Land Surface Snow Phenology Based on an Improved Downscaling Method in the Southern Gansu Plateau, China
Abstract
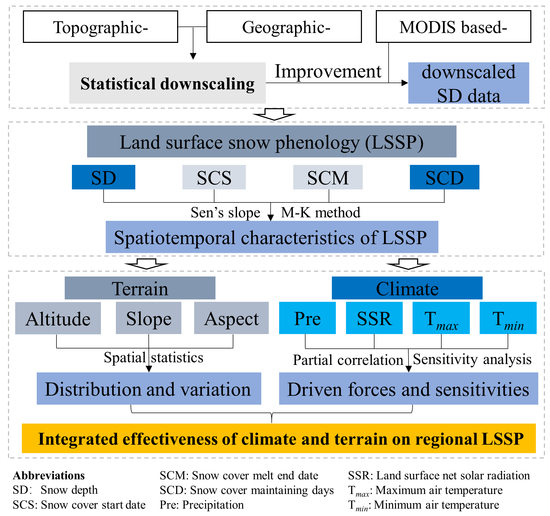
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. SD Data Downscaling
3.2.2. LSSP Indicator Extraction
3.2.3. Trend Analysis
3.2.4. Analysis of Climate-Driven Influences
3.2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation of the Improved SD Downscaling Method
4.2. LSSP Characteristics
4.2.1. Spatiotemporal Distributions
4.2.2. Spatiotemporal Variations
4.3. Terrain Influence on LSSP
4.3.1. Terrain-Based Distribution
4.3.2. Terrain-Based Variation
4.4. Climate Influence on LSSP
4.4.1. Partial Correlation Analysis
4.4.2. Sensitivity Analysis
4.5. Integrated Effectiveness of Climate and Terrain
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSSP | Land surface snow phenology |
| SGP | Southern Gansu Plateau |
| SD | Snow depth |
| MVC | Maximum value composite |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| SHY | Snow hydrological year |
| CDS | Cumulative days of snow |
| ADS | Accumulation days of snow |
| SCD | Snow cover maintaining days |
| SCS | Snow cover start date |
| SCM | Snow cover melt end date |
| Tmax | Maximum air temperature |
| Tmin | Minimum air temperature |
| SSR | Land surface net solar radiation |
References
- Yi, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, K.; Xie, F.; Saifullah, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of snow cover in the central and western Karakoram Mountains based on a refined MODIS product during 2002–2018. Atmos. Res. 2020, 250, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, T.; Kang, S.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal variability of snow cover timing and duration over the Eurasian continent during 1966–2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, T.A.; Williams, M.W.; Winstral, A. Persistence of topographic controls on the spatial distribution of snow in rugged mountain terrain, Colorado, United States. Water. Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W04014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bavay, M.; Grunewald, T.; Lehning, M. Response of snow cover and runoff to climate change in high Alpine catchments of Eastern Switzerland. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 55, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Z. Quantifying the contributions of snow/glacier meltwater to river runoff in the Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Global Planet. Chang. 2019, 174, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarca, G.; Guglielmin, M.; Convey, P.; Worland, W.R.; Cannone, N. Small-scale spatial–temporal variability in snow cover and relationships with vegetation and climate in maritime Antarctica. Catena 2021, 208, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jonas, T.; Rixen, C.; Jong, R.; Garonna, I.; Notarnicola, C.; Asam, S.; Schaepman, M.E.; Kneubuhler, M. Land surface phenology and greenness in Alpine grasslands driven by seasonal snow and meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.; Brauchli, T.; Mariethoz, G.; Brunner, P. Efficient multi-objective calibration and uncertainty analysis of distributed snow simulations in rugged alpine terrain. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehning, M.; Lowe, H.; Ryser, M.; Raderschall, N. Inhomogeneous precipitation distribution and snow transport in steep terrain. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W07404. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Thapa, A.; Nepal, S. Assessing the snow cover dynamics and its relationship with different hydro-climatic characteristics in Upper Ganges river basin and its sub-basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, G.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Xiao, C. Snow cover loss compounding the future economic vulnerability of western China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juras, R.; Blocher, J.; Jenicek, M.; Hotovy, O.; Markonis, Y. What affects the hydrological response of rain-on-snow events in low-altitude mountain ranges in Central Europe? J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Immerzeel, W.; Zhang, F.; Kok, R.; Chen, D.; Yan, W. Snow cover persistence reverses the altitudinal patterns of warming above and below 5000 m on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 803, 149889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepal, S.; Khatiwada, K.; Pradhananga, S.; Kralisch, S.; Samyn, D.; Bromand, M.T.; Jamal, N.; Dildar, M.; Durrani, F.; Rassouly, F.; et al. Future snow projections in a small basin of the Western Himalaya. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ishtiaque, A.; Estoque, R.; Eakin, H.; Parajuli, J.; Rabby, Y. IPCC’s current conceptualization of ‘vulnerability’ needs more clarification for climate change vulnerability assessments. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, T.; Su, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; et al. Impacts of landscape and climatic factors on snow cover in the Altai Mountains, China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2021, 12, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collados-Lara, A.; Pardo-Iguzquiza, E.; Pulido- Veelazquez, D. A distributed cellular automata model to simulate potential future impacts of climate change on snow cover area. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 124, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jin, F.; Si, Y.; Li, Z. Runoff change controlled by combined effects of multiple environmental factors in a headwater catchment with cold and arid climate in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. Understanding climate-induced changes of snow hydrological processes in the Kaidu River Basin through the CemaNeige-GR6J model. Catena 2022, 212, 106082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Kang, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Paudyal, R.; Sun, X.; Qin, D. Insights into mercury in glacier snow and its incorporation into meltwater runoff based on observations in the southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Rheinwalt, A.; Bookhagen, B. Topography and climate in the upper Indus Basin: Mapping elevation-snow cover relationships. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydi, M.; Ding, J. Impacts of topographic factors on regional snow cover characteristics. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehning, M.; Grunewald, T.; Schirmer, M. Mountain snow distribution governed by an altitudinal gradient and terrain roughness. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L19504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, G.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gu, H. Streamflow response to snow regime shift associated with climate variability in four mountain watersheds in the US Great Basin. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaaftink, C.; Mott, R.; Lehning, M. Seasonal simulation of drifting snow sublimation in Alpine terrain. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helbig, N.; Herwijnen, A. Subgrid parameterization for snow depth over mountainous terrain from flat field snow depth. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaremehrjardy, M.; Razzavi, S.; Faramarzi, M. Assessment of the cascade of uncertainty in future snow depth projections across watersheds of mountainous, foothill, and plain areas in northern latitudes. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 125735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Wu, F.; Yang, W.; He, X. Snow removal alters soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in a Tibetan alpine forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 76, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Xing, Z.; Bourque, C.; Meng, F. A new soil-temperature module for SWAT application in regions with seasonal snow cover. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collados-Lara, A.; Pardo-Iguzquiza, E.; Pulido-Velazquez, D. Assessing the impact of climate change–and its uncertainty–on snow cover areas by using cellular automata models and stochastic weather generators. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inatsu, M.; Tanji, S.; Sato, Y. Toward predicting expressway closures due to blowing snow events. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2020, 177, 103123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseri, Y.; Diaz, A.; Trinh, T.; Kavvas, M.; Ishida, K.; Anderson, M.L.; Ohara, N.; Snider, E.D. Dynamical downscaling of global reanalysis data for high-resolution spatial modeling of snow accumulation/melting at the central/southern Sierra Nevada watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittger, K.; Krock, M.; Kleiber, W.; Bair, E.; Brodzik, M.J.; Stephenson, T.R.; Rajagopalan, B.; Bormann, K.J.; Painter, T.H. Multi-sensor fusion using random forests for daily fractional snow cover at 30 m. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Long, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Dai, L.; Sun, Z. A dual state-parameter updating scheme using the particle filter and high-spatial-resolution remotely sensed snow depths to improve snow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C. Remote sensing, hydrological modeling and in situ observations in snow cover research: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.; Hik, D.S.; Gamon, J.; Jarosch, A.; Anslow, F.; Clarke, G.K.C.; Rupp, T.S. Spring and summer monthly MODIS LST is inherently biased compared to air temperature in snow covered sub-Arctic mountains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Huang, X.; Ma, X.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T. Downscaling Algorithm and Verification of AMSR2 Snow Cover Depth Products in North Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2016, 33, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Dziubanski, D.J.; Franz, K.J. Assimilation of AMSR-E snow water equivalent data in a spatially lumped snow model. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Guo, Z.; Ren, J. An application of MODIS data to snow cover monitoring in a pastoral area: A case study in Northern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Liang, T. AMSR2 snow depth downscaling algorithm based on a multifactor approach over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Komma, J.; Bloschl, G. Mapping snow cover from daily Collection 6 MODIS products over Austria. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Janjic, Z.; Dudhia, J.; Vasic, R.; Sales, F. A review on regional dynamical downscaling in intraseasonal to seasonal simulation/prediction and major factors that affect downscaling ability. Atoms. Res. 2014, 147–148, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stegmann, P.; Tang, G.; Yang, P.; Johnson, B.T. A stochastic model for density-dependent microwave Snow- and Graupel scattering coefficients of the NOAA JCSDA community radiative transfer model. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 211, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, X.; Shao, W.; Li, X. Support vector regression snow-depth retrieval algorithm using passive microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawej, M.; Faour, G.; Fayad, A.; Shaban, A. Towards an enhanced method to map snow cover areas and derive snow-water equivalent in Lebanon. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, H.; Prokop, A.; Eckerstorfer, M.; Hendrikx, J. Combining high spatial resolution snow mapping and meteorological analyses to improve forecasting of destructive avalanches in Longyearbyen, Svalbard. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, W.; Helmke, P.; Baker, J. High-resolution snow-water equivalent measurement by gamma-ray spectroscopy. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 83, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, M.; Homaee, M. Spatiotemporal changes of snow metrics in mountainous data-scarce areas using reanalyses. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lyu, S.; Chen, H.; Ao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X. Changes in climate and snow cover and their synergistic influence on spring runoff in the source region of the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Armstrong, R.; Zhang, T.J. Snow depth derived from passive microwave remote-sensing data in China. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Zhou, F.; Li, L. Patterns in snow depth maximum and snow cover days during 1961–2015 period in the Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Y.; Che, T.; Ding, Y.J. Inter-calibrating SMMR, SSM/I and SSMI/S data to improve the consistency of snow-depth products in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7212–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, D.; Pepin, N.; Yang, K.; Sun, J.; Li, D. Local changes in snow depth dominate the evolving pattern of elevation-dependent warming on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R. Relationship between vegetation phenology and snow cover changes during 2001–2018 in the Qilian Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, A.; Kuenzer, C.; Conrad, C. Snow cover variability in Central Asia between 2000 and 2011 derived from improved MODIS daily snow cover products. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3879–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, M.; Nguyen, L.; Henebry, G. Land surface phenology in the highland pastures of montane Central Asia: Interactions with snow cover seasonality and terrain characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Cheng, A.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, R.; et al. Study on the contribution of cryosphere to runoff in the cold alpine basin: A case study of Hulugou River Basin in the Qilian Mountains. Global Planet. Change 2014, 122, 345–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, K.; Kumar, P. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrical 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Qi, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, P. An analytical approach to separate climate and human contributions to basin streamflow variability. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, R.; Liu, C.; Sato, Y.; Fukushima, Y. Responses of streamflow to climate and land surface change in the headwaters of the Yellow River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, A.; English, M.; Derksen, C.; Toose, P.; Sillis, A. Observations of late winter Canadian tundra snow cover properties. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 3962–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, R.; Yoshida, T.; Masumoto, T. Uncertainty analysis of impacts of climate change on snow processes: Case study of interactions of GCM uncertainty and an impact model. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, R.; Rimmer, A.; Litaor, M.; Shamir, E.; Furman, A. Snow surface energy and mass balance in a warm temperate climate mountain. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Climate and topographic controls on snow phenology dynamics in the Tienshan Mountains, Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Yan, G.; Qi, J.; Mu, X.; Li, L.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, D.; Wild, M. Quantitative analysis of terrain reflected solar radiation in snow-covered mountains: A case study in Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Kumar, A.; Bhambri, R.; Hartashya, U.; Verma, A.; Dobhal, D.P.; Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, G.; Upadhyay, R. Topographic and climatic influence on seasonal snow cover: Implications for the hydrology of ungauged Himalayan basins, India. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revuelto, J.; Cluzet, B.; Duran, N. Fructus.; Lafaysse, M.; Cosme, E.; Dumont, M. Assimilation of surface reflectance in snow simulations: Impact on bulk snow variables. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Yang, Q.; Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Shen, M. Complex responses of spring alpine vegetation phenology to snow cover dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essery, R.; Li, L.; Pnmeroy, J. A distributed model of blowing snow over complex terrain. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 2424–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharova, O.; Matyshak, G.; Epstein, H.; Sefilian, A.; Bobrik, A. Influence of snow cover on soil temperatures: Meso- and micro-scale topographic effects (a case study from the northern West Siberia discontinuous permafrost zone). Catena 2019, 183, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.; Letcher, T.; Skiles, S. An evaluation of high-resolution regional climate model simulations of snow cover and albedo over the Rocky Mountains, with implications for the simulated snow-albedo feedback. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9069–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comola, F.; Schaefli, B.; Ronco, P.; Botter, G.; Bavay, M.; Rinaldo, A.; Lehning, M. Scale-dependent effects of solar radiation patterns on the snow-dominated hydrologic response. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3895–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Q.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Review of snow cover variation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on the broad climate system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, W.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T. Impact of climate and elevation on snow cover using integrated remote sensing snow products in Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedieu, J.; Lessard-Fontaine, A.; Ravazzani, G.; Cremonese, E.; Shalpykova, G.; Beniston, M. Shifting mountain snow patterns in a changing climate from remote sensing retrieval. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Lv, X.; He, Y. Features of climate change and their effects on glacier snow melting in Xinjiang, China. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2013, 345, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibike, Y.; Eum, H.; Prowse, T. Modelling the Athabasca watershed snow response to a changing climate. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wu, Z.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Sun, W.; Gu, C. Spatiotemporal changes in snow cover over China during 1960–2013. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; Nawaz, Z. Integrated assessment on the vulnerability of animal husbandry to snow disasters under climate change in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Global Planet. Change 2017, 157, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qi, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Zou, S.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W. Spatiotemporal characteristics of alpine snow and ice melt under a changing regional climate: A case study in Northwest China. Quat. Int. 2015, 358, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Dash, S.; Bhaskaran, B.; Pattnayak, K. Investigation of the snow-monsoon relationship in a warming atmosphere using Hadley Centre climate model. Global Planet. Change 2016, 147, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shenvi, M.; Sandu, C.; Untaroiu, C. Review of compressed snow mechanics: Testing methods. J. Terramechanics 2022, 100, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainieri, R.; Favillier, A.; Lopez-Saez, J.; Eckert, N.; Zgheib, T.; Morel, P.; Saulnier, M.; Peiry, J.; Stoffel, M.; Corona, C. Impacts of land-cover changes on snow avalanche activity in the French Alps. Anthropocene 2020, 30, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; He, C.; Shen, M. Spatial variations in snow cover and seasonally frozen ground over northern China and Mongolia, 1988–2010. Global Planet. Change 2014, 116, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.S.M.; Valera, C.A.; Zanata, M.; Santos, R.M.B.; Abdala, V.L.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Pissarra, T.C.T. Potential Impacts of Land Use Changes on Water Resources in a Tropical Headwater Catchment. Water 2021, 13, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnard, C.; Bzeouich, G.; Assani, A. Impacts of summer and winter conditions on summer river low flows in low elevation, snow-affected catchments. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carword, C.; Manson, S.; Bauer, M.; Hall, D. Multitemporal snow cover mapping in mountainous terrain for Landsat climate data record development. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Poulin, A.; Brissette, F.; Leconte, R.; Arsenault, R.; Malo, J. Uncertainty of hydrological modelling in climate change impact studies in a Canadian, snow-dominated river basin. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, A.; Tedesco, M.; Lee, S.; Foster, J.; Hall, D.K.; Kelly, R.; Robinson, D.A. A review of global satellite-derived snow products. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]














| Driving Force | t Test-P | t Test-SSR | t Test-Tmax | t Test-Tmin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [P] | |t| > t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 |
| [SSR] | |t| < t0.01 | |t| > t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 |
| [P + SSR] | |t| > t0.01 | |t| > t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 |
| ...... | ...... | ...... | ...... | ...... |
| [P + SSR + Tmax + Tmin] | |t| > t0.01 | |t| > t0.01 | |t| > t0.01 | |t| > t0.01 |
| [NC] | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 | |t| < t0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Li, C.; Xie, X.; Lv, J.; Zou, S.; Zhou, X.; Shen, N. Land Surface Snow Phenology Based on an Improved Downscaling Method in the Southern Gansu Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122848
Wu L, Li C, Xie X, Lv J, Zou S, Zhou X, Shen N. Land Surface Snow Phenology Based on an Improved Downscaling Method in the Southern Gansu Plateau, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122848
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lei, Changbin Li, Xuhong Xie, Jianan Lv, Songbing Zou, Xuan Zhou, and Na Shen. 2022. "Land Surface Snow Phenology Based on an Improved Downscaling Method in the Southern Gansu Plateau, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122848
APA StyleWu, L., Li, C., Xie, X., Lv, J., Zou, S., Zhou, X., & Shen, N. (2022). Land Surface Snow Phenology Based on an Improved Downscaling Method in the Southern Gansu Plateau, China. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122848