Change of CO Concentration Due to the COVID-19 Lockdown in China Observed by Surface and Satellite Observations
Abstract
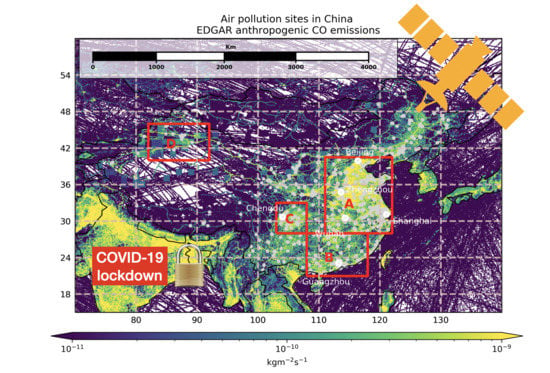
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Method
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. CO Surface Concentration
3.2. CO Column Observed from Satellites
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, B.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Li, B.; Cai, J.; Xu, B.; Yang, Q.; et al. An investigation of transmission control measures during the first 50 days of the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Science 2020, 368, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Nguyen, T.v.T.; Zhong, J.; Liu, J. A COVID-19 descriptive study of life after lockdown in Wuhan, China. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, G.; Abbas, S.; Qamer, F.M.; Wong, M.S.; Rasul, G.; Irteza, S.M.; Shahzad, N. Environmental impacts of shifts in energy, emissions, and urban heat island during the COVID-19 lockdown across Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R. The COVID-19 pandemic: Impacts on cities and major lessons for urban planning, design, and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petetin, H.; Bowdalo, D.; Soret, A.; Guevara, M.; Jorba, O.; Serradell, K.; Pérez García-Pando, C. Meteorology-normalized impact of the COVID-19 lockdown upon NO2 pollution in Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11119–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasemi, A.S.; Hereher, M.E.; Kaplan, G.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F.; Saibi, H. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown upon the air quality and surface urban heat island intensity over the United Arab Emirates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Azad, M.A.K.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Salam, R.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Hoque, M.M.M. How air quality and COVID-19 transmission change under different lockdown scenarios? A case from Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbulat, B.; Apte, J.S.; Millet, D.B.; Robinson, A.L.; Wells, K.C.; Presto, A.A.; Marshall, J.D. Changes in criteria air pollution levels in the US before, during, and after Covid-19 stay-at-home orders: Evidence from regulatory monitors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Deng, Z.; Lei, R.; Davis, S.J.; Feng, S.; Zheng, B.; Cui, D.; Dou, X.; Zhu, B.; et al. Near-real-time monitoring of global CO2 emissions reveals the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Geng, G.; Ciais, P.; Davis, S.J.; Martin, R.V.; Meng, J.; Wu, N.; Chevallier, F.; Broquet, G.; Boersma, F.; et al. Satellite-based estimates of decline and rebound in China’s CO2 emissions during COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, M.; Compernolle, S.; Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.F.; van Gent, J.; Eskes, H.; Levelt, P.F.; van der, A.R.; Veefkind, J.P.; Vlietinck, J.; et al. Impact of Coronavirus Outbreak on NO2 Pollution Assessed Using TROPOMI and OMI Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Ju, W.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ding, A. NOx Emission Changes Over China During the COVID-19 Epidemic Inferred From Surface NO2 Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschi, M.; Largo, A. Reactivity of gaseous protonated ozone: A computational investigation on the carbon monoxide oxidation reaction. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 228, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, P.C.; Masarie, K.A.; Lang, P.M. Distributions and recent changes of carbon monoxide in the lower troposphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 19015–19033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Bond, T.; D’Angiola, A.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Huang, G.; Guizzardi, D.; Koffi, E.; Muntean, M.; Schieberle, C.; Friedrich, R.; Janssens-Maenhout, G. High resolution temporal profiles in the Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T. Impact of city lockdown on the air quality of COVID-19-hit of Wuhan city. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Brasseur, G.P. The Response in Air Quality to the Reduction of Chinese Economic Activities During the COVID-19 Outbreak. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.L.; Kondo, Y.; Oshima, N.; Matsui, H.; Kita, K.; Sahu, L.K.; Kato, S.; Kajii, Y.; Takami, A.; Miyakawa, T. Seasonal variations of the transport of black carbon and carbon monoxide from the Asian continent to the western Pacific in the boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, C.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Li, Z.; Elnashar, A.; Allam, M.; de Leeuw, G. The Impact of the Control Measures during the COVID-19 Outbreak on Air Pollution in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Bowman, K.; Sekiya, T.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, X.; Eskes, H.; Ru, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shindell, D. Air Quality Response in China Linked to the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Lockdown. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, J.; aan de Brugh, J.; Scheepmaker, R.; Borsdorff, T.; Hu, H.; Houweling, S.; Butz, A.; Aben, I.; Hasekamp, O. Carbon monoxide total column retrievals from TROPOMI shortwave infrared measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4955–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurtmans, D.; Coheur, P.F.; Wespes, C.; Clarisse, L.; Scharf, O.; Clerbaux, C.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; George, M.; Turquety, S. FORLI radiative transfer and retrieval code for IASI. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2012, 113, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerzenmacher, T.; Dils, B.; Kumps, N.; Blumenstock, T.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F.; Demoulin, P.; García, O.; George, M.; Griffith, D.W.T.; et al. Validation of IASI FORLI carbon monoxide retrievals using FTIR data from NDACC. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.A. The New VIIRS 375m active fire detection data product: Algorithm description and initial assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; De Luccia, F.J.; Xiong, X.; Wolfe, R.; Weng, F. Early On-Orbit Performance of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Onboard the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2014, 52, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T. Long-term historical trends in air pollutant emissions in Asia: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 3. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12761–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.W.; Heil, A.; Andreae, M.O.; Benedetti, A.; Chubarova, N.; Jones, L.; Morcrette, J.J.; Razinger, M.; Schultz, M.G.; Suttie, M.; et al. Biomass burning emissions estimated with a global fire assimilation system based on observed fire radiative power. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Orlando, J.J.; Soja, A.J. The Fire INventory from NCAR (FINN): A high resolution global model to estimate the emissions from open burning. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Gao, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, D.; Qi, X.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Nie, W.; et al. Enhanced secondary pollution offset reduction of primary emissions during COVID-19 lockdown in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yung, Y.L.; Li, G.; Seinfeld, J.H. Unexpected air pollution with marked emission reductions during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Science 2020, 369, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Arellano, A.F., Jr. Interannual variability in global biomass burning emissions from 1997 to 2004. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3423–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, B.; Chevallier, F.; Ciais, P.; Yin, Y.; Deeter, M.N.; Worden, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. Rapid decline in carbon monoxide emissions and export from East Asia between years 2005 and 2016. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.I.; Woo, J.H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inness, A.; Blechschmidt, A.M.; Bouarar, I.; Chabrillat, S.; Crepulja, M.; Engelen, R.J.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; Gaudel, A.; Hendrick, F.; et al. Data assimilation of satellite-retrieved ozone, carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide with ECMWF’s Composition-IFS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5275–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| BCNY | ACNY | 3/11–4/10 | 4/11–5/10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China (1375 sites) | 1.1 ± 24.3% | −18.7 ± 22.2% | −6.2 ± 20.2% | −4.8 ± 23.6% |
| Beijing (12 sites) | −12.5 ± 5.6% | −8.0 ± 11.3% | −15.6 ± 14.4% | 13.1 ± 5.2% |
| Shanghai (10 sites) | 8.9 ± 2.6% | −20.3 ± 3.1% | −25.4 ± 2.1% | 7.1 ± 3.1% |
| Wuhan (11 sites) | −20.0 ± 2.4% | 0.4 ± 2.7% | −6.5 ± 4.8% | −23.1 ± 2.7% |
| Chengdu (10 sites) | 1.1 ± 2.8% | −27.0 ± 3.4% | −16.2 ± 5.1% | −15.8 ± 6.1% |
| Zhengzhou (9 sites) | −3.1 ± 5.3% | −25.0 ± 6.0% | −12.4 ± 4.1% | −17.2 ± 2.1% |
| Guangzhou (12 sites) | −13.7 ± 1.9% | −25.9 ± 2.3% | −6.9 ± 4.0% | −10.5 ± 3.7% |
| BCNY | ACNY | 3/11–4/10 | 4/11–5/10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Region A | −5.9% | −25.1% | −9.4% | −7.0% |
| Region B | −16.7% | −23.1% | −7.3% | −16.4% | |
| Region C | −2.4% | −15.8% | −7.0% | −2.6% | |
| Region D | −1.7% | −18.2% | −19.8% | −14.0% | |
| TROPOMI | Region A | −1.3% | −10.5% | 0.6% | 5.5% |
| Region B | 0.2% | 8.8% | 11.7% | −6.4% | |
| Region C | 7.0% | −1.9% | 3.0% | 3.7% | |
| Region D | 0.1% | −4.6% | 1.8% | 3.9% | |
| IASI | Region A | 3.5% | −13.3% | 2.8% | 4.1% |
| Region B | −2.9% | 36.7% | 20.6% | −3.2% | |
| Region C | 9.4% | −1.8% | 16.6% | 3.8% | |
| Region D | −0.3% | −3.6% | 0.8% | 0.6% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Jiang, J.; Langerock, B.; Dils, B.; Sha, M.K.; De Mazière, M. Change of CO Concentration Due to the COVID-19 Lockdown in China Observed by Surface and Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061129
Zhou M, Jiang J, Langerock B, Dils B, Sha MK, De Mazière M. Change of CO Concentration Due to the COVID-19 Lockdown in China Observed by Surface and Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061129
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Minqiang, Jingyi Jiang, Bavo Langerock, Bart Dils, Mahesh Kumar Sha, and Martine De Mazière. 2021. "Change of CO Concentration Due to the COVID-19 Lockdown in China Observed by Surface and Satellite Observations" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061129
APA StyleZhou, M., Jiang, J., Langerock, B., Dils, B., Sha, M. K., & De Mazière, M. (2021). Change of CO Concentration Due to the COVID-19 Lockdown in China Observed by Surface and Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061129