
- Finally, the relative errors involved in the aerosol mass flux retrieval are evaluated. The sample error is the dominating error in flux retrieval and it increases with height, except during 12:00–13:12 LST. The instrument error which could be retrieved from the power spectra is much smaller than the sample error . Additionally, the aerosol optical properties retrieval error is 21% and error introduced from regularization method is less than 50%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 571–657. [Google Scholar]
- Buzorius, G.; Rannik, Ü.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Vesala, T.; Kulmala, M. Vertical aerosol particle fluxes measured by eddy covariance technique using condensational particle counter. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzorius, G.; Rannik, Ü.; Nilsson, D.; Kulmala, M. Vertical fluxes and micrometeorology during aerosol particle formation events. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2001, 53, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, J.; Nemitz, E.; Gallagher, M.; Fowler, D.; Williams, P.; Bower, K.; Beswick, K. Direct measurements and parameterisation of aerosol flux, concentration and emission velocity above a city. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårtensson, E.; Nilsson, E.; Buzorius, G.; Johansson, C. Eddy covariance measurements and parameterisation of traffic related particle emissions in an urban environment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemitz, E.; Dorsey, J.; Flynn, M.; Gallagher, M.; Hensen, A.; Erisman, J.-W.; Owen, S.; Dämmgen, U.; Sutton, M. Aerosol fluxes and particle growth above managed grassland. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1627–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruuskanen, T.M.; Kaasik, M.; Aalto, P.P.; Horrak, U.; Vana, M.; Mårtensson, M.; Yoon, Y.; Keronen, P.; Mordas, G.; Ceburnis, D.; et al. Concentrations and fluxes of aerosol particles during the LAPBIAT measurement campaign at Värriö field station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 3683–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldocchi, D.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Olson, R.; Hollinger, D.; Running, S.; Anthoni, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Davis, K.; Evans, R.; et al. FLUXNET: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, R.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Žeromskis, E.; Althausen, D.; Wehner, B. Lidar observations of the vertical aerosol flux in the planetary boundary layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Chen, T.; Xu, M.; Eberhard, W.L. Estimations of atmospheric boundary layer fluxes and other turbulence parameters from Doppler lidar data. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 18409–18423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Peña, A.; Bingöl, F.; Wagner, R.; Courtney, M. Lidar scanning of momentum flux in and above the atmospheric surface layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalikho, I.N.; Banakh, V.A. Measurements of wind turbulence parameters by a conically scanning coherent Doppler lidar in the atmospheric boundary layer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4191–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penndorf, R. Tables of the refractive index for standard air and the Rayleigh scattering coefficient for the spectral region between 0.2 and 20.0 μ and their application to atmospheric optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1957, 47, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, W.; Cooper, D.; Kao, J.; Chen, L.; Hipps, L.; Prueger, J. Estimation of spatially distributed latent heat flux over complex terrain from a Raman lidar. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrendt, A.; Wulfmeyer, V.; Senff, C.; Muppa, S.K.; Späth, F.; Lange, D.; Kalthoff, N.; Wieser, A. Observation of sensible and latent heat flux profiles with lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3221–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiemle, C.; Ehret, G.; Fix, A.; Wirth, M.; Poberaj, G.; Brewer, W.; Hardesty, R.; Senff, C.; LeMone, M. Latent heat flux profiles from collocated airborne water vapor and wind lidars during IHOP_2002. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorani, L.; Colao, F.; Palucci, A.; Poreh, D.; Aiuppa, A.; Giudice, G. First-time lidar measurement of water vapor flux in a volcanic plume. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giez, A.; Ehret, G.; Schwiesow, R.L.; Davis, K.J.; Lenschow, D.H. Water vapor flux measurements from ground-based vertically pointed water vapor differential absorption and Doppler lidars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linné, H.; Hennemuth, B.; Bösenberg, J.; Ertel, K. Water vapour flux profiles in the convective boundary layer. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007, 87, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, C.; Bösenberg, J.; Peters, G. Measurement of water vapor flux profiles in the convective boundary layer with lidar and radar-RASS. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1994, 11, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Dai, G.; Song, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, L. Observations of water vapor mixing ratio profile and flux in the Tibetan Plateau based on the lidar technique. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibert, F.; Koch, G.J.; Beyon, J.Y.; Hilton, T.W.; Davis, K.J.; Andrews, A.; Flamant, P.H.; Singh, U.N. Can CO2 turbulent flux be measured by lidar? A preliminary study. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiuppa, A.; Fiorani, L.; Santoro, S.; Parracino, S.; Nuvoli, M.; Chiodini, G.; Minopoli, C.; Tamburello, G. New ground-based lidar enables volcanic CO2 flux measurements. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorani, L.; Santoro, S.; Parracino, S.; Maio, G.; Nuvoli, M.; Aiuppa, A. Early detection of volcanic hazard by lidar measurement of carbon dioxide. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, C.; Alvarez, R.; Mayor, S.; Zhao, Y. Ozone Flux Profiles in the Boundary Layer Observed with an Ozone DIAL/Doppler Lidar Combination. In Advances in Atmospheric Remote Sensing with Lidar; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997; pp. 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, M.; Edner, H.; Grönlund, R.; Sjöholm, M.; Svanberg, S.; Ferrara, R. Joint application of Doppler Lidar and differential absorption lidar to estimate the atomic mercury flux from a chlor-alkali plant. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A. Microphysical particle parameters from extinction and backscatter lidar data by inversion with regularization: Theory. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 2346–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouza, F.; Reitebuch, O.; Benedetti, A.; Weinzierl, B. Saharan dust long-range transport across the Atlantic studied by an airborne Doppler wind lidar and the MACC model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11581–11600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; Xiang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, N.; Chu, B.; et al. Observations of particle extinction, PM2.5 mass concentration profile and flux in north China based on mobile lidar technique. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chai, W.; Liu, W. Comprehensive study of regional haze in the North China Plain with synergistic measurement from multiple mobile vehicle-based lidars and a lidar network. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; He, L.; Pi, D.; Zhao, J.; Lin, L.; He, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Yan, P.; et al. Integrating LIDAR data and four-dimensional flux method to analyzing the transmission of PM2. 5 in Shenzhen. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 110, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhai, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; et al. Wind turbine wake visualization and characteristics analysis by Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A762–A780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, B.; Song, X.; Yin, J. Shipborne Wind Measurement and Motion-Induced Error Correction of a Coherent Doppler Lidar over the Yellow Sea in 2014. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, B. Doppler lidar investigation of wind turbine wake characteristics and atmospheric turbulence under different surface roughness. Opt. Express 2017, 25, A515–A529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Mattis, I.; Tesche, M.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D.; Pisani, G. Aerosol-type-dependent lidar ratios observed with Raman lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, K.; Wu, S.-H.; Song, X.; Li, R.; Yin, J.; Wang, X. Calibration and retrieval of aerosol optical properties measured with Coherent Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dingenen, R.; Raes, F.; Putaud, J.-P.; Baltensperger, U.; Charron, A.; Facchini, M.-C.; Decesari, S.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hansson, H.-C. A European aerosol phenomenology—1: Physical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2561–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X. Ten-year global particulate mass concentration derived from space-borne CALIPSO lidar observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Nicolae, D.; Kokkalis, P.; Binietoglou, I.; Talianu, C.; Belegante, L.; Tsaknakis, G.; Cazacu, M.; Vetres, I.; Ilic, L. Optical, size and mass properties of mixed type aerosols in Greece and Romania as observed by synergy of lidar and sunphotometers in combination with model simulations: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarig, M.; Walser, A.; Ansmann, A.; Dollner, M.; Althausen, D.; Sauer, D.; Farrell, D.; Weinzierl, B. Profiles of cloud condensation nuclei, dust mass concentration, and ice-nucleating-particle-relevant aerosol properties in the Saharan Air Layer over Barbados from polarization lidar and airborne in situ measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13773–13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, J.; Groß, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Wiegner, M. Volcanic ash from Iceland over Munich: Mass concentration retrieved from ground-based remote sensing measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2209–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Hua, W.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J.; Xie, H. Profiling Dust Mass Concentration in Northwest China Using a Joint Lidar and Sun-Photometer Setting. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Duhl, T.; Salam, M.T.; House, J.M.; Flagan, R.C.; Avol, E.L.; Gilliland, F.D.; Guenther, A.; Chung, S.H.; Lamb, B.K. Development of a regional-scale pollen emission and transport modeling framework for investigating the impact of climate change on allergic airway disease. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chouza, F.; Reitebuch, O.; Jähn, M.; Rahm, S.; Weinzierl, B. Vertical wind retrieved by airborne lidar and analysis of island induced gravity waves in combination with numerical models and in situ particle measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4675–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenschow, D.; Mann, J.; Kristensen, L. How long is long enough when measuring fluxes and other turbulence statistics? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1994, 11, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Height (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12:00–13:12 LST | 13:12–14:24 LST | 14:24–15:36 LST | |||
| 480 | 25% | 29% | 25% | 21% | <50% |
| 780 | 41% | 36% | 32% | ||
| 1080 | 40% | 38% | 39% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Dai, G.; Wu, S.; Sun, K.; Song, X.; Chen, W.; Li, R.; Yin, J.; Wang, X. Retrieval and Calculation of Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes by a Coherent Doppler Lidar and a Sun Photometer. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163259
Wang X, Dai G, Wu S, Sun K, Song X, Chen W, Li R, Yin J, Wang X. Retrieval and Calculation of Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes by a Coherent Doppler Lidar and a Sun Photometer. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163259
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoye, Guangyao Dai, Songhua Wu, Kangwen Sun, Xiaoquan Song, Wenzhong Chen, Rongzhong Li, Jiaping Yin, and Xitao Wang. 2021. "Retrieval and Calculation of Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes by a Coherent Doppler Lidar and a Sun Photometer" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163259
APA StyleWang, X., Dai, G., Wu, S., Sun, K., Song, X., Chen, W., Li, R., Yin, J., & Wang, X. (2021). Retrieval and Calculation of Vertical Aerosol Mass Fluxes by a Coherent Doppler Lidar and a Sun Photometer. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163259