Spatio-Temporal Variations and Driving Forces of Harmful Algal Blooms in Chaohu Lake: A Multi-Source Remote Sensing Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Environmental and Meteorological Data
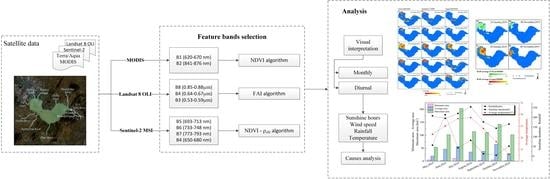
3. Methods
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Extraction Algorithm of HAB
3.2.1. Normalized Vegetation Index (NDVI)
3.2.2. Floating Algae Index (FAI)
3.2.3. Chlorophyll Reflection Peak Intensity Algorithm
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
4.1. Accuracy of HAB Algorithms
4.2. Monthly Variations of HAB
4.3. Diurnal Variation of HAB
5. Discussion
5.1. Driving Forces of HAB
5.2. Advantages of Multi-Source Satellite Remote Sensing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K. Current status of lake ecological environmental quality in China and countermeasures and suggestions. World Environ. 2018, 2, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jeremy, T.W.; Kevin, H.W.; Jason, C.D.; Rubenstein, E.M.; Rober, A.R. Hot and toxic: Tempera-ture regulates microcystin release from cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 786. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Xi, P.; Tang, T.; Chen, L. Influence of the mid-route of south-to-north water transfer project on the water quality of the mid-lower reach of Hanjiang river. J. Saf. Environ. 2009, 9, 82–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.M.; Liu, J.P.; Song, K.S.; Liang, C.; Gao, J. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics and driving factors of blue alga blooms in Chaohu Lake based on Landsat images. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, A.O.; Randy, A.D.; Michae, L.D. The upside-down river: Reservoirs, algal blooms, and tributaries affect temporal and spatial patterns in nitrogen and phosphorus in the Klamath river, USA. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, N.N.; Qi, Y.K.; Meng, S.L.; Chen, J.C. Research progress of eutrophic lake restoration technology. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 35, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.K.; Yu, L.X.; Ou, X.K.; Li, F.R. Relationship between the occurrence frequency of cyanobacteria bloom and meteorological factors in Dianchi Lake. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 534–545. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, Y.M.; Lin, C.; Huang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, A.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Carbon and nitrogen burial in a plateau lake during eutrophication and phytoplankton blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W.; Billen, G.; Swaney, D.; Townsend, A.; Jaworski, N.; Lajtha, K.; Downing, J.A.; Elmgren, R.; Caraco, N.; Jordan, T.; et al. Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N&P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic ocean: Natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 75–139. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N&P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, S.P.; Vicente, E.; Urrego, P.; Pereira-Sandoval, M.; Ruíz-Verdú, A.; Delegido, J.; Soria, J.M.; Moreno, J. Remote sensing of cyanobacterial blooms in a hypertrophic lagoon (Albufera of València, Eastern Iberian Peninsula) using multitemporal Sentinel-2 images. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 698, 134305. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Effects of water level fluctuation on phytoplankton succession in Poyang lake, China–A five-year study. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2016, 16, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.F.; Peng, N.Y.; Zhong, J.Y.; Yang, P.; Zou, B.; Chen, H.; Lou, Q.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W. Effect of metals on microcystin abundance and environmental fate. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sha, H.M.; Li, X.S.; Yang, W.B.; Li, J.L. Preliminary study on MODIS satellite remote sensing monitoring of cyanobacteria in Taihu lake. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Yin, X.; She, B.; Ding, Y.W.; Liang, D.; Huang, L.S.; Zhao, J.L.; Gao, Y.B. Study on the monitoring of blue algae to bloom in Chaohu Lake with multi-source satellite remote sensing data. Infrared Laser Eng. 2019, 48, 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.R. Information Extraction of Cyanobacteria Blooms in Taihu Lake from Domestic Satellite Remote Sensing Images. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Reinart, A.; Kutser, T. Comparison of different satellite sensors in detecting cyanobacterial bloom events in the Baltic sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.Q.; Shang, S.L. Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2010, 115, C04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Pan, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Ren, W.W. Blue algae bloom recognition method based on remote sensing image spectrum analysis. J. Tongji Univ. Nat. Sci. 2011, 39, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, K.; Wilson, J.; Tedesco, L.; Li, L.; Pascual, D.L.; Soyeux, E. Hyperspectral remote sensing of cyanobacteria in turbid productive water using optically active pigments, chlorophyll a, and phycocyanin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4009–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Mitchell, B.G.; Diaz, A. Using MODIS medium-resolution bands to monitor harmful algal blooms. Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2005, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, R.K.; Qin, X.; Mckay, R.M.L.; Miner, J.; Czajkowski, K.; Savino, J. Phycocyanin detection from LANDSAT TM data for mapping cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Erie. Remote Sens Environ. 2004, 89, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z.C.; Jiang, S. The application of CCD data from the HJ-1 satellite in remote sensing monitoring of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake. Admin. Tech. Environ. Monit. 2010, 22, 53–56, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, J.F. Recognition method of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu lake based on remote sensing data. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 2, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.T.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, Y.Z. Remote sensing monitoring method for cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu lake. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 2, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lekki, J.; Deutsch, E.; Sayers, M.; Bosse, K.; Anderson, R.; Tokarsa, R.; Sawtell, R. Determining remote sensing spatial resolution requirements for the monitoring of harmful algal blooms in the Great Lakes. J. Great Lak. Res. 2019, 45, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Tian, L.Q. HJ-1B and Landsat satellite cyanobacteria bloom monitoring capability evaluation –taking Erhai Lake as an example. J. Water Res. Water Eng. 2016, 27, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, X.L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K.N. Analysis of the variation trend of water quality in Chaohu lake from 2012 to 2018 and suggestions on cyanobacteria prevention and control. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, G.P.; Shang, J.C. Spatial and temporal variations of eutrophication in western Chaohu lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kong, F.X. The eutrophication process, spatial distribution, and management strategy of Chaohu lake (1984–2013). J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 791–798. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.B.; Deng, J.C.; Shao, S.G.; Gao, F.; Gao, J.F.; Fan, C.X. Distribution characteristics and toxicity assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.J.; He, W.; Liu, W.X.; Qin, N. The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Kong, F. Spatial and seasonal shifts in bloom-forming cyanobacteria in lake Chaohu: Patterns and driving factors. Phycol. Res. 2016, 64, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Ding, S.W. Characteristics of runoff loss of farmland nutrients under different tillage and fertilization methods in Chaohu lake Basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 26, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. Quantitative Analysis of Influencing Factors of Eutrophication in the West Half of Chaohu Lake. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Anhui, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Y.; Sun, P. Discussion on the Causes of Eutrophication of Chaohu Lake; Anhui Science Association Annual Meeting and Anhui Water Conservancy Forum: Anhui, China, 2009; pp. 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, P.; Abhishek, K.; Deepak, R. A novel cross-satellite based assessment of the spatio-temporal development of a cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.W.; Niu, Z.C.; Jiang, S.; Jin, Y. Satellite image-based remote sensing intensity index and grade division algorithm design for cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu lake. Adm. Techn. Envir. Monit. 2011, 23, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.D.; Sun, J.Y.; Huang, Z.J.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.L. Temporal and spatial distribution of cyanobacterial blooms in Chaohu lake based on MODIS data. Yangtze River 2019, 50, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Tang, J.; Wang, D. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery using the ultraviolet wavelength for highly turbid waters. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Optics 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaire, T.; Tiit, K.; Alo, L.; Margot, S.; Birgot, P.; Tiina, N. First experiences in mapping lake water quality parameters with sentinel-2 MSI imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Zhang, M.Z.; Jiang, K.P.; Zhu, D.H.; Huang, J.X.; Wang, P.X. Sentinel-2 satellite image atmospheric correction method. Acta Opt. Sin. 2018, 38, 322–331. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Yan, M.; Zhang, X.J.; Zou, S.J.; Cao, H.P.; Zhang, L. Study on the method of extracting water information by Gaofen-1 image. Agricult. Technol. 2018, 38, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.H.; Kong, W.J.; Duan, H.T.; Zhang, S.X. Estimation of phycocyanin content during the outbreak of cyanobacteria in Taihu lake based on MODIS images. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.X. High-Precision Calculation Method and Application of Cyanobacterial Bloom Area in Taihu Lake Based on MODIS image. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Oyama, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Matsushita, B.; Matsuzaki, H.; Kamiya, K.; Kobinata, H. Monitoring levels of cyanobacterial blooms using the visual cyanobacteria index (VCI) and floating algae index (FAI). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 38, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prangsma, G.J.; Roozekrans, J.N. Using NOAA AVHRR imagery in assessing water quality parameters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Leppänen, J.M.; Rud, O. Cyanobacterial blooms cause heating of the sea surface. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 101, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Stumpf, R.P.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Michalak, A.M. Using Landsat to extend the historical record of lacustrine phytoplankton blooms: A lake Erie case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W. Monitoring the Vernal Advancement and Retrogradation (Green Wave Effect) of Natural Vegetation. Nasa/gsfct Type Final Rep; 1974; p. E74-10113. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19740004927 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Wynne, T.T.; Stumpf, R.P.; Tomlinson, M.C.; Warner, R.A.; Tester, P.A.; Dyble, J.; Fahnenstiel, G.L. Relating spectral shape to cyanobacterial blooms in the Laurentian great lakes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3665–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W. Landsat-7 SLC-OFF ETM remote sensing data download and its application in cyanobacteria bloom monitoring in Taihu Lake. Adm. Tech. Environ. Monit. 2009, 3, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Binding, C.E.; Greenberg, T.A.; Bukata, R.P. The MERIS Maximum Chlorophyll Index; its merits and limitations for inland water algal bloom monitoring. J. Great Lakes Res. 2013, 39 (Suppl. 1), 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; Carder, K.L.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hardy, R. Remote detection of Trichodesmium blooms in optically complex coastal waters: Examples with MODIS full-spectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, P.; Ahn, Y.H.; Ram, P.S. SeaWiFS sensing of hazardous algal blooms and their underlying mechanisms in shelf-slope waters of the Northwest Pacific during summer. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3248–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Greenberg, T.A.; Mccullough, G.; Watson, S.B.; Page, E. An analysis of satellite-derived chlorophyll and algal bloom indices on lake Winnipeg. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhou, B. Remote sensing of cyanobacterial blooms in inland waters: Present knowledge and future challenges. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1540–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baillarin, S.; Aimé, M.; Cécile, D.; Martimort, P.; Petrucci, B.; Lachérade, S.; Isola, C.; Duca, R.; Spoto, F.; Henry, P.; et al. Sentinel-2 level 1 products and image processing performances. In Proceedings of the ISPRS—International Archives of the Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.F.; Tang, D.L.; Wang, S. Distribution of chlorophyll and harmful algal blooms (HABs): A review on space-based studies in the coastal environments of Chinese marginal seas. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Duan, H.T.; Shi, X.L.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F. Contributions of meteorology to the phenology of cyanobacterial blooms: Implications for future climate change. Water Res. 2011, 46, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, K.; Liu, J.J.; Deng, J.M.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y. Meteorological and hydrological conditions driving the formation and disappearance of black blooms, an ecological disaster phenomena of eutrophication and algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Ma, R.H.; Zhang, M.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Xu, J. Fourteen-year record (2000–2013) of the spatial and temporal dynamics of floating algae blooms in lake Chaohu, observed from time series of modis images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10523–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.Y.; Ma, X.S.; Wu, Y.L. Spatial-temporal variation analysis of Chaohu Lake bloom time series by combined multi-source optical and radar remote sensing. Environ. Monit. Manag. Technol. 2019, 31, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, X.Q. Chaohu lake algae remote sensing monitoring and meteorological factor analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 32, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, K. Remote sensing monitoring and analysis of the effect of surface temperature on Chaohu Lake bloom. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 3323–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Justin, D.C.; Douglas, D.K.; Alex, J. Effectiveness of a fixed-depth sensor deployed from a buoy to estimate water-column cyanobacterial biomass depends on wind speed. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 93, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.X.; Jin, S.J.; Zhou, P. Analysis of distribution characteristics and meteorological conditions of cyanobacteria blooms in Chaohu lake. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 191–193, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Xun, S.P.; He, B.F.; Wu, W.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Zhang, H.Q.; Yang, Y.J. Discussion on meteorological factors of Cyanobacteria outbreak potential forecast. In Proceedings of the Healthy Lakes and Beautiful China-The Third China Lake Forum and the Seventh Hubei Science and Technology Forum, Hubei, China, 24 October 2013; pp. 356–365. [Google Scholar]
















| 2019 | Resolution | Revisit Period | May | June | July | August | September | October | November |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terra/MODIS | 250 m | 1 day | 4 | 13 | 10 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Aqua/MODIS | 250 m | 1 day | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Landsat8 OLI | 30 m | 16 days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sentinel-2A MSI | 20 m | 10 days | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Sentinel-2B MSI | 20 m | 10 days | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | - | - | 8 | 17 | 13 | 20 | 17 | 19 | 18 |
| Class | HAB | Water | Cloud | Total | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 MSI 22 May 2019 | HAB | 78.47 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.92 | Overall Accuracy = (17,105,160/17,189,550) 99.5091% Kappa Coefficient = 0.9002 |
| Water | 20.57 | 99.76 | 0.26 | 97.49 | ||
| Cloud | 0.96 | 0.23 | 99.73 | 1.58 | ||
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ||
| Landsat 8 OLI 19 August 2019 | HAB | 95.93 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 1.62 | Overall Accuracy = (1,907,160/1,909,950) = 99.8539% Kappa Coefficient = 0.9972 |
| Water | 4.07 | 99.99 | 8.07 | 97.51 | ||
| Cloud | 0.00 | 0.00 | 91.40 | 0.77 | ||
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ||
| Terra/MODIS 1 August 2019 | HAB | 93.86 | 0.00 | 18.29 | 2.71 | Overall Accuracy = (6124/6237) 98.1882% Kappa Coefficient = 0.8605 |
| Water | 6.14 | 100.00 | 12.98 | 93.55 | ||
| Cloud | 0.00 | 0.00 | 68.73 | 3.74 | ||
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Extraction Method | Extracted Area (km2) | Omission Area (km2) | Overestimated Area (km2) | Correct Area (km2) | Missing Rate (%) | Over-Extraction Rate (%) | Correct Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 August 2019 | FAI | 16.30 | 0.02 | 3.31 | 12.98 | 0.12% | 25.49% | 99.88% |
| NDVI | 16.98 | 0.52 | 4.49 | 12.48 | 3.97% | 34.57% | 96.03% | |
| Visual interpretation | 13.00 | |||||||
| 4 October 2019 | Sentinel | 0.55 | 3.75 | 13.27 | 3.99% | 27.12% | 96.01% | |
| Visual interpretation | 13.82 | |||||||
| 3 November 2019 | MODIS | 1.84 | 18.88 | 10.21 | 3.92% | 40.16% | 96.08% | |
| Visual interpretation | 47.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Jin, S.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Shang, W. Spatio-Temporal Variations and Driving Forces of Harmful Algal Blooms in Chaohu Lake: A Multi-Source Remote Sensing Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030427
Ma J, Jin S, Li J, He Y, Shang W. Spatio-Temporal Variations and Driving Forces of Harmful Algal Blooms in Chaohu Lake: A Multi-Source Remote Sensing Approach. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(3):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030427
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jieying, Shuanggen Jin, Jian Li, Yang He, and Wei Shang. 2021. "Spatio-Temporal Variations and Driving Forces of Harmful Algal Blooms in Chaohu Lake: A Multi-Source Remote Sensing Approach" Remote Sensing 13, no. 3: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030427
APA StyleMa, J., Jin, S., Li, J., He, Y., & Shang, W. (2021). Spatio-Temporal Variations and Driving Forces of Harmful Algal Blooms in Chaohu Lake: A Multi-Source Remote Sensing Approach. Remote Sensing, 13(3), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030427