A Comparison of Volumetric Reconstruction Methods of Archaeological Deposits Using Point-Cloud Data from Ahuahu, Aotearoa New Zealand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. 3D Data Recording
3. Uses of 3D Data
4. Case Study: Waitetoke, Ahuahu Great Mercury Island
5. Data Acquisition and Processing
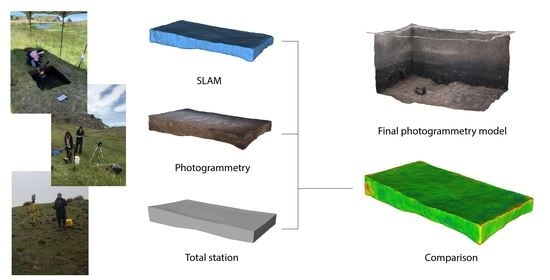
5.1. Total Station
5.2. Photogrammetry
5.3. SLAM
6. Surface and Volume Construction
6.1. Idealized Volumes
6.2. Actual Volumes
7. Results
7.1. Surface Comparison
7.2. Volume Comparison
7.3. Artefact Densities
8. Discussion
8.1. Time
8.2. Cost
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emmitt, J.J.; Mackrell, T.; Armstrong, J. Digital Modelling in Museum and Private Collections: A Case Study on Early Italic Armour. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2021, 4, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, Å.; Dell’Unto, N.; Forte, M.; Haddow, S.; Hodder, I.; Issavi, J.; Lercari, N.; Mazzucato, C.; Mickel, A.; Taylor, J.S. Revisiting reflexive archaeology at Çatalhöyük: Integrating digital and 3D technologies at the trowel’s edge. Antiquity 2015, 89, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, S.T.; Huber, N.; Hoyer, C.; Floss, H. Portable and low-cost solutions to the imaging of Paleolithic art objects: A comparison of photogrammetry and reflectance transformation imaging. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 10, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.T.; Roussel, M.; Soressi, M. A Simple Photogrammetry Rig for the Reliable Creation of 3D Artifact Models in the Field. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. J. Soc. Am. Archeaol. 2016, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, M.; Demesticha, S.; Jimenez, C.; Papadopoulou, C.; Katsouri, I. A Living Shipwreck: An integrated three-dimensional analysis for the understanding of site formation processes in archaeological shipwreck sites. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 35, 102731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmitt, J.; Littleton, J.; Young, R.; Phillipps, R. Digitizing Roonka: The creation of a 3D representation from archival records. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2019, 13, e00094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavryushkina, M. The potential and problems of volumetric 3D modeling in archaeological stratigraphic analysis: A case study from Chlorakas-Palloures, Cyprus. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2021, 21, e00184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, H.L. Measurement of Artifact Provenience with an Electronic Theodolite. J. Field Archaeol. 1987, 14, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Dibble, H.L.; McPherron, S.P. On the Computerization of Archaeological Projects. J. Field Archaeol. 1988, 15, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdaway, S.; Irwin, G. Electronic recording systems used during the excavation of S11/20, Ponui Island, Hauraki Gulf. Archaeol. N. Z. 1993, 36, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Losier, L.M.; Pouliot, J.; Fortin, M. 3D geometrical modeling of excavation units at the archaeological site of Tell ‘Acharneh (Syria). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipps, R.; Holdaway, S.J.; Ramsey, R.; Wendrich, W.; Emmitt, J. Approaches to Paleoenvironment and Landscape Use. In The Desert Fayum Reinvestigated. The Early to Mid-Holocene Landscape Archaeology of the Fayum North Shore, Egypt; Cotsen Institute of Archaeology Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- McPherron, S.J.P. Artifact orientations and site formation processes from total station proveniences. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Laugier, E.J.; Hill, A.C.; Reese, K.M.; Ferwerda, C.; McCoy, M.D.; Ladefoged, T. Exploring archaeological landscapes using drone-acquired lidar: Case studies from Hawai’i, Colorado, and New Hampshire, USA. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 39, 103133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.D.; Casana, J.; Hill, A.C.; Laugier, E.J.; Mulrooney, M.A.; Ladefoged, T.N. Unpiloted Aerial Vehicle Acquired Lidar for Mapping Monumental Architecture. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. J. Soc. Am. Archeaol. 2021, 9, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, R.S.; Ryzewski, K.; Cherry, J.F.; Moloney, B. Using airborne LiDAR Survey to explore historic-era archaeological landscapes of Montserrat in the eastern Caribbean. J. Field Archaeol. 2015, 40, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masini, N.; Coluzzi, R.; Lasaporana, R. On the Airborne Lidar Contribution in Archaeology: From Site Identification to Landscape Investigation. In Laser Scanning, Theory and Applications; Wang, C.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIvor, I.H. Monumental Ideology: A GIS Spatial Analysis of Interior Features of Matakawau Pā, Ahuahu (Stingray Point Pā, Great Mercury Island), New Zealand. J. Polyn. Soc. 2015, 124, 269–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.P.; Holdaway, S.J.; Fanning, P.C.; Mackrell, T.; Shiner, J.I. Shape as an outcome of formation history: Terrestrial Laser Scanning of shell mounds from far north Queensland, Australia. Quat. Int. 2017, 427, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmitt, J.; Allely, K.; Davies, B.; Hoffman, E.; Holdaway, S.J. Preliminary archaeological survey and remote-sensing of shell mounds at Kwokkunum, Albatross Bay, Cape York Peninsula, Australia. Qld. Archaeol. Res. 2020, 23, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabbia, A.; Sammartano, G.; Spanò, A. Fostering Etruscan heritage with effective integration of UAV, TLS and SLAM-based methods. In Proceedings of the IMEKO TC-4 International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, Trento, Italy, 22–24 October 2020; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.M.; Olstad, C.S.; Buhagiar, K.; Gambin, T. Archaeology via underwater robots: Mapping and localization within maltese cistern systems. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, Hanoi, Vietnam, 17 December 2008; pp. 662–667. [Google Scholar]
- Magnani, M.; Douglass, M.; Schroder, W.; Reeves, J.; Braun, D.R. The Digital Revolution to Come: Photogrammetry in Archaeological Practice. Am. Antiq. 2020, 85, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolles, R.C.; Baker, H.H.; Marimont, D.H. Epipolar-plane image analysis: An approach to determining structure from motion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1987, 1, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, M.; Lin, S.; Chodoronek, M. The Application of 3D Photogrammetry for In-Field Documentation of Archaeological Features. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. J. Soc. Am. Archeaol. 2015, 3, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.B.; Jiménez, G.A.; Romero, M.S.; García, E.A.; Martín, S.F.; Medina, A.L.; Guerrero, J.A.E. 3D modelling in archaeology: The application of Structure from Motion methods to the study of the megalithic necropolis of Panoria (Granada, Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 10, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J. Multi-image photogrammetry as a practical tool for cultural heritage survey and community engagement. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 43, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reu, J.; Plets, G.; Verhoeven, G.; De Smedt, P.; Bats, M.; Cherretté, B.; De Maeyer, W.; Deconynck, J.; Herremans, D.; Laloo, P.; et al. Towards a three-dimensional cost-effective registration of the archaeological heritage. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C. Digital photogrammetry and GIS-based analysis of the bio-geomorphological evolution of Sakurajima Volcano, diachronic analysis from 1947 to 2006. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2014, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Unto, N.; Landeschi, G.; Apel, J.; Poggi, G. 4D recording at the trowel’s edge: Using three-dimensional simulation platforms to support field interpretation. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 12, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.B.; Roosevelt, C.H.; Nobles, G.R.; Luke, C. Born-Digital Logistics: Impacts of 3D Recording on Archaeological Workflow, Training, and Interpretation. Open Archaeol. 2021, 7, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Lin, S.C.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, X. The Application of SfM Photogrammetry Software for Extracting Artifact Provenience from Palaeolithic Excavation Surfaces. J. Field Archaeol. 2017, 42, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapirstein, P. A high-precision photogrammetric recording system for small artifacts. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 31, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, F.; Sunding, T.P.; Linde, J.; Smith, O.; Jensen, I.K.; Köppl, C.J.; Butts, M.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) observations of water surface elevation in a small stream: Comparison of radar altimetry, LIDAR and photogrammetry techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendrich, W.; Simpson, B.; Elgewely, E. Karanis in 3D: Recording, Monitoring, Recontextualizing, and the Representation of Knowledge and Conjecture. Near East. Archaeol. 2014, 77, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, K.; Eisenbeiss, H.; Sauerbier, M.; Kupferschmidt, D.; Gaisecker, T.; Sotoodeh, S.; Hanusch, T. Combining photogrammetry and laser scanning for the recording and modelling of the Late Intermediate Period site of Pinchango Alto, Palpa, Peru. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerma, J.L.; Navarro, S.; Cabrelles, M.; Villaverde, V. Terrestrial laser scanning and close range photogrammetry for 3D archaeological documentation: The Upper Palaeolithic Cave of Parpalló as a case study. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G. Mesh Is More—Using All Geometric Dimensions for the Archaeological Analysis and Interpretative Mapping of 3D Surfaces. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2017, 24, 999–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holata, L.; Plzák, J.; Světlík, R.; Fonte, J. Integration of Low-Resolution ALS and Ground-Based SfM Photogrammetry Data. A Cost-Effective Approach Providing an ‘Enhanced 3D Model’ of the Hound Tor Archaeological Landscapes (Dartmoor, South-West England). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Fernández, A.; Benito-Calvo, A.; Campaña, I.; Ortega, A.I.; Karampaglidis, T.; de Castro, J.M.B.; Carbonell, E. 3D monitoring of Paleolithic archaeological excavations using terrestrial laser scanner systems (Sierra de Atapuerca, Railway Trench sites, Burgos, N Spain). Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2020, 19, e00156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, H.A. Combining terrestrial stereophotogrammetry, DGPS and GIS-based 3D voxel modelling in the volumetric recording of archaeological features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 76, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dell’Unto, N.; Landeschi, G.; Touati, A.-M.L.; Dellepiane, M.; Callieri, M.; Ferdani, D. Experiencing Ancient Buildings from a 3D GIS Perspective: A Case Drawn from the Swedish Pompeii Project. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2016, 23, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gonzálvez, P.; Fernández-Palacios, B.J.; Muñoz-Nieto, Á.L.; Arias-Sanchez, P.; González-Aguilera, D. Mobile LiDAR System: New Possibilities for the Documentation and Dissemination of Large Cultural Heritage Sites. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roosevelt, C.H.; Cobb, P.; Moss, E.; Olson, B.R.; Ünlüsoy, S. Excavation is Destruction Digitization: Advances in Archaeological Practice. J. Field Archaeol. 2015, 40, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobles, G.R.; Roosevelt, C.H. Filling the Void in Archaeological Excavations: 2D Point Clouds to 3D Volumes. Open Archaeol. 2021, 7, 589–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmitt, J.; Sefton, B.; Phillipps, R.; Wendrich, W.; Holdaway, S. Reimag(in)ing the Past: Adding the Third Dimension to Archaeological Section Drawings. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. J. Soc. Am. Archeaol. 2017, 5, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, S. Human Ecology and Prehistoric Settlement on Some Offshore Islands (East Cape to Cape Reinga). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Furey, L. Great Mercury Island: Archaeological Site Survey Forestry Development Block; Report; PF Olsen Ltd.: Rotorua, New Zealand, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Furey, L.; Emmitt, J.; Wallace, R. Matakawau Stingray Point Pa excavation, Ahuahu Great Mercury Island 1955-56. Rec. Auckl. Mus. 2017, 52, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golson, J. New Zealand Archaeological Association. J. Polyn. Soc. 1955, 64, 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, G. Archaeological excavations at Waipirau Pa, Ahuahu/Great Mercury Island, 1984. Archaeol. N. Z. 2015, 58, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.; Ladefoged, T.N. Variable horticulture within a small garden on Ahuahu (Great Mercury Island). Rapa Nui J. 2013, 27, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Furey, L. Brief interim report for excavations on Ahuahu Great Mercury Island, June 2014 to February 2017. Archaeol. N. Z. 2017, 60, 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Furey, L.; Phillipps, R.; Jorgensen, A.; Holdaway, S.J.; Ladefoged, T. Investigations on Ahuahu Great Mercury Island 2012. Archaeol. N. Z. 2013, 56, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Holdaway, S.J.; Emmitt, J.; Furey, L.; Jorgensen, A.; O’Regan, G.; Phillipps, R.; Prebble, M.; Wallace, R.; Ladefoged, T.N. Māori settlement of New Zealand: The Anthropocene as a process. Archaeol. Ocean. 2019, 54, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furey, L.; Phillipps, R.; Emmitt, J.; McAlister, A.; Holdaway, S. A large trolling lure shank from Ahuahu Great Mercury Island, New Zealand. J. Polyn. Soc. 2020, 129, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prebble, M.; Anderson, A.J.; Augustinus, P.; Emmitt, J.; Fallon, S.J.; Furey, L.L.; Holdaway, S.J.; Jorgensen, A.; Ladefoged, T.N.; Matthews, P.J.; et al. Early tropical crop production in marginal subtropical and temperate Polynesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8824–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIvor, I.H.; Ladefoged, T.N. A multi-scalar analysis of Māori land use on Ahuahu (Great Mercury Island), New Zealand. Archaeol. Ocean. 2016, 51, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.; Holdaway, S.P.D. Archaeological charcoal analysis in New Zealand. J. Pac. Archaeol. 2017, 8, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Phillipps, R. Interim report on archaeological investigations Ahuahu Great Mercury Island, November 2012-February 2014. Archaeol. N. Z. 2014, 57, 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Holdaway, S.; Emmitt, J.; Phillipps, R.; Masoud-Ansari, S. A Minimalist Approach to Archaeological Data Management Design. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2019, 26, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agisoft. Agisoft Metashape Professional; Version 1.7.2; Agisoft: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Landeschi, G.; Apel, J.; Lundström, V.; Storå, J.; Lindgren, S.; Dell’Unto, N. Re-enacting the sequence: Combined digital methods to study a prehistoric cave. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2019, 11, 2805–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsianis, M.; Tsipidis, S.; Kotsakis, K.; Kousoulakou, A. A 3D digital workflow for archaeological intra-site research using GIS. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignoni, P.; Callieri, M.; Corsini, M.; Dellepiane, M.; Ganovelli, F.; Ranzuglia, G. Meshlab: An Open-Source Mesh Processing Tool; The Eurographics Association: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Layer | Deposit | FCR | Rock | SA | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 42717 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 13 |
| 2 | 43017 | 76 | 13 | 5 | 94 |
| 3 | 43019 | 33 | 3 | 1 | 37 |
| 4 | 43020 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| 5 | 43021 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 8 |
| 6 | 43022 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 43023 | 83 | 21 | 7 | 111 |
| 8 | 42024 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Deposit | Triangulated Mesh | Convex Hull | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLAM | PG | TS | SLAM | PG | TS | Artefacts | |
| 1 | 4.533 | 4.781 | 4.753 | 5.198 | 4.997 | 4.800 | 1.41 |
| 2 | 5.801 | 5.735 | 5.664 | 6.186 | 5.895 | 5.692 | 3.84 |
| 3 | 5.328 | 5.491 | 5.273 | 5.772 | 5.717 | 5.355 | 3.14 |
| 4 | 4.653 | 4.762 | 4.578 | 5.072 | 4.950 | 4.630 | 1.77 |
| 5 | 4.630 | 4.693 | 4.495 | 5.185 | 4.963 | 4.628 | 1.39 |
| 6 | 4.698 | 5.045 | 4.771 | 5.202 | 5.279 | 4.812 | 0.31 |
| 7 | 5.394 | 5.491 | 4.593 | 6.100 | 5.723 | 5.380 | 3.86 |
| 8 | 1.901 | 1.795 | 1.985 | 1.970 | 1.873 | 2.025 | 2.41 |
| Comparison | Shapiro–Wilk p-Value | Test Statistic | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh | |||
| PG vs. TS | 0.078 | t = 1.892, df = 7 | 0.100 |
| PG vs. SLAM | 0.902 | t = 2.015, df = 7 | 0.084 |
| TS vs. SLAM | 0.025 | V = 13 | 0.547 |
| Mesh vs. convex hull | |||
| PG | 0.215 | t = −9.547, df = 7 | <0.001 |
| TS | <0.001 | V = 0 | 0.008 |
| SLAM | 0.423 | t = −6.705, df = 7 | <0.001 |
| Convex hull | |||
| PG vs. TS | 0.058 | t = 3.190, df = 7 | 0.006 |
| PG vs. SLAM | 0.997 | t = −3.188, df = 7 | 0.015 |
| TS vs. SLAM | 0.105 | t = −5.383, df = 7 | 0.001 |
| Deposit | Triangulated Mesh | Convex Hull | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLAM | PG | TS | SLAM | PG | TS | Artefact | |
| 1 | 0.119 | 0.256 | 0.228 | 0.332 | 0.369 | 0.284 | 0.010 |
| 2 | 0.580 | 0.593 | 0.571 | 0.732 | 0.654 | 0.592 | 0.330 |
| 3 | 0.424 | 0.440 | 0.411 | 0.579 | 0.566 | 0.465 | 0.200 |
| 4 | 0.203 | 0.204 | 0.194 | 0.312 | 0.309 | 0.241 | 0.030 |
| 5 | 0.176 | 0.176 | 0.157 | 0.345 | 0.304 | 0.237 | 0.030 |
| 6 | 0.205 | 0.268 | 0.261 | 0.353 | 0.436 | 0.313 | 0.180 |
| 7 | 0.286 | 0.261 | 0.251 | 0.518 | 0.309 | 0.360 | 0.250 |
| 8 | 0.101 | 0.085 | 0.126 | 0.164 | 0.142 | 0.150 | 0.210 |
| Comparison | Shapiro–Wilk p-Value | Test Statistic | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh | |||
| PG vs. TS | 0.010 | V = 28 | 0.195 |
| PG vs. SLAM | 0.040 | V = 26 | 0.313 |
| TS vs. SLAM | 0.108 | t = 0.778, df = 7 | 0.462 |
| Mesh vs. convex hull | |||
| PG | 0.471 | t = −6.751, df = 7 | <0.001 |
| TS | 0.436 | t = −5.400, df = 7 | 0.001 |
| SLAM | 0.827 | t = −8.180, df = 7 | <0.001 |
| Convex hull | |||
| PG vs. TS | 0.244 | t = 2.727, df = 7 | 0.029 |
| PG vs. SLAM | 0.417 | t = −1.006, df = 7 | 0.348 |
| TS vs. SLAM | 0.784 | t = −4.806, df = 7 | 0.002 |
| Layer | n. | PG | TS | SLAM | Artefact Point | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh | CH | Mesh | CH | Mesh | CH | CH | ||
| FCR | ||||||||
| 1 | 10 | 39.13 | 27.14 | 43.9 | 35.26 | 84.35 | 30.11 | 867.75 |
| 2 | 76 | 128.14 | 116.16 | 132.99 | 128.34 | 131.01 | 103.87 | 232.15 |
| 3 | 33 | 75.03 | 58.26 | 80.35 | 71.02 | 77.88 | 57.02 | 167.09 |
| 4 | 9 | 44.11 | 29.16 | 46.35 | 37.4 | 44.38 | 28.85 | 304.53 |
| 5 | 6 | 34.02 | 19.76 | 38.33 | 25.28 | 34.03 | 17.38 | 171.58 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 83 | 317.66 | 268.63 | 330.78 | 230.28 | 290.66 | 160.19 | 331.9 |
| 8 | 3 | 35.09 | 21.19 | 23.72 | 19.99 | 29.85 | 18.27 | 14.01 |
| Rock | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 3.91 | 2.71 | 4.39 | 3.53 | 8.43 | 3.01 | 86.78 |
| 2 | 13 | 21.92 | 19.87 | 22.75 | 21.95 | 22.41 | 17.77 | 39.71 |
| 3 | 3 | 6.82 | 5.3 | 7.3 | 6.46 | 7.08 | 5.18 | 15.19 |
| 4 | 1 | 4.9 | 3.24 | 5.15 | 4.16 | 4.93 | 3.21 | 33.84 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 21 | 80.37 | 67.97 | 83.69 | 58.26 | 73.54 | 40.53 | 83.97 |
| 8 | 1 | 11.7 | 7.06 | 7.91 | 6.66 | 9.95 | 6.09 | 4.67 |
| Stone Artefact | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 7.83 | 5.43 | 8.78 | 7.05 | 16.87 | 6.02 | 173.55 |
| 2 | 5 | 8.43 | 7.64 | 8.75 | 8.44 | 8.62 | 6.83 | 15.27 |
| 3 | 1 | 2.27 | 1.77 | 2.43 | 2.15 | 2.36 | 1.73 | 5.06 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | 11.34 | 6.59 | 12.78 | 8.43 | 11.34 | 5.79 | 57.19 |
| 6 | 1 | 3.73 | 2.3 | 3.84 | 3.2 | 4.87 | 2.84 | 5.62 |
| 7 | 7 | 26.79 | 22.66 | 27.9 | 19.42 | 24.51 | 13.51 | 27.99 |
| 8 | 1 | 11.7 | 7.06 | 7.91 | 6.66 | 9.95 | 6.09 | 4.67 |
| Total | ||||||||
| 1 | 13 | 50.87 | 35.28 | 57.07 | 45.83 | 109.65 | 39.14 | 39.14 |
| 2 | 94 | 158.49 | 143.67 | 164.48 | 158.74 | 162.03 | 128.48 | 128.48 |
| 3 | 37 | 84.12 | 65.33 | 90.09 | 79.63 | 87.32 | 63.93 | 63.93 |
| 4 | 10 | 49.01 | 32.4 | 51.5 | 41.56 | 49.31 | 32.06 | 32.06 |
| 5 | 8 | 45.36 | 26.35 | 51.11 | 33.7 | 45.37 | 23.17 | 23.17 |
| 6 | 1 | 3.73 | 2.3 | 3.84 | 3.2 | 4.87 | 2.84 | 2.84 |
| 7 | 111 | 424.82 | 359.25 | 442.37 | 307.97 | 388.72 | 214.23 | 214.23 |
| 8 | 5 | 58.49 | 35.32 | 39.53 | 33.31 | 49.75 | 30.45 | 30.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emmitt, J.; Pillay, P.; Barrett, M.; Middleton, S.; Mackrell, T.; Floyd, B.; Ladefoged, T.N. A Comparison of Volumetric Reconstruction Methods of Archaeological Deposits Using Point-Cloud Data from Ahuahu, Aotearoa New Zealand. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13194015
Emmitt J, Pillay P, Barrett M, Middleton S, Mackrell T, Floyd B, Ladefoged TN. A Comparison of Volumetric Reconstruction Methods of Archaeological Deposits Using Point-Cloud Data from Ahuahu, Aotearoa New Zealand. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(19):4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13194015
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmmitt, Joshua, Patricia Pillay, Matthew Barrett, Stacey Middleton, Timothy Mackrell, Bruce Floyd, and Thegn N. Ladefoged. 2021. "A Comparison of Volumetric Reconstruction Methods of Archaeological Deposits Using Point-Cloud Data from Ahuahu, Aotearoa New Zealand" Remote Sensing 13, no. 19: 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13194015
APA StyleEmmitt, J., Pillay, P., Barrett, M., Middleton, S., Mackrell, T., Floyd, B., & Ladefoged, T. N. (2021). A Comparison of Volumetric Reconstruction Methods of Archaeological Deposits Using Point-Cloud Data from Ahuahu, Aotearoa New Zealand. Remote Sensing, 13(19), 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13194015