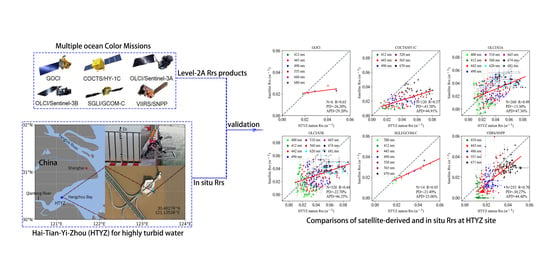
Evaluation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Products from Multiple Ocean Color Missions in Highly Turbid Water (Hangzhou Bay)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. In Situ Rrs Data Measured in HZB
2.2. In Situ Rrs Data at ARIAKE Site
2.3. Satellite Data
2.4. Matchup between Satellite and In Situ Rrs Data
2.5. Evaluation Methods
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Spectral Consistency
3.2. Time-Series Comparisons
3.3. Scatter Plot Comparisons at HTYZ Site
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in APD with Water Turbidity
4.2. Different Performances in High and Moderate Turbidity Waters
4.3. Analysis of Possible Reasons for the Performance of Multi-Source Remote Sensing Products at HTYZ Site
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Gordon, H.R. A Simple, Moderately Accurate, Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Seawifs. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, G.; Franz, B.A.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; McClain, C.R. Corrections to the Calibration of MODIS Aqua Ocean Color Bands Derived From SeaWiFS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2012, 50, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products; Reports and Monographs of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG): Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Gordon, H.R. Radiance reflected from the ocean-atmosphere system: Synthesis from individual components of the aerosol size distribution. Appl. Optics 1994, 33, 7088–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, J.W.; Evans, R.H. Exact Rayleigh scattering calculations for use with the Nimbus-7 Coastal Zone Color Scanner. Appl. Optics 1988, 27, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Surface-roughness considerations for atmospheric correction of ocean color sensors. 1: The Rayleigh-scattering component. Appl. Optics 1992, 31, 4247–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, S.; Knaeps, S.; Kratzer, S.; Ruddick, K. SIMilarity Environment Correction (SIMEC) applied to MERIS data over inland and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.; Schmechtig, C. Adjacency effects on water surfaces: Primary scattering approximation and sensitivity study. Appl. Optics 2000, 39, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, B.; Kiselev, V.; Zibordi, G. Simulation and analysis of adjacency effects in coastal waters: A case study. Appl. Optics 2014, 53, 1523–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, W.J.; Sterckx, S.; Montes, M.J.; De Keukelaere, L.; Knaeps, E. Atmospheric correction for inland waters. In Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlevan, N.; Roger, J.-C.; Ahmad, Z. Revisiting short-wave-infrared (SWIR) bands for atmospheric correction in coastal waters. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 6015–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z.; Franz, B.A.; McClain, C.R.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Werdell, J.; Shettle, E.P.; Holben, B.N. New aerosol models for the retrieval of aerosol optical thickness and normalized water-leaving radiances from the SeaWiFS and MODIS sensors over coastal regions and open oceans. Appl. Optics 2010, 49, 5545–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Tang, J.; Wang, D. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery using the ultraviolet wavelength for highly turbid waters. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20754–20770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Shanmugam, P.; He, X.; Schroeder, T. UV-NIR approach with non-zero water-leaving radiance approximation for atmospheric correction of satellite imagery in inland and coastal zones. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A1118–A1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Optics 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Turbid wakes associated with offshore wind turbines observed with Landsat 8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.C.; Montes, M.J.; Ahmad, Z.; Davis, C.O. Atmospheric correction algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing of ocean color from space. Appl. Optics 2000, 39, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knaeps, E.; Ruddick, K.G.; Doxaran, D.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Nechad, B.; Raymaekers, D.; Sterckx, S. A SWIR based algorithm to retrieve total suspended matter in extremely turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doerffer, R.; Schiller, H. The MERIS Case 2 water algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, H.; Doerffer, R. Neural network for emulation of an inverse model operational derivation of Case II water properties from MERIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.K.; Gordon, H.R.; Voss, K.J.; Ge, Y.; Broenkow, W.; Trees, C. Validation of atmospheric correction over the oceans. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1997, 102, 17209–17217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.K.; Yarbrough, M.A.; Feinholz, M.; Flora, S.; Broenkow, W.; Kim, Y.S.; Johnson, B.C.; Brown, S.W.; Yuen, M.; Mueller, J.L. MOBY, a radiometric buoy for performance monitoring and vicarious calibration of satellite ocean color sensors: Measurement and data analysis protocols. Ocean Optics 2003, 4, 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zibordi, G.; Doyle, J.P.; Hooker, S.B. Offshore tower shading effects on in-water optical measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Antoine, D.; Gentili, B. Bidirectional reflectance of oceanic waters: Accounting for Raman emission and varying particle scattering phase function. Appl. Optics 2002, 41, 6289–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Hooker, S.B.; Berthon, J.F.; D’Alimonte, D. Autonomous above-water radiance measurements from an offshore platform: A field assessment experiment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Melin, F.; Hooker, S.B.; D’Alimonte, D.; Holbert, B. An autonomous above-water system for the validation of ocean color radiance data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.; Hooker, S.B.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.-F.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; Vandemark, D.; Feng, H.; Rutledge, K.; et al. A network for standardized ocean color validation measurements. Eos Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union 2006, 87, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zibordi, G.; Melin, F.; Berthon, J.F. A time-series of above-water radiometric measurements for coastal water monitoring and remote sensing product validation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Strombeck, N.; Melin, F.; Berthon, J.F. Tower-based radiometric observations at a coastal site in the Baltic Proper. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; D’Alimonte, D.; Melin, F.; Berthon, J.-F.; Vandemark, D.; Feng, H.; Schuster, G.; et al. AERONET-OC: A Network for the Validation of Ocean Color Primary Products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Carder, K.L.; Muller-Karger, F.E. How precise are SeaWiFS ocean color estimates? Implications of digitization-noise errors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, V.E.; Lovell, J.L.; King, E.A.; Boadle, D.; Scott, R.; Schroeder, T. The Potential of Autonomous Ship-Borne Hyperspectral Radiometers for the Validation of Ocean Color Radiometry Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hlaing, S.; Gilerson, A.; Foster, R.; Wang, M.; Arnone, R.; Ahmed, S. Radiometric calibration of ocean color satellite sensors using AERONET-OC data. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 23385–23401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Gilerson, A.; Hlaing, S.; Ioannou, I.; Wang, M.; Weidemann, A.; Arnone, R.A. Evaluation of VIIRS ocean color data using measurements from the AERONET-OC sites. In Proceedings of the Conference on Ocean Sensing and Monitoring V, Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 April–1 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Son, S.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Tan, L.; Mikelsons, K.; Wang, X.; Lance, V. VIIRS ocean color products: A progress update. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 5848–5851. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Tan, L.; Naik, P.; Mikelsons, K.; Wang, X.; et al. VIIRS ocean color research and applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 2911–2914. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, D.; d’Ortenzio, F.; Hooker, S.B.; Becu, G.; Gentili, B.; Tailliez, D.; Scott, A.J. Assessment of uncertainty in the ocean reflectance determined by three satellite ocean color sensors (MERIS, SeaWiFS and MODIS-A) at an offshore site in the Mediterranean Sea (BOUSSOLE project). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Shi, W.; Rausch, K.; Voss, K. Impacts of VIIRS SDR performance on ocean color products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10347–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Barbosa, C.; Belanger, S.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; et al. ACIX-Aqua: A global assessment of atmospheric correction methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over lakes, rivers, and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Seamless retrievals of chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in inland and coastal waters: A machine-learning approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Lee, B.; Oh, I.S. Development of Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Ocean Sci. 2012, 47, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, W.; Lee, B.; Oh, I.S. Vicarious calibration of the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 23236–23258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pan, D. A practical method of atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters. In Proceedings of the Conference on Ocean Remote Sensing and Applications, Hangzhou, China, 24–26 October 2003; pp. 494–505. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Gong, F. The Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for HY-1A/COCTS; SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5977. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhu, Q. The Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for HY-1B/COCTS; SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 7147. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F. Primary Analysis of the Ocean Color Remote Sensing Data of the HY-1B/COCTS; SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 7150. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M.H. Retrieval of Water-Leaving Radiance and Aerosol Optical-Thickness over the Oceans with Seawifs—A Preliminary Algorithm. Appl. Optics 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Han, H.J.; Yang, H.; Moon, J.E.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, B.R.; Min, J.E.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, K.S.; et al. GOCI Level 2 Ocean Color Products (GDPS 1.3) Brief Algorithm Description; Korea Ocean Satellite Center, Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology Ansan: Ansan, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Doerffer, R. OLCI Level 2: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document—Ocean Colour Turbid Water; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Doerffer, R. OLCI Level 2: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document—Alternative Atmospheric Correction; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, D. OLCI Level 2: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document—Atmospheric Correction over Case 1 Waters; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Ogata, K. GCOM-C/SGLI Capability for Coastal Observation; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2018; Volume 10778. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhiro Toratani, K.O.; Hajime, F. SGLI Algorithm Technical Background Document—Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Ocean Color. Tokai University: Shibuya City, Tokyo, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Detection of turbid waters and absorbing aerosols for the MODIS ocean color data processing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, M. Improved near-infrared ocean reflectance correction algorithm for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 21657–21678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.-E.; Park, Y.-J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Choi, J.-K.; Ahn, J.-H.; Min, J.-E.; Son, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Ahn, Y.-H. Initial Validation of GOCI Water Products against in situ Data Collected around Korean Peninsula for 2010-2011. Ocean Sci. J. 2012, 47, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Han, B.; Jamet, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, T. Evaluation of Four Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for GOCI Images over the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.-j. Adaptability Analysis of Various Versions of GDPS Based on QA Score for GOCI Data Processing in the Yellow Sea. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; He, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, F.; Li, P. Assessment of Normalized Water-Leaving Radiance Derived from GOCI Using AERONET-OC Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z. Turbidity Estimation from GOCI Satellite Data in the Turbid Estuaries of China’s Coast. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lin, H.; He, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, J. Tide-Induced Variability and Mechanisms of Surface Suspended Sediment in the Zhoushan Archipelago along the Southeastern Coast of China Based on GOCI Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L. Atmospheric correction using near-infrared bands for satellite ocean color data processing in the turbid western Pacific region. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, S.; Xue, C.; Lin, M.; Du, K.; Li, S.; Ma, C.; Tang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Vicarious calibration of COCTS-HY1C at visible and near-infrared bands for ocean color application. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A1615–A1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Du, K.; Lee, Z.; Liu, J.; Song, Q.; Xue, C.; Wang, D.; Lin, M.; Tang, J.; Ma, C. Performance of COCTS in Global Ocean Color Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Melin, F.; Berthon, J.-F. A Regional Assessment of OLCI Data Products. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Pardo, S.; Dall, G.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Nencioli, F.; Dessailly, D.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Casal, T.; Donlon, C. Performance of Ocean Colour Chlorophyll a algorithms for Sentinel-3 OLCI, MODIS-Aqua and Suomi-VIIRS in open-ocean waters of the Atlantic. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, F.; Hunt, B.P.V.; Jacoby, D.; Costa, M. Performance of OLCI Sentinel-3A satellite in the Northeast Pacific coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, E.; Tote, C.; Sterckx, S.; Adriaensen, S.; Henocq, C.; Bruniquel, J.; Scifoni, S.; Dransfeld, S. iCOR Atmospheric Correction on Sentinel-3/OLCI over Land: Intercomparison with AERONET, RadCalNet, and SYN Level-2. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of Sentinel-3/OLCI data for mapping of suspended particulate matter and chlorophyll-a concentration in Belgian turbid coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Uiboupin, R.; Arikas, A.; Vahter, K.; Paavel, B. Mapping Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-3 Ocean and Land Colour Instrument Imagery in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mograne, M.A.; Jamet, C.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A. Evaluation of Five Atmospheric Correction Algorithms over French Optically-Complex Waters for the Sentinel-3A OLCI Ocean Color Sensor. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Roettgers, R.; Ramirez-Perez, M.; Dinter, T.; Steinmetz, F.; Noethig, E.-M.; Hellmann, S.; Wiegmann, S.; Bracher, A. Underway spectrophotometry in the Fram Strait (European Arctic Ocean): A highly resolved chlorophyll a data source for complementing satellite ocean color. Opt. Express 2018, 26, A678–A696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Jamet, C.; Zhu, J.; Han, B.; Li, T.; Yang, A.; Guo, K.; Jia, D. Error Budget in the Validation of Radiometric Products Derived from OLCI around the China Sea from Open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kritten, L.; Preusker, R.; Fischer, J. A New Retrieval of Sun-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Water from Ocean Colour Measurements Applied on OLCI L-1b and L-2. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, J.; Matthews, M.; Bernard, S.; Griffith, D. Application of Sentinel 3 OLCI for chl-a retrieval over small inland water targets: Successes and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glukhovets, D.; Kopelevich, O.; Yushmanova, A.; Vazyulya, S.; Sheberstov, S.; Karalli, P.; Sahling, I. Evaluation of the CDOM Absorption Coefficient in the Arctic Seas Based on Sentinel-3 OLCI Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyryliuk, D.; Kratzer, S. Evaluation of Sentinel-3A OLCI Products Derived Using the Case-2 Regional CoastColour Processor over the Baltic Sea. Sensors 2019, 19, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Selmes, N. Complementary water quality observations from high and medium resolution Sentinel sensors by aligning chlorophyll-a and turbidity algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Kratzer, S.; Wang, J.; Shi, T.; Hu, Z.; Yang, C.; Hu, S.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Estimating ultraviolet reflectance from visible bands in ocean colour remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.L.; Pratolongo, P.D.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Arena, M.; Celleri, C.; Garzon Cardona, J.E.; Martinez, A. Evaluation of MODIS-Aqua and OLCI Chlorophyll-a products in contrasting waters of the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Ocean Coast. Res. 2021, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Stumpf, R.P.; Meredith, A. Preliminary Assessment of Turbidity and Chlorophyll Impact on Bathymetry Derived from Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-3A Satellites in South Florida. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blix, K.; Li, J.; Massicotte, P.; Matsuoka, A. Developing a New Machine-Learning Algorithm for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Optically Complex Waters: A Case Study for High Northern Latitude Waters by Using Sentinel 3 OLCI. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinmetz, F.; Ramon, D. Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI consistent ocean colour products using POLYMER. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing of the Open and Coastal Ocean and Inland Waters, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–25 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Soomets, T.; Uudeberg, K.; Jakovels, D.; Brauns, A.; Zagars, M.; Kutser, T. Validation and Comparison of Water Quality Products in Baltic Lakes Using Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilerson, A.; Malinowski, M.; Herrera, E.; Tomlinson, M.; Stumpf, R.; Ondrusek, M. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Complex Coastal Waters from Satellite Imagery; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2021; Volume 11752. [Google Scholar]
- Gilerson, A.; Herrera, E.; Klein, Y.; Foster, R.; Gross, B.; Arnone, R.; Ahmed, S. Comparison of aerosol models from the Ocean Color satellite sensors and AERONET-OC and their impact on reflectance spectra in coastal waters. In Proceedings of the Conference on Ocean Sensing and Monitoring X, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–18 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gilerson, A.; Herrera, E.; Klein, Y.; Foster, R.; Gross, B.; Arnone, R.; Ahmed, S. Characterization of aerosol parameters over ocean from the Ocean Color satellite sensors and AERONET-OC data. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions, Warsaw, Poland, 11–12 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gossn, J.I.; Ruddick, K.G.; Dogliotti, A.I. Atmospheric Correction of OLCI Imagery over Extremely Turbid Waters Based on the Red, NIR and 1016 nm Bands and a New Baseline Residual Technique. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hieronymi, M. Spectral band adaptation of ocean color sensors for applicability of the multi-water biogeo-optical algorithm ONNS. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A707–A724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieronymi, M.; Mueller, D.; Doerffer, R. The OLCI Neural Network Swarm (ONNS): A Bio-Geo-Optical Algorithm for Open Ocean and Coastal Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gossn, J.I.; Ruddick, K.G.; Dogliotti, A.I. Atmospheric correction of OLCI imagery over very turbid waters based on the RED/NIR/SWIR bands. In 2017 XVII Workshop on Information Processing and Control (RPIC); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Sano, I.; Nakata, M. Efficient algorithms for aerosol retrieval from GCOM-C/SGLI. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 7614–7617. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Sano, I.; Nakata, M. Effective Characterization of Aerosols in the Severe Events Using Multi-Channel Measurements Including Polarization with GCOM-C/SGLI; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2020; Volume 11531. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Sano, I.; Nakata, M. Inheritance of aerosol retrieval by GCOM-C/SGLI from ADEOS-2/GLI. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere XXIV, Strasbourg, France, 11–12 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Sano, I.; Nakata, M. Algorithms for the classification and characterization of aerosols: Utility verification of near-UV satellite observations. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 014527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukai, S.; Sano, I.; Nakata, M. Discrimination and retrieval of aerosol types using multi-channels including near-UV and polarization for GCOM-C/SGLI. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere, Clouds, and Precipitation VII, Honolulu, HI, USA, September 24–26 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Fujito, T.; Nakata, M.; Sano, I. Detection of aerosols above CLOUDS based on GCOM-C/SGLI measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Electr Network, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 5489–5492. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, S.; Fujito, T.; Nakata, M.; Sano, I. Role of near ultraviolet wavelength measurements in the detection and retrieval of absorbing aerosols from space. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere XXII, Warsaw, Poland, 12–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, T.Y.; Ishida, H.; Nagao, T.M.; Hori, M.; Letu, H.; Higuchi, R.; Tamaru, N.; Imoto, N.; Yamazaki, A. Theoretical basis of the algorithms and early phase results of the GCOM-C (Shikisai) SGLI cloud products. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toratani, M.; Ogata, K.; Suzuki, K.; Ishizaka, J.; Hirawake, T.; Hirata, T.; Isada, T.; Higa, H.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Hooker, S.B.; et al. GCOM-C/SGLI ocean standard products and early validation results. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 4741–4744. [Google Scholar]
- Urabe, T.; Xiong, X.; Hashiguchi, T.; Ando, S.; Okamura, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Mokuno, M. Lunar calibration inter-comparison of sgli, modis and viirs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 8481–8484. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jiang, L.; Shi, W.; Son, S.; Park, Y.-J.; Ryu, J.-H. Ocean color products from the Korean Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Opt. Express 2013, 21, 3835–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Tan, L.; Naik, P.; Mikelsons, K.; Wang, X.; et al. Evaluation of VIIRS ocean color products. In Proceedings of the Ocean Remote Sensing and Monitoring from Space, SPIE Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing, Beijing, China, 10 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Son, S.; Voss, K. Technique for monitoring performance of VIIRS reflective solar bands for ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 14446–14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Voss, K. NIR- and SWIR-based on-orbit vicarious calibrations for satellite ocean color sensors. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 20437–20453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaing, S.; Harmel, T.; Gilerson, A.; Foster, R.; Weidemann, A.; Arnone, R.; Wang, M.; Ahmed, S. Evaluation of the VIIRS ocean color monitoring performance in coastal regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; He, X.; Jia, Y.; Bai, Y.; Ye, X.; Gong, F. Advances in marine satellite remote sensing technology in China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 41, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Huang, N.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Cui, Q. Using geostationary satellite ocean color data to map the diurnal dynamics of suspended particulate matter in coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; De Vriend, H.J. Modeling the tidal channel morphodynamics in a macro-tidal embayment, Hangzhou Bay, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Zhuo, H.C.; Gao, S. Sedimentary facies and evolution in the Qiantang River incised valley, eastern China. Mar. Geol. 2005, 219, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F.; Li, H.; Li, J. High-frequency and tidal period observations of suspended particulate matter in coastal waters by AHI/Himawari-8. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 27387–27404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Optics 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Pan, D.-l.; He, X.-q.; Zhu, Q.-k.; Gong, F.; Huang, H.-g. High-Frequency Observation of Water Spectrum and Its Application in Monitoring of Dynamic Variation of Suspended Materials in the Hangzhou Bay. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2015, 35, 3247–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.; Munk, W. Measurement of the Roughness of the Sea Surface from Photographs of the Suns Glitter. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1954, 44, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bailey, S.W. Correction of sun glint contamination on the SeaWiFS ocean and atmosphere products. Appl. Optics 2001, 40, 4790–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuillier, G.; Herse, M.; Labs, D.; Foujols, T.; Peetermans, W.; Gillotay, D.; Simon, P.C.; Mandel, H. The solar spectral irradiance from 200 to 2400 nm as measured by the SOLSPEC spectrometer from the ATLAS and EURECA missions. Sol. Phys. 2003, 214, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Goes, J.I.; Tian, H.; Maure, E.d.R.; Ishizaka, J. Effects of Spring-Neap Tidal Cycle on Spatial and Temporal Variability of Satellite Chlorophyll-A in a Macrotidal Embayment, Ariake Sea, Japan. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, T.; Gilerson, A.; Hlaing, S.; Tonizzo, A.; Legbandt, T.; Weidemann, A.; Arnone, R.; Ahmed, S. Long Island Sound Coastal Observatory: Assessment of above-water radiometric measurement uncertainties using collocated multi and hyperspectral systems. Appl. Optics 2011, 50, 5842–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamet, C.; Thiria, S.; Moulin, C.; Crépon, M. Use of a neurovariational inversion for retrieving oceanic and atmospheric constituents from ocean color imagery: A feasibility study. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajard, J.; Jamet, C.; Moulin, C.; Thiria, S. Use of a neuro-variational inversion for retrieving oceanic and atmospheric constituents from satellite ocean colour sensor: Application to absorbing aerosols. Neural Netw. 2006, 19, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, T.; Behnert, I.; Schaale, M.; Fischer, J.; Doerffer, R. Atmospheric correction algorithm for MERIS above case-2 waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.B.; Cannizzaro, J.P.; English, D.C.; Hu, C. Validation of VIIRS and MODIS reflectance data in coastal and oceanic waters: An assessment of methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Carder, K.L.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery over turbid coastal waters: A practical method (vol 74, pg 195, 2000). Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; De Cauwer, V.; Park, Y.J.; Moore, G. Seaborne measurements of near infrared water-leaving reflectance: The similarity spectrum for turbid waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y. Diurnal Dynamics and Seasonal Variations of Total Suspended Particulate Matter in Highly Turbid Hangzhou Bay Waters Based on the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F. A vector radiative transfer model of coupled ocean–atmosphere system using matrix-operator method for rough sea-surface. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1426–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. An assessment of the black ocean pixel assumption for MODIS SWIR bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Son, S. The Viirs Ocean Color Product Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Version 1.0; NOAA NESDIS STAR: College Park, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR atmospheric correction algorithms using SeaBASS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W. Evaluation of shortwave infrared atmospheric correction for ocean color remote sensing of Chesapeake Bay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| GOCI | COCTS/HY1C | OLCI/S3A | OLCI/S3B | SGLI/GCOM-C | VIIRS/SNPP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTYZ | 10/1 | 38/20 | 72/26 | 76/32 | 7/2 | 80/51 |
| ARIAKE | 392/154 | 58/27 | 72/22 | 77/29 | 82/30 | 163/48 |
| COCTS/HY1C | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||||
| 412 | 443 | 490 | 520 | 565 | 670 | ||||||
| N | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 120 | ||||
| R | −0.14 | −0.21 | −0.26 | −0.36 | −0.52 | −0.33 | 0.57 | ||||
| PD (%) | −49.33 | −51.17 | −46.69 | −37.75 | −38.72 | −36.63 | −43.38 | ||||
| APD (%) | 54.09 | 53.68 | 47.26 | 39.06 | 38.72 | 36.63 | 44.91 | ||||
| OLCI/S3A | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||||
| 400 | 412 | 442 | 490 | 510 | 560 | 620 | 665 | 674 | 681 | ||
| N | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 260 |
| R | −0.31 | −0.3 | −0.27 | −0.26 | −0.25 | −0.24 | −0.30 | −0.31 | −0.32 | −0.33 | 0.49 |
| PD (%) | −1.24 | −9.99 | −13.07 | −15.59 | −15.75 | −15.62 | −15.78 | −15.43 | −15.41 | −15.09 | −13.30 |
| APD (%) | 93.40 | 83.54 | 63.71 | 48.22 | 43.28 | 32.35 | 27.79 | 27.27 | 27.06 | 27.00 | 47.36 |
| OLCI/S3B | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||||
| 400 | 412 | 442 | 490 | 510 | 560 | 620 | 665 | 674 | 681 | ||
| N | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 320 |
| R | −0.36 | −0.38 | −0.31 | −0.29 | −0.28 | −0.29 | −0.30 | −0.28 | −0.28 | −0.28 | 0.45 |
| PD (%) | −19.40 | −17.50 | −24.05 | −26.13 | −25.63 | −23.63 | −22.64 | −22.23 | −22.21 | −22.25 | −22.57 |
| APD (%) | 75.27 | 68.65 | 56.15 | 47.07 | 43.83 | 37.28 | 33.69 | 33.43 | 33.01 | 32.79 | 46.12 |
| VIIRS/SNPP | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||||
| 410 | 443 | 486 | 551 | 671 | |||||||
| N | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 255 | |||||
| R | −0.26 | −0.27 | −0.2 | −0.09 | 0.04 | 0.70 | |||||
| PD (%) | −57.66 | −37.92 | −24.66 | −7.33 | −23.75 | −30.27 | |||||
| APD (%) | 81.32 | 54.63 | 38.92 | 21.38 | 26.16 | 44.48 | |||||
| GOCI | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||
| 412 | 443 | 490 | 555 | 660 | |||||
| N | 154 | 154 | 154 | 154 | 154 | 770 | |||
| R | 0.11 | 0.4 | 0.65 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.77 | |||
| PD (%) | 64.64 | 23.61 | 1.18 | –18.53 | –6.01 | 12.98 | |||
| APD (%) | 72.72 | 40.69 | 22.31 | 21.17 | 20.04 | 35.38 | |||
| COCTS/HY1C | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||
| 412 | 443 | 490 | 520 | 565 | 670 | ||||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 162 | ||
| R | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.70 | ||
| PD (%) | −53.22 | −45.11 | −29.49 | −16.79 | −23.24 | −49.89 | −36.29 | ||
| APD (%) | 83.98 | 65.71 | 39.47 | 28.40 | 27.15 | 63.33 | 51.34 | ||
| OLCI/S3A | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||
| 400 | 412 | 442 | 490 | 510 | 560 | 620 | 665 | ||
| N | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 176 |
| R | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.57 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.87 |
| PD (%) | −17.16 | −46.82 | −23.71 | −6.52 | −6.42 | −2.94 | 1.61 | −3.23 | −13.15 |
| APD (%) | 59.10 | 58.99 | 34.86 | 16.47 | 12.78 | 8.44 | 13.27 | 19.02 | 27.87 |
| OLCI/S3B | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||
| 400 | 412 | 442 | 490 | 510 | 560 | 620 | 665 | ||
| N | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 232 |
| R | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.83 |
| PD (%) | −8.79 | −13.71 | −4.72 | 2.58 | −2.41 | −1.12 | 2.33 | −3.42 | −3.66 |
| APD (%) | 75.38 | 51.39 | 33.96 | 18.67 | 15.63 | 10.87 | 19.70 | 23.04 | 31.08 |
| SGLI/GCOM-C | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||
| 412 | 443 | 490 | 530 | 565 | 670 | ||||
| N | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 180 | ||
| R | 0 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 0.62 | ||
| PD (%) | −77.45 | −48.88 | −25.50 | −26.07 | −20.84 | −9.19 | −34.65 | ||
| APD (%) | 108.61 | 77.85 | 46.51 | 37.32 | 30.92 | 42.52 | 57.29 | ||
| VIIRS/SNPP | Wavelength (nm) | Total | |||||||
| 410 | 443 | 486 | 551 | 671 | |||||
| N | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 240 | |||
| R | 0.03 | 0.49 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.87 | |||
| PD (%) | −42.20 | −12.46 | −1.34 | 7.52 | −9.71 | −11.64 | |||
| APD (%) | 56.41 | 28.95 | 17.43 | 14.62 | 24.29 | 28.34 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, X. Evaluation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Products from Multiple Ocean Color Missions in Highly Turbid Water (Hangzhou Bay). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214267
Xu Y, He X, Bai Y, Wang D, Zhu Q, Ding X. Evaluation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Products from Multiple Ocean Color Missions in Highly Turbid Water (Hangzhou Bay). Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214267
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yuzhuang, Xianqiang He, Yan Bai, Difeng Wang, Qiankun Zhu, and Xiaosong Ding. 2021. "Evaluation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Products from Multiple Ocean Color Missions in Highly Turbid Water (Hangzhou Bay)" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214267
APA StyleXu, Y., He, X., Bai, Y., Wang, D., Zhu, Q., & Ding, X. (2021). Evaluation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Products from Multiple Ocean Color Missions in Highly Turbid Water (Hangzhou Bay). Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214267