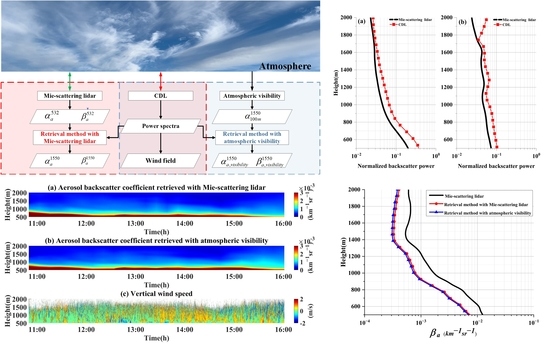
Two Practical Methods to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instruments and Datasets
2.1. Coherent Wind Lidar
2.2. Mie-Scattering Lidar
2.3. AERONET Datasets
2.4. Atmospheric Visibility Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Retrieving Aerosol Optical Properties with Mie-Scattering Lidar
3.2. Retrieving Aerosol Optical Properties with Atmospheric Visibility
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experiment Information
4.2. Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Properties with Mie-Scattering Lidar
4.3. The Retrieval Method with Atmospheric Visibility
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 571–892. ISBN 978-1-107-66182-0. [Google Scholar]
- Milonni, D.P.W. Lidar. Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere, in the Springer Series in Optical Sciences, Vol. 102, Edited by Claus Weitkamp. Contemp. Phys. 2009, 50, 601–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wandinger, U.; Linne, H.; Bosenberg, J. Turbulent aerosol fluxes determined from combined observations with doppler wind and raman aerosol lidar. In Proceedings of the 22nd Internation Laser Radar Conference, Matera, Italy, 12–16 July 2004; Volume 561, p. 743. [Google Scholar]
- Bou Karam, D.; Flamant, C.; Knippertz, P.; Reitebuch, O.; Pelon, J.; Chong, M.; Dabas, A. Dust Emissions over the Sahel Associated with the West African Monsoon Intertropical Discontinuity Region: A Representative Case-Study. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumann, U.; Weinzierl, B.; Reitebuch, O.; Schlager, H.; Minikin, A.; Forster, C.; Baumann, R.; Sailer, T.; Graf, K.; Mannstein, H.; et al. Airborne Observations of the Eyjafjalla Volcano Ash Cloud over Europe during Air Space Closure in April and May 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2245–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinzierl, B.; Sauer, D.; Minikin, A.; Reitebuch, O.; Dahlkötter, F.; Mayer, B.; Emde, C.; Tegen, I.; Gasteiger, J.; Petzold, A.; et al. On the Visibility of Airborne Volcanic Ash and Mineral Dust from the Pilot’s Perspective in Flight. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2012, 45, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bufton, J.L.; Hoge, F.E.; Swift, R.N. Airborne Measurements of Laser Backscatter from the Ocean Surface. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, R.T.; Tratt, D.M. Airborne CO2 Coherent Lidar for Measurements of Atmospheric Aerosol and Cloud Backscatter. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J. Lidar Inversion with Variable Backscatter/Extinction Ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böckmann, C.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; Amiridis, V.; Boselli, A.; Delaval, A.; Tomasi, F.D.; Frioud, M.; Grigorov, I.V.; et al. Aerosol Lidar Intercomparison in the Framework of the EARLINET Project. 2. Aerosol Backscatter Algorithms. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.W.; Gatt, P.; Rees, D.; Huffaker, R.M. Wind Lidar. In Laser Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 487–740. ISBN 0-429-13574-2. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, R.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Žeromskis, E.; Althausen, D.; Wehner, B. Lidar Observations of the Vertical Aerosol Flux in the Planetary Boundary Layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouza, F.; Reitebuch, O.; Groß, S.; Rahm, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Toledano, C.; Weinzierl, B. Retrieval of Aerosol Backscatter and Extinction from Airborne Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2909–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, K.; Wu, S.; Song, X.; Li, R.; Yin, J.; Wang, X. Calibration and Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Properties Measured with Coherent Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, P. Portable Coherent Doppler Light Detection and Ranging for Boundary-Layer Wind Sensing. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, P.; Chen, B. Experimental Determination of Raman Lidar Geometric Form Factor Combining Raman and Elastic Return. Opt. Commun. 2014, 332, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Guo, P. Aerosol Characteristics Inversion Based on the Improved Lidar Ratio Profile with the Ground-Based Rotational Raman–Mie Lidar. Opt. Commun. 2018, 416, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.A.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Byrne, D.M. A Method for Inferring Total Ozone Content from the Spectral Variation of Total Optical Depth Obtained with a Solar Radiometer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.; Reid, J.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’neill, N.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength Dependence of the Optical Depth of Biomass Burning, Urban, and Desert Dust Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebuloni, R. Empirical Relationships between Extinction Coefficient and Visibility in Fog. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Central Meteorological Observatory. Available online: http://www.nmc.cn/publish/sea/seaplatform1.html (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Löhle, F. Uber Die Lichtzerstreuung Im Nebel. Phys. Zeits 1944, 45, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, W.E.K. Vision through the Atmosphere. In Vision Through the Atmosphere; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2019; ISBN 1-4875-8614-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of Atmospheric Lidar Observations: Some Comments. Appl Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Mattis, I.; Tesche, M.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D.; Pisani, G. Aerosol-Type-Dependent Lidar Ratios Observed with Raman Lidar. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Smoothed Accumulated Spectra Based WDSWF Method for Real-Time Wind Vector Estimation of Pulsed Coherent Doppler Lidar. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earth Data. Available online: https://earthdata.nasa.gov/earth-observation-data/near-real-time/hazards-and-disasters/dust-storms (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Grubbs, F.E. Procedures for Detecting Outlying Observations in Samples. Technometrics 1969, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefansky, W. Rejecting Outliers in Factorial Designs. Technometrics 1972, 14, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Qualification | Specification |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (nm) | 1550 |
| Pulse energy (μJ) | 50 |
| Pulse width (ns) | 400 (100, 200, 400, adjustable) |
| Pulse repetition rate (kHz) | 10 |
| The linewidth of laser (kHz) | 15 |
| Range resolution (m) | 60 |
| Measurement range (m) | 100 to boundary layer 1 |
| Temporal resolution (s) | 1 |
| Telescope aperture (mm) | 50 |
| Focal length | ∞ |
| Beam diameter (mm) | 40 |
| Sampling frequency (GHz) | 1 |
| Detection mode | Stare mode |
| Detector mode | Balanced detector |
| Bandwidth (MHz) | 200 |
| Qualification | Specification |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (nm) | 532 |
| Pulse energy (mJ) | 180 |
| Pulse repetition rate (Hz) | 20 |
| Telescope | Newtonian |
| Range resolution (m) | 2.5 |
| Measurement range (m) | 500 to max 10,000 |
| Temporal resolution (s) | 60 |
| Telescope diameter (mm) | 400 |
| Field of view (mrad) | 0.9 |
| Mode | Coaxial |
| Half-width of detection channel (nm) | 1 |
| Retrieval Method | Date | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| With Mie-scattering aerosol lidar | September 1st to December 14th | Retrieval and validation |
| With atmospheric visibility | September 1st to December 14th | Calibration of reliable |
| December 16th to December 31st | Retrieval and validation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, W.; Guo, P.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Lin, R.; Chen, S.; Chen, H. Two Practical Methods to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112700
Zhang Y, Zheng Y, Tan W, Guo P, Xu Q, Chen S, Lin R, Chen S, Chen H. Two Practical Methods to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Lidar. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112700
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yinchao, Yize Zheng, Wangshu Tan, Pan Guo, Qingyue Xu, Su Chen, Ruiqi Lin, Siying Chen, and He Chen. 2022. "Two Practical Methods to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Lidar" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112700
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zheng, Y., Tan, W., Guo, P., Xu, Q., Chen, S., Lin, R., Chen, S., & Chen, H. (2022). Two Practical Methods to Retrieve Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Lidar. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112700