A Coherent Integration Segment Searching Based GRT-GRFT Hybrid Integration Method for Arbitrary Fluctuating Target
Abstract
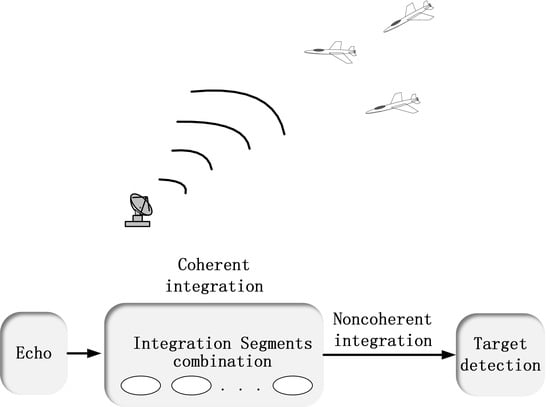
:1. Introduction
2. Signal Model and Problem Analysis
3. Hybrid Integration Detection Algorithm
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Individual Target Integration Results
4.2. Processing of the Measured Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Pulse compressed signal. | |
| Slow-time sampling point number. | |
| in-pulse fast-time sampling point number. | |
| Speed of light. | |
| Signal bandwidth. | |
| Range resolution. | |
| Wavelength. | |
| Carrier frequency. | |
| Radial range of the target. | |
| Complex backscattering coefficient. | |
| Noise. | |
| Correlation function. | |
| Radar pulse repetition cycle. | |
| Echo decorrelation time. | |
| Phase compensation function. | |
| Totally integrated pulses. | |
| Coherent integration segments. | |
| Number of pulses in each coherent integration segment. | |
| Coherent integration result in coherent integration segment. | |
| Hybrid integration result. | |
| The minimum coherent time. | |
| Minimum number in coherent integration segment. | |
| Detection threshold. | |
| Covariance matrix of the observation matrix. | |
| Covariance matrix of the target echo signal. | |
| Integration matrix. | |
| Matrix of echo signal. | |
| Coherent integration result via level-i data. | |
| Hybrid integration result via level-i data. | |
| Hermitian transpose operation. | |
| Round-up-to-integer operation. |
Appendix A
References
- Xu, J.; Peng, Y.; Xia, X.; Farina, A. Focus-before-detection radar signal processing: Part I—Challenges and methods. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2017, 32, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, S. Efficient angular chirp-Fourier transform and its application to high-speed target detection. Signal Process. 2019, 164, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y. Radar highspeed small target detection based on keystone transform and linear canonical transform. Digit. Signal Process. 2018, 82, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Analysing and compensating the effects of range and Doppler frequency migrations in linear frequency modulation pulse compression radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2010, 5, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Baker, C.J.; Pooni, S. Range and Doppler cell migration in wideband automotive radar. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 5527–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Lin, C.; Liu, N. Low-observable maneuvering target detection based on Radon-advanced discrete chirp Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 0735–0738. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, M.A.; Scheer, J.A.; Holm, W.A. Principles of Modern Radar: Basic Principles; Scitech: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 259–261. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Demaio, A.; Piezzo, M. Performance prediction of the incoherent radar detector for correlated generalized swerling-chi fluctuating targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 49, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerling, P. Probability of detection for fluctuating targets. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 1960, 6, 269–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerling, P. Radar probability of detection for some additional fluctuating target cases. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1997, 33, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, A.D.; Farina, A.; Foglia, G. Target fluctuation models and their application to radar performance prediction. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2004, 151, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Maio, A.D.; Carotenuto, V. Performance prediction of the incoherent detector for a weibull fluctuating target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W. A hybrid integration method for moving target detection with GNSS-based passive radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, G. Motion parameter estimation of high-speed manoeuvering targets based on hybrid integration and synchrosqueezing transform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 852–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.D.; Evans, E.D.; Wilson, S.L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. I. System concept. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.D.; Evans, E.D.; Wilson, S.L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. II. Detection statistics. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.D.; Evans, E.D.; Wilson, S.L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. III. Detection performance with binary integration. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqiseh, A.; Nayebi, M.M. Combinational Hough transform for surveillance radar target detection in a 3-D data map. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, L.R.; Spak, J.; Lamanna, P. A multi-dimensional Hough transform-based track-before-detect technique for detecting weak targets in strong clutter backgrounds. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 3062–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, D.; Venturino, L.; Lops, M.; Ricci, G. Space-time adaptive algorithms for track-before-detect in clutter environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference, Bordeaux, France, 12–16 October 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Yi, W.; Cui, G.; Kong, L.; Yang, X. Track-before-detect strategies for range distribution target detection in compound-Gaussian clutter. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, D.; Venturino, L.; Lops, M.; Ricci, G. Track-before-detect strategies for step radars. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Morelande, M.R.; Kong, L.; Yang, J. An efficient multi-frame track-before-detect algorithm for multi-target tracking. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2013, 7, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Morelande, M.R.; Kong, L.; Yang, J. A computationally efficient particle filter for multi-target tracking using an independence approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, T.; Long, T.; Yuan, H. Dim target detection based on keystone transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 9–12 May 2005; pp. 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Pignol, F.; Colone, F.; Martelli, T. Lagrange-polynomial-interpolation-based keystone transform for a passive radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1151–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.; Long, T.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Farina, A. Adaptive Radon-Fourier transform for weak radar target detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1641–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Zhong, T.; Tao, H.; Xie, J.; Su, J. Improved axis rotation MTD algorithm and its analysis. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 30, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Zhu, W.; He, X.; Liu, Q. Radar high-speed target detection based on the scaled inverse Fourier transform. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Liu, H.; Liao, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Radar high-speed target detection based on the frequency-domain Deramp-Keystone transform. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Xing, M.; Wang, G.; Bao, Z. High-speed multi-target detection with narrowband radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2010, 4, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, G.; Yi, W.; Kong, L. Maneuvering target detection based on keystone transform and Lv’s distribution. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Cao, Z.; Min, R.; Pi, Y. Radar maneuvering target detection based on two steps scaling and fractional Fourier transform. Signal Process. 2018, 155, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Tao, H.; Xie, J.; Su, J.; Li, W. Long-time coherent integration detection of weak manoeuvring target via integration algorithm, improved axis rotation discrete chirp-Fourier transform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, F.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, S. Coherent integration detection method for maneuvering target based on dynamic programming. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 73, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tao, H.; Chen, W.; Song, D. Maneuvering target detection based on subspace subaperture joint coherent integration. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xia, X.; Peng, S.; Yu, J.; Qian, L. Radar maneuvering target motion estimation based on generalized Radon-Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 6190–6201. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhou, J. A fast algorithm of generalized Radon-Fourier transform for weak maneuvering target detection. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2016, 2016, 4315616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Cui, G.; Yi, W.; Kong, L. Radar maneuvering target detection and motion parameter estimation based on TRT-SGRFT. Signal Process. 2017, 133, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, J.; Jiu, B.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y. Deep neural network-aided coherent integration method for maneuvering target detection. Signal Process. 2021, 182, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achim, A.; Buxton, B.; Tzagkarakis, G.; Tsakalides, P. Compressive sensing for ultrasound RF echoes using a-stable distributions. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 4304–4307. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Michailovich, O.V. Derivative compressive sampling with application to phase unwrapping. In Proceedings of the 2009 17th European Signal Processing Conference, Glasgow, UK, 24–28 August 2009; pp. 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, M.; Cheung, N.M.; Quek, T.Q. Compressed sensing of diffusion fields under heat equation constraint. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 4271–4274. [Google Scholar]
- Pastina, D.; Santi, F.; Pieralice, F.; Bucciarelli, M.; Ma, H.; Tzagkas, D.; Antoniou, M.; Cherniakov, M. Maritime moving target long time integration for GNSS-based passive bistatic radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 3060–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; He, Z. Detection of weak target for MIMO radar based on Hough transform. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2009, 20, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Qian, L.; Xia, X.; Long, T. Hybrid integration for highly maneuvering radar target detection based on generalized Radon-Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; You, P.; Qian, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Long, T. A subspace hybrid integration method for high-speed and maneuvering target detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qian, L.; Ding, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, W.; You, P.; Long, T. Radar detection of moderately fluctuating target based on optimal hybrid integration detector. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 55, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunk, G.V. Detection results for scanning radars employing feedback integration. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1970, 1, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A. Fundamentals of Matrix Computations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rencher, A.C. Methods of Multivariate Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P. Some theorems on quadratic forms applied in the study of analysis of variance problems, I. Effect of inequality of variance in the one-way classification. Ann. Math. Stat. 1954, 25, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency () | 3 GHz |
| Sampling frequency () | 20 MHz |
| Bandwidth () | 10 MHz |
| Pulse width () | 51 μs |
| PRT () | 1 ms |
| Pulse number () | 1024 |
| Integration time () | 1.024 s |
| The SNR of the individual pulses | −20 dB |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Initial range () | 800 km | 800 km |
| Initial velocity () | 60 m/s | 3400 m/s |
| Acceleration | 0 m/s2 | −10 m/s2 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency () | 77 GHz |
| Sampling frequency () | 10 MHz |
| Bandwidth () | 800 MHz |
| Modulation time () | 320 μs |
| Integration time () | 2.4576 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Liu, N.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. A Coherent Integration Segment Searching Based GRT-GRFT Hybrid Integration Method for Arbitrary Fluctuating Target. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112695
Zhang Z, Liu N, Hou Y, Zhang S, Zhang L. A Coherent Integration Segment Searching Based GRT-GRFT Hybrid Integration Method for Arbitrary Fluctuating Target. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112695
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenghe, Nan Liu, Yongning Hou, Shiyu Zhang, and Linrang Zhang. 2022. "A Coherent Integration Segment Searching Based GRT-GRFT Hybrid Integration Method for Arbitrary Fluctuating Target" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112695
APA StyleZhang, Z., Liu, N., Hou, Y., Zhang, S., & Zhang, L. (2022). A Coherent Integration Segment Searching Based GRT-GRFT Hybrid Integration Method for Arbitrary Fluctuating Target. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112695