Effect of Reduced Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality in Lake Vembanad, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Observations
2.3. In Situ Observations
2.4. Comparison of Remote Sensing and In Situ Observations
2.5. Data Analyses
2.6. Ancillary Data
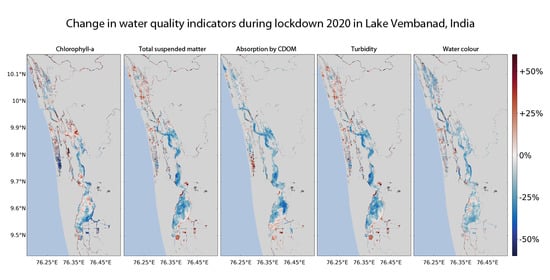
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beiras, R. Marine Pollution: Sources, Fate and Effects of Pollutant in Coastal Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- UN Environment. Global Manual on Ocean Statistics. Towards a Definition of Indicator Methodologies; UN Environment: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Häder, D.P.; Banaszak, A.T.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic pollution of aquatic ecosystems: Emerging problems with global implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Dick Vethaak, A.; Lavorante, B.R.B.O.; Lundebye, A.K.; Guilhermino, L. Marine microplastic debris: An emerging issue for food security, food safety and human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, N.N.; Balchand, A.N.; Menon, N.R. Hydrobiology of the Cochin backwater system—A review. Hydrobiologia 2000, 430, 149–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WISA. Conservation and Wise Use of Vemabanad-Kol: An Integrated Management Planning Framework; Wetlands International—South Asia: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran, K.K.; Nair, K.K.C.; Achuthankutty, C.T.; Nair, S.; Wafar, M.V.W.; Ramesh, R.; Saramma, U.P.; Rosamma, S.; Haridas, P.; Jayalakshmy, K.V.; et al. Ecosystem Modelling of Cochin Backwaters 2002–2007; Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2007.
- Ramasamy, E.V.; Jayasooryan, K.K.; Chandran, M.S.S.; Mohan, M. Total and methyl mercury in the water, sediment, and fishes of Vembanad, a tropical backwater system in India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sruthy, S.; Ramasamy, E.V. Microplastic pollution in Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: The first report of microplastics in lake and estuarine sediments in India. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Giridhar, R.; Anas, A.; Loka Bharathi, P.A.; Nair, S. Heavy metal pollution exerts reduction/adaptation in the diversity and enzyme expression profile of heterotrophic bacteria in Cochin estuary, India. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeba, V.A.; Abdulaziz, A.; Gireeshkumar, T.R.; Ram, A.; Rakesh, P.S.; Jasmin, C.; Parameswaran, P.S. Role of heavy metals in structuring the microbial community associated with particulate matter in a tropical estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhi, K.S. Vembanad Route to Track CRZ Violations in Kerala. Available online: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/vembanad-route-to-track-crz-violations-in-state/article29493876.ece (accessed on 19 February 2021).
- Menon, N.; George, G.; Ranith, R.; Sajin, V.; Murali, S.; Abdulaziz, A.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Sathyendranath, S. Citizen science tools reveal changes in estuarine water quality following demolition of buildings. Remote Sens. 2021. (Submitted). [Google Scholar]
- Vincy, M.V.; Rajan, B.; Pradeep Kumar, A.P. Water Quality Assessment of a Tropical Wetland Ecosystem with Special Reference to Backwater Tourism, Kerala, South India. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Deng, Z.; Lei, R.; Davis, S.J.; Feng, S.; Zheng, B.; Cui, D.; Dou, X.; Zhu, B.; et al. Near-real-time monitoring of global CO2 emissions reveals the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, M.; Zheng, M. Effects of COVID-19 lockdown on global air quality and health. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 755, 142533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hama, S.; Omidvarborna, H.; Sharma, A.; Sahani, J.; Abhijith, K.V.; Debele, S.E.; Zavala-Reyes, J.C.; Barwise, Y.; Tiwari, A. Temporary reduction in fine particulate matter due to ‘anthropogenic emissions switch-off’ during COVID-19 lockdown in Indian cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Wang, L.; Mazur, K.; Carchia, M.; Depalma, G.; Azimi, R.; Mravca, S.; Neitzel, R.L. Impacts of COVID-19-related social distancing measures on personal environmental sound exposures. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A.; Sanchez-Alcalde, L. Indirect effects of COVID-19 on the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, A.P.; Masago, Y.; Hijioka, Y. COVID-19 and surface water quality: Improved lake water quality during the lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.R.; Kumar, A.; Muduli, P.R.; Equeenuddin, S.M.; Rastogi, G.; Acharyya, T.; Swain, D. Decline in Phytoplankton Biomass along Indian Coastal Waters due to COVID-19 Lockdown. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adyel, T.M. Accumulation of plastic waste during COVID-19. Science 2020, 369, 1314–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Owusu, P.A. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on waste management. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avtar, R.; Kumar, P.; Supe, H.; Jie, D.; Sahu, N.; Mishra, B.K.; Yunus, A.P. Did the COVID-19 lockdown-induced hydrological residence time intensify the primary productivity in lakes? Observational results based on satellite remote sensing. Water 2020, 12, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaziz, A.; Krishna, K.; Syamkumar, V.; George, G.; Menon, N.; Kulk, G.; Jasmin, C.; Ciambelli, A.; Hridya, K.V.; Tharakan, B.; et al. Dyanmics of Vibrio cholera in a typical tropical lake and estuarine system: Potential of remote sensing for risk mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Menon, N.N.; Abdulaziz, A.; Brewin, R.J.; Pranav, P.; Achanveetil, G.; Mini, K.G.; Kuriakose, S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. Citizen scientists contribute to real-time monitoring of lakewater quality using 3D printed mini Secchi disks. Front. Water 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, P.T.; Shynamma, C.S.; Balchand, A.N.; Kurup, P.G.; Nambisan, P.N.K. Distribution and seasonal variation of temperature and salinity in Cochin backwaters. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 1982, 11, 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of metre-scale optical satellite data for inland and coastal water applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Ritchie-2003-RS tech to assess water quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernand, M.R.; van der Woerd, H.J. Spectral analysis of the Forel-Ule ocean colour comparator scale. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. 2010, 5, 10014s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Brewin, T.G.; Phillips, J.; Rose, S.; Abdulaziz, A.; Wimmer, W.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. A printable device for measuring clarity and colour in lake and nearshore waters. Sensors 2019, 19, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Kuring, N.; Werdell, P.J. Ocean color measurements with the Operational Land Imager on Landsat-8: Implementation and evaluation in SeaDAS. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. ACOLITE For Sentinel-2: Aquatic Applications of MSI imagery. In Proceedings of the 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; p. SP-740. [Google Scholar]
- van der Woerd, H.J.; Wernand, M.R. Hue-angle product for low to medium spatial resolution optical satellite sensors. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhuyan, M.; Jayaram, C.; Menon, N.N.; Joseph, K.A. Satellite-Based Study of Seasonal Variability in Water Quality Parameters in a Tropical Estuary along the Southwest Coast of India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; O’Brien, M.; Siegel, D.; Toole, D.; Menzies, D.; Smith, R.; Mueller, J.; Mitchell, B.; Kahru, M.; et al. SeaWiFS Postlaunch Calibration and Validation Analyses, Part 3. In NASA Tech. Memo. 2000-206892; Hooker, S., Firestone, E., Eds.; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2000; Volume 11, p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.N.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Estimation of Colored Dissolved Organic Matter from Landsat-8 Imagery for Complex Inland Water: Case Study of Lake Huron. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, L. Remote estimation of colored dissolved organic matter and chlorophyll-a in Lake Huron using Sentinel-2 measurements. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Monitoring dissolved organic carbon by combining Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites: Case study in Saginaw River estuary, Lake Huron. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Neukermans, G. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of turbidity in coastal waters. In Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, and Large Water Regions 2009; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7473, p. 74730H. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernand, M.R.; Hommersom, A.; Van Der Woerd, H.J. MERIS-based ocean colour classification with the discrete Forel-Ule scale. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ganguly, S.; Dungan, J.L.; Wang, W.; Nemani, R.R. Sentinel-2 MSI radiometric characterization and cross-calibration with Landsat-8 OLI. Adv. Remote Sens. 2017, 6, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vantrepotte, V.; Mélin, F. Temporal variability of 10-year global SeaWiFS time-series of phytoplankton chlorophyll a concentration. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacCallum, S.N.; Merchant, C.J. Surface water temperature observations of large lakes by optimal estimation. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrea, L.; Embury, O. Datasets related to in-land water for limnology and remote sensing applications: Distance-to-land, distance-to-water, water-body identifier and lake-centre co-ordinates. Geosci. Data J. 2015, 2, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, N.C.; Venot, J.P. Drivers of change in fragile environments: Challenges to governance in Indian wetlands. Nat. Resour. Forum 2009, 33, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Tanaka, M. Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: A review and synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 624–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Establishing a Framework for the Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, J.; Prabhakar, R.N. Water Quality Activities in Central Water Commission; Ministry of Jal Shakti: New Delhi, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Davies-Colley, R.J.; Smith, D.G. Turbidity, suspended sediment and water clarity: A reviews. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1085–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global water pollution and human health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.A.; Salman, M.S.; Yunus, A.P. COVID-19 and its impact on environment: Improved pollution levels during the lockdown period—A case from Ahmedabad, India. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Aggarwal, S.P.; Chauhan, P. Changes in turbidity along Ganga River using Sentinel-2 satellite data during lockdown associated with COVID-19. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 1175–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priju, C.P.; Narayana, A.C. Heavy and trace metals in Vembanad Lake sediments. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2007, 1, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Hooghly Cochin Shipyard Limited. 3rd Annual Report 2019-20; Hooghly Cochin Shipyard Limited: Cochin, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vinita, J.; Revichandran, C.; Manoj, N.T. Suspended sediment dynamics in Cochin estuary, West Coast, India. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 21, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balchand, A.N.; Rasheed, K. Assessment of Short Term Environmental Impacts on Dredging in a Tropical Estuary; Terra Aqua: Voorburg, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sooria, P.M.; Menon, N.N.; Ranith, R.; Nair, M.; Anjusha, A.; Shivaprasad, A.; Joseph, K.A.; Saramma, A.V. Occurrence of enhanced herbivory in the microbial food web of a tropical estuary during southwest monsoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 246, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppley, R.W. Temperature and phytoplankton growth in the sea. Fish. Bull. 1972, 70, 1063–1085. [Google Scholar]
- CRZ. The Coastal Regulation Zone Notifications, The Gazette of India, S.O. 114; The Gazette of India: New Delhi, India, 1991; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Abdulaziz, A.; Menon, N.; George, G.; Evers-King, H.; Kulk, G.; Colwell, R.; Jutla, A.; Platt, T. Building Capacity and Resilience Against Diseases Transmitted via Water Under Climate Perturbations and Extreme Weathers Stress. In Space Capacity Building in the XXI Century; Ferretti, S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]








| Band | Sentinel-2a | Sentinel-2b | Landsat-8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | 443 | 442 | 443 |
| Green | 560 | 559 | 561 |
| Red | 665 | 665 | 655 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulk, G.; George, G.; Abdulaziz, A.; Menon, N.; Theenathayalan, V.; Jayaram, C.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Sathyendranath, S. Effect of Reduced Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality in Lake Vembanad, India. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091631
Kulk G, George G, Abdulaziz A, Menon N, Theenathayalan V, Jayaram C, Brewin RJW, Sathyendranath S. Effect of Reduced Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality in Lake Vembanad, India. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091631
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulk, Gemma, Grinson George, Anas Abdulaziz, Nandini Menon, Varunan Theenathayalan, Chiranjivi Jayaram, Robert J. W. Brewin, and Shubha Sathyendranath. 2021. "Effect of Reduced Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality in Lake Vembanad, India" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091631
APA StyleKulk, G., George, G., Abdulaziz, A., Menon, N., Theenathayalan, V., Jayaram, C., Brewin, R. J. W., & Sathyendranath, S. (2021). Effect of Reduced Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality in Lake Vembanad, India. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091631