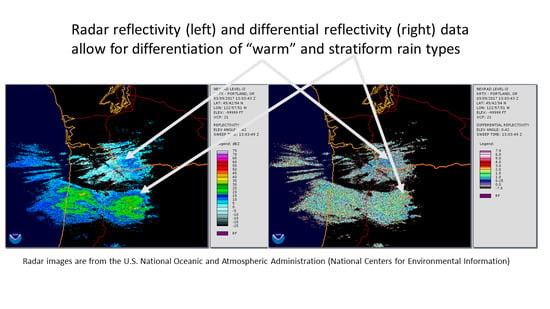
Distinguishing between Warm and Stratiform Rain Using Polarimetric Radar Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
Identification of Different Rain Types
3. Results
3.1. Mean ZDR–Ze Correspondences for Different Rain Types
3.2. Differences in Ze–R Estimators for Warm and Stratiform Rains
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, N.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y. Polarimetric signatures of midlatitude warm-rain precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, P.V.; Rangno, A.L. Super-large raindrops. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martner, B.E.; Yuter, S.E.; White, A.B.; Matrosov, S.Y.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Ralph, F.M. Raindrop size distributions and rain characteristics in California coastal rainfall for periods with and without a radar bright band. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Clark, K.A.; Kingsmill, D.E. A polarimetric radar approach to identify rain, melting-layer and snow regions for applying corrections to vertical profiles of reflectivity. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K.; Matrosov, S.; Campbell, J. CloudSat spaceborne 94 GHz radar bright bands in the melting layer: An attenuation-driven upside-down lidar analog. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L16818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Cifelli, R.; Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B. Radar rain-rate estimators and their variability due to rainfall type: An assessment based on hydrometeorology testbed data from the Southeastern United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Martinaitis, S.; et al. Multi-radar multi-sensor (MRMS) quantitative precipitation estimation: Initial operating capabilities. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y. Evaluating polarimetric X-band radar rainfall estimators during HMT. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zrnic, D.S. Radar Polarimetry for Weather Observations; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; p. 486. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Corrigendum. J. Appl. Meteor. 2005, 44, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B. Quantitative assessment of operational weather radar rainfall estimates over California’s Northern Sonoma county using HMT-West data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matrosov, S.Y. Observations of winter-time US West coast precipitating systems with W-band satellite radar and other spaceborne instruments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y. Characteristics of landfalling atmospheric rivers inferred from satellite observations over eastern North Pacific Ocean. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 3757–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. A real-time automated convective and stratiform precipitation segregation algorithm in native radar coordinates. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Joss, J. An optical disdrometer for measuring size and velocity of hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Ocenanic Technol. 2000, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.V. Terminal velocity and shapes of cloud and precipitation drops aloft. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Travis, L.D. T-matrix computations of light scattering by larger spheroidal particles. Opt. Commun. 1994, 109, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Strem, E.T.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J. An automated brightband height detection algorithm for use with Doppler radar spectral moments. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2002, 19, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doviak, R.J.; Zrnic, D.S. Doppler Radar and Weather Observations; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; p. 562. [Google Scholar]
- Zrnic, D.; Doviak, R.; Zhang, G.; Ryzhkov, A. Bias in differential Reflectivity due to cross coupling through the radiation patterns of polarimetric weather radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1624–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.reflectivity |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matrosov, S.Y. Distinguishing between Warm and Stratiform Rain Using Polarimetric Radar Measurements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020214
Matrosov SY. Distinguishing between Warm and Stratiform Rain Using Polarimetric Radar Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatrosov, Sergey Y. 2021. "Distinguishing between Warm and Stratiform Rain Using Polarimetric Radar Measurements" Remote Sensing 13, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020214
APA StyleMatrosov, S. Y. (2021). Distinguishing between Warm and Stratiform Rain Using Polarimetric Radar Measurements. Remote Sensing, 13(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020214