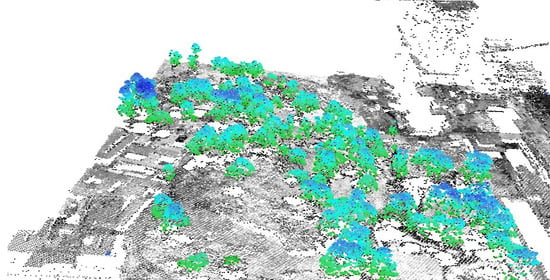
Tree Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data in Urban Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ground and Flat Roof Point Removal
2.2. Coarse Extraction of Tree Points
2.3. Fine Extraction of Tree Points
2.4. Evaluation
2.5. Data
2.5.1. Airborne LiDAR Data
2.5.2. UAV LiDAR Data
3. Results
3.1. Tree Extraction in Airborne LiDAR Data
3.2. Tree Extraction in UAV LiDAR Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Point Density
4.2. Canopy Structure
4.3. Other Points’ Number—OPN
4.4. Time Complexity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, S.; Byrne, J.; Pickering, C. A systematic quantitative review of urban tree benefits, costs, and assessment methods across cities in different climatic zones. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, C.; Atchison, J. Seeing the trees for the (urban) forest: More-than-human geographies and urban greening. Aust. Geogr. 2018, 51, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Yue, W.; Shu, S.; Tan, W.; Hu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, H. A Voxel-Based Method for Automated Identification and Morphological Parameters Estimation of Individual Street Trees from Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Remote. Sens. 2013, 5, 584–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Q.; McPherson, E.G. Rainfall interception by Santa Monica’s municipal urban forest. Urban Ecosyst. 2002, 6, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, J.; Konarska, J.; Lindberg, F.; Johansson, L.; Thorsson, S. Mapping leaf area of urban greenery using aerial LiDAR and ground-based measurements in Gothenburg, Sweden. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 26, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Remote Sensing of Above-Ground Biomass. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, Z. Assessing of urban vegetation biomass in combination with LiDAR and high-resolution remote sensing images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 964–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, M.; Tucker, C.; Kariryaa, A.; Rasmussen, K.; Abel, C.; Small, J.; Chave, J.; Rasmussen, L.; Hiernaux, P.; Diouf, A.; et al. An unexpectedly large count of trees in the West African Sahara and Sahel. Nature 2020, 587, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.; Cohen, W.; Parker, G.; Harding, D. Lidar Remote Sensing for Ecosystem Studies. BioScience 2009, 52, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridhosseini, A. Using Airborne Lidar to Differentiate Cottonwood Trees in a Riparian Area and Refine Riparian Water Use Estimates; The University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Li, P. A tree species mapping method from UAV images over urban area using similarity in tree-crown object histograms. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Chen, W.; Qian, T.; Shen, D.; Wang, J. The Extraction of Vegetation Points from LiDAR Using 3D Fractal Dimension Analyses. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10815–10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonzo, M.; Bookhagen, B.; Roberts, D.A. Urban tree species mapping using hyperspectral and lidar data fusion. Remote Sens Environ. 2014, 148, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matasci, G.; Coops, N.C.; Williams, D.A.; Page, N. Mapping tree canopies in urban environments using airborne laser scanning (ALS): A Vancouver case study. For. Ecosyst. 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Man, Q.; Dong, P.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Han, R. Automatic Extraction of Grasses and Individual Trees in Urban Areas Based on Airborne Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowright, A.A.; Coops, N.C.; Eskelson, B.N.; Sheppard, S.R.; Aven, N.W. Assessing urban tree condition using airborne light detection and ranging. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 19, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Liang, C. Hierarchical Instance Recognition of Individual Roadside Trees in Environmentally Complex Urban Areas from UAV Laser Scanning Point Clouds. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehr, A.; Lohr, U. Airborne laser scanning—an introduction and overview. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wu, R.; Luo, Z.; Wang, C. Rapid urban roadside tree inventory using a mobile laser scanning system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3690–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dai, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Lin, S. Estimating Leaf Area Density of Individual Trees Using the Point Cloud Segmentation of Terrestrial LiDAR Data and a Voxel-Based Model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Extracting Wood Point Cloud of Individual Trees Based on Geometric Features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; You, H.; He, Z.; Su, Z. Retrieval of Canopy Gap Fraction From Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data Based on the Monte Carlo Method. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2021, PP, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, S.; Ye, N.; Zhu, F. Automatic extraction of street trees’ nonphotosynthetic components from MLS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.; Vaishya, R.C. Detection and thinning of street trees for calculation of morphological parameters using mobile laser scanner data. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 13, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Deep learning-based tree classification using mobile LiDAR data. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, Z.; Schlosser, A.; Túri, Z.; Szabó, S. A review of climatic and vegetation surveys in urban environment with laser scanning: A literature-based analysis. Geogr. Pannonica 2019, 23, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Höfle, B.; Hollaus, M.; Hagenauer, J. Urban vegetation detection using radiometrically calibrated small-footprint full-waveform airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2012, 67, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitberger, J.; Krzystek, P.; Stilla, U. Analysis of full waveform LiDAR data for the classification of deciduous and coniferous trees. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1407–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Bouten, W.; Koma, Z.; Kissling, W.; Seijmonsbergen, A. Identification of linear vegetation elements in a rural landscape using LiDAR point clouds. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, W.; Shen, A.; Mellado, N.; Cai, S.; Luo, L.; Wang, N.; Yan, G.; Zhou, G. Seed point set-based building roof extraction from airborne LiDAR point clouds using a top-down strategy. Autom. Constr. 2021, 126, 103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, J.; Koch, B. Exploring full-waveform LiDAR parameters for tree species classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2011, 13, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J. An object-based two-stage method for a detailed classification of urban landscape components by integrating airborne LiDAR and color infrared image data: A case study of downtown Houston. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Yang, B.; Dong, Z.; Shaker, A. A new method for 3D individual tree extraction using multispectral airborne LiDAR point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2018, 144, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Pang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liang, X.; Chen, B.; Lu, H.; Weinacker, H.; Koch, B. Individual Tree Crown Segmentation of a Larch Plantation Using Airborne Laser Scanning Data Based on Region Growing and Canopy Morphology Features. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, T.; Jiang, K.; Li, G.; Eichhorn, M.P.; Fan, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, B.; An, F.; Cao, L. Individual tree crown segmentation from airborne LiDAR data using a novel Gaussian filter and energy function minimization-based approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Quackenbush, L.J. A review of methods for automatic individual tree-crown detection and delineation from passive remote sensing. Int. J. Remote. 2011, 32, 4725–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyyppä, J.; Yu, X.; Hyyppä, H.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Vaaja, M.; Koskinen, J.; et al. Advances in Forest Inventory Using Airborne Laser Scanning. Remote. Sens. 2012, 4, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vega, C.; Hamrouni, A.; El Mokhtari, S.; Morel, J.; Bock, J.; Renaud, J.-P.; Bouvier, M.; Durrieu, S. PTrees: A point-based approach to forest tree extraction from lidar data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Jing, L.; Judah, A. Improving the efficiency and accuracy of individual tree crown delineation from high-density LiDAR data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véga, C.; Durrieu, S. Multi-level filtering segmentation to measure individual tree parameters based on Lidar data: Application to a mountainous forest with heterogeneous stands. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyyppa, J.; Kelle, O.; Lehikoinen, M.; Inkinen, M. A segmentation-based method to retrieve stem volume estimates from 3-D tree height models produced by laser scanners. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2001, 39, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-A.; Lee, W.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Biging, G.S.; Gong, P. Detection of individual trees and estimation of tree height using LiDAR data. J. For. Res. 2007, 12, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hyyppa, J.; Liang, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Yu, X.; Lindberg, E.; Holmgren, J.; Qin, Y.; Mallet, C.; Ferraz, A.; et al. International Benchmarking of the Individual Tree Detection Methods for Modeling 3-D Canopy Structure for Silviculture and Forest Ecology Using Airborne Laser Scanning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2016, 54, 5011–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, S.C.; Whitman, D. A progressive morphological filter for removing nonground measurements from airborne LiDAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sithole, G.; Vosselman, G. The Full Report: ISPRS Comparison of Existing Automatic Filters. Available online: http://www.itc.nl/isprswgIII-3/filtertest/ (accessed on 19 August 2015).
- Meng, X.; Currit, N.; Zhao, K. Ground filtering algorithms for airborne LiDAR data: A review of critical issues. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 833–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zlinszky, A.; Boergens, E.; Glira, P.; Pfeifer, N. Airborne Laser Scanning for calibration and validation of inshore satellite altimetry: A proof of concept. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Yao, W.; Chi, W.; Zhao, X. Comprehensive quality evaluation of airborne lidar data. In Proceedings of the SPIE 8286, International Symposium on Lidar and Radar Mapping 2011: Technologies and Applications, Nanjing, China, 26–29 May 2011; p. 828604. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Scaioni, M.; Si, Q. Coarse-to-Fine Classification of Road Infrastructure Elements from Mobile Point Clouds Using Symmetric Ensemble Point Network and Euclidean Cluster Extraction. Sensors 2019, 20, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pontius, R.G.; Millones, M. Death to Kappa: Birth of quantity disagreement and allocation disagreement for accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4407–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Ma, M. WATER: Dataset of Airborne LiDAR Mission in the Zhangye-Yingke Flight Zone on Jun. 20 2008; A Big Earth Data Platform for Three Poles: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson, P. Processing of laser scanner data—algorithms and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 1999, 54, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.; Mazzotti, G.; Essery, R.; Jonas, T. Enhancing airborne LiDAR data for improved forest structure representation in shortwave transmission models. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Stark, S.; Chazdon, R.; Nelson, B.; Cesar, R.; Meli, P.; Gorgens, E.; Duarte, M.; Valbuena, R.; Moreno, V.; et al. The effectiveness of lidar remote sensing for monitoring forest cover attributes and landscape restoration. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 438, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.; Kattenborn, T.; Straub, C.; Vauhkonen, J. Segmentation of forest to tree objects. In Forestry Applications of Airborne Laser Scanning; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 89–112. [Google Scholar]















| Data | Tree Points (Predicted) | Non-Tree Points (Predicted) |
|---|---|---|
| Tree points (Actual) | TN | FP |
| Non-tree points (Actual) | FN | TP |
| Airborne LiDAR Data | Tree Points (Predicted) | Non-Tree Points (Predicted) |
|---|---|---|
| Tree points (Actual) | 1,058,408 | 3979 |
| Non-tree points (Actual) | 9208 | 1,415,515 |
| UAV LiDAR Data | Tree Points (Predicted) | Non-Tree Points (Predicted) |
|---|---|---|
| Tree points (Actual) | 5,196,268 | 15,895 |
| Non-tree points (Actual) | 124,905 | 12,314,421 |
| Sample No. | Point Count | Time(s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31,779 | 12.28 |
| 2 | 15,818 | 3.399 |
| 3 | 18,424 | 4.286 |
| 4 | 184,361 | 398.3 |
| 5 | 187,941 | 420 |
| Chunk No. | Point Count | Time for Ground and Flat-Roof Point Removal (s) | Time for Coarse Extraction (s) | Time for Fine Extraction (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 96,431 | 139.3 | 0.1636 | 2.486 |
| 2 | 103,393 | 157.2 | 0.3221 | 4.115 |
| 3 | 86,857 | 116.9 | 0.4495 | 4.563 |
| 4 | 93,904 | 133.9 | 0.4415 | 4.833 |
| 5 | 108,370 | 173.0 | 0.3749 | 5.059 |
| 6 | 98,016 | 144.4 | 0.1847 | 2.402 |
| 7 | 87,571 | 118.5 | 0.9525 | 6.088 |
| 8 | 104,104 | 161.1 | 0.6637 | 6.805 |
| 9 | 105,428 | 165.0 | 0.4308 | 5.213 |
| 10 | 116,034 | 193.7 | 0.5291 | 6.476 |
| 11 | 106,838 | 171.4 | 0.5035 | 5.755 |
| 12 | 60,882 | 67.5 | 1.0400 | 4.267 |
| 13 | 105,461 | 164.2 | 1.1700 | 8.251 |
| 14 | 111,570 | 182.9 | 0.2320 | 3.663 |
| 15 | 108,180 | 172.8 | 0.2170 | 3.160 |
| 16 | 105,307 | 164.4 | 0.5126 | 5.868 |
| 17 | 101,178 | 152.2 | 0.6608 | 6.153 |
| 18 | 108,810 | 173.7 | 2.3400 | 10.740 |
| 19 | 105,804 | 166.4 | 0.3484 | 4.601 |
| 20 | 96,951 | 142.4 | 0.2378 | 3.098 |
| 21 | 98,828 | 146.7 | 1.8070 | 7.540 |
| 22 | 100,058 | 164.3 | 0.6765 | 5.981 |
| 23 | 82,548 | 106.9 | 1.1220 | 6.358 |
| 24 | 94,422 | 134.7 | 0.3687 | 4.586 |
| 25 | 100,165 | 148.1 | 0.9651 | 7.466 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, H.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, D. Tree Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173428
You H, Li S, Xu Y, He Z, Wang D. Tree Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data in Urban Areas. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(17):3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173428
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Hangkai, Shihua Li, Yifan Xu, Ze He, and Di Wang. 2021. "Tree Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data in Urban Areas" Remote Sensing 13, no. 17: 3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173428
APA StyleYou, H., Li, S., Xu, Y., He, Z., & Wang, D. (2021). Tree Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data in Urban Areas. Remote Sensing, 13(17), 3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173428