UAV Remote Sensing for High-Throughput Phenotyping and for Yield Prediction of Miscanthus by Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
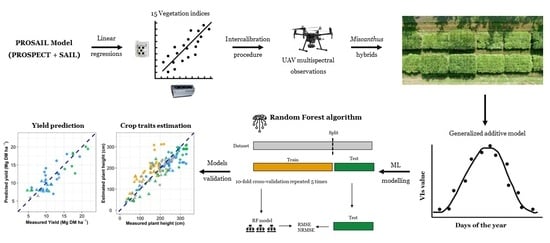
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Phenotypic and Yield Measurements
2.3. UAV Multispectral Data and Vegetation Indices
2.4. Using the PROSAIL Model to Intercalibrate VIs from Different Multispectral Sensors
2.5. Time Series of VIs and Peak Derivation
3. Results
3.1. PROSAIL Model for Intercalibration of VIs Derived from Different Multispectral Sensors
3.2. Importance of Variables in Machine Learning Models
3.3. Machine Learning Model for Crop Traits Estimation
3.4. Machine Learning Model for Yield Prediction
3.5. Time Series of VIs and Yield Prediction Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. The Importance of VIs Intercalibration Procedure for Multi-Sensor Interoperability
4.2. Estimating Miscanthus Traits with Machine Learning
4.3. Yield Prediction Using Machine Learning and Peak of VIs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewandowski, I.; Clifton-Brown, J.C.; Scurlock, J.M.O.; Huisman, W. Miscanthus: European Experience with a Novel Energy Crop. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton-Brown, J.; Hastings, A.; Mos, M.; McCalmont, J.P.; Ashman, C.; Awty-Carroll, D.; Cerazy, J.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Cosentino, S.; Cracroft-Eley, W.; et al. Progress in Upscaling Miscanthus Biomass Production for the European Bio-Economy with Seed-Based Hybrids. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clifton-Brown, J.C.; Lewandowski, I.; Andersson, B.; Basch, G.; Christian, D.G.; Kjeldsen, J.B.; J⊘rgensen, U.; Mortensen, J.V.; Riche, A.B.; Schwarz, K.-U.; et al. Performance of 15 Miscanthus Genotypes at Five Sites in Europe. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.B.; Zimmermann, J.; Clifton-Brown, J. Long-Term Yields and Soil Carbon Sequestration from Miscanthus: A Review. In Perennial Biomass Crops for a Resource-Constrained World; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Clifton-Brown, J.; Harfouche, A.; Casler, M.D.; Dylan Jones, H.; Macalpine, W.J.; Murphy-Bokern, D.; Smart, L.B.; Adler, A.; Ashman, C.; Awty-Carroll, D.; et al. Breeding Progress and Preparedness for Mass-scale Deployment of Perennial Lignocellulosic Biomass Crops Switchgrass, Miscanthus, Willow and Poplar. GCB Bioenergy 2019, 11, 118–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewandowski, I.; Clifton-Brown, J.; Trindade, L.M.; van der Linden, G.C.; Schwarz, K.-U.U.; Müller-Sämann, K.; Anisimov, A.; Chen, C.-L.L.; Dolstra, O.; Donnison, I.S.; et al. Progress on Optimizing Miscanthus Biomass Production for the European Bioeconomy: Results of the EU FP7 Project OPTIMISC. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Cruijsen, K.; Al Hassan, M.; van Erven, G.; Dolstra, O.; Trindade, L.M. Breeding Targets to Improve Biomass Quality in Miscanthus. Molecules 2021, 26, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton-Brown, J.; Schwarz, K.-U.; Awty-Carroll, D.; Iurato, A.; Meyer, H.; Greef, J.; Gwyn, J.; Mos, M.; Ashman, C.; Hayes, C.; et al. Breeding Strategies to Improve Miscanthus as a Sustainable Source of Biomass for Bioenergy and Biorenewable Products. Agronomy 2019, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastings, A.; Mos, M.; Yesufu, J.A.; McCalmont, J.; Schwarz, K.; Shafei, R.; Ashman, C.; Nunn, C.; Schuele, H.; Cosentino, S.; et al. Economic and Environmental Assessment of Seed and Rhizome Propagated Miscanthus in the UK. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pancaldi, F.; Trindade, L.M. Marginal Lands to Grow Novel Bio-Based Crops: A Plant Breeding Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Wit, A.J.W.; van Diepen, C.A. Crop Growth Modelling and Crop Yield Forecasting Using Satellite-Derived Meteorological Inputs. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, B.; Carberry, P.; Hammer, G.; Probert, M.; Robertson, M.; Holzworth, D.; Huth, N.; Hargreaves, J.N.; Meinke, H.; Hochman, Z.; et al. An Overview of APSIM, a Model Designed for Farming Systems Simulation. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKerron, D.K.L.; Haverkort, A.J. (Eds.) Decision Support Systems in Potato Production; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 978-90-76998-30-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, A.; Clifton-Brown, J.; Wattenbach, M.; Mitchell, C.P.; Smith, P. The Development of MISCANFOR, a New Miscanthus Crop Growth Model: Towards More Robust Yield Predictions under Different Climatic and Soil Conditions. GCB Bioenergy 2009, 1, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hastings, A.; Clifton-Brown, J.C.; Jiang, D.; Faaij, A.P.C. Modeled Spatial Assessment of Biomass Productivity and Technical Potential of Miscanthus × Giganteus, Panicum Virgatum L., and Jatropha on Marginal Land in China. GCB Bioenergy 2020, 12, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henner, D.N.; Hastings, A.; Pogson, M.; McNamara, N.P.; Davies, C.A.; Smith, P. PopFor: A New Model for Estimating Poplar Yields. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 134, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shang, J.; Qian, B.; Huffman, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, T.; Jing, Q.; Martin, T. Crop Yield Estimation Using Time-Series MODIS Data and the Effects of Cropland Masks in Ontario, Canada. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, G.M.; Agostini, F.; Barker, A.; Costomiris, D.; Qi, A. Assessing On-Farm Productivity of Miscanthus Crops by Combining Soil Mapping, Yield Modelling and Remote Sensing. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 85, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Impollonia, G.; Croci, M.; Martani, E.; Ferrarini, A.; Kam, J.; Trindade, L.M.; Clifton-Brown, J.; Amaducci, S. Moisture Content Estimation and Senescence Phenotyping of Novel Miscanthus Hybrids Combining UAV-based Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. GCB Bioenergy 2022, 14, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, A.B.; George-Jaeggli, B.; Chapman, S.C.; Laws, K.; Suárez Cadavid, L.A.; Wixted, J.; Watson, J.; Eldridge, M.; Jordan, D.R.; Hammer, G.L. Multi-Spectral Imaging from an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Enables the Assessment of Seasonal Leaf Area Dynamics of Sorghum Breeding Lines. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancon, J.; Dutartre, D.; Tixier, M.-H.H.; Weiss, M.; Comar, A.; Praud, S.; Baret, F. A High-Throughput Model-Assisted Method for Phenotyping Maize Green Leaf Area Index Dynamics Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, G.; Impollonia, G.; Croci, M.; Potenza, E.; Marcone, A.; Amaducci, S. Evaluating Biostimulants via High-Throughput Field Phenotyping: Biophysical Traits Retrieval through PROSAIL Inversion. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongschaap, R.E.E. Run-Time Calibration of Simulation Models by Integrating Remote Sensing Estimates of Leaf Area Index and Canopy Nitrogen. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 24, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévot, L.; Chauki, H.; Troufleau, D.; Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Brisson, N. Assimilating Optical and Radar Data into the STICS Crop Model for Wheat. Agronomie 2003, 23, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferchichi, A.; Abbes, A.B.; Barra, V.; Farah, I.R. Forecasting Vegetation Indices from Spatio-Temporal Remotely Sensed Data Using Deep Learning-Based Approaches: A Systematic Literature Review. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 68, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Zumpf, C.R.; Cacho, J.F.; Lee, D.; Lin, C.-H.; Boe, A.; Heaton, E.; Mitchell, R.; Negri, M.C.; Rescia, A.; et al. Remote Sensing-Based Estimation of Advanced Perennial Grass Biomass Yields for Bioenergy. Land 2021, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Badenhorst, P.; Phelan, A.; Pembleton, L.; Shi, F.; Cogan, N.; Spangenberg, G.; Smith, K. Using Sensors and Unmanned Aircraft Systems for High-Throughput Phenotyping of Biomass in Perennial Ryegrass Breeding Trials. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Piasecki, C.; Millwood, R.J.; Wolfe, B.; Mazarei, M.; Stewart, C.N. High-Throughput Switchgrass Phenotyping and Biomass Modeling by UAV. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Su, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, T.; Liu, J.; Guo, Q. The Transferability of Random Forest in Canopy Height Estimation from Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upreti, D.; Huang, W.; Kong, W.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S.; Zhou, X.; Ye, H.; Casa, R. A Comparison of Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithms for the Retrieval of Wheat Biophysical Variables from Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Yang, G.; Dai, H.; Xu, B.; Yang, H.; Feng, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. Modeling Maize Above-Ground Biomass Based on Machine Learning Approaches Using UAV Remote-Sensing Data. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Ismail, R. Estimating Standing Biomass in Papyrus ( Cyperus Papyrus L.) Swamp: Exploratory of in Situ Hyperspectral Indices and Random Forest Regression. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, J.; Malenovský, Z.; Van der Tol, C.; Camps-Valls, G.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P.; Lewis, P.; North, P.; Moreno, J. Quantifying Vegetation Biophysical Variables from Imaging Spectroscopy Data: A Review on Retrieval Methods. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 589–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Z.; Guo, W. Estimation of Biomass in Wheat Using Random Forest Regression Algorithm and Remote Sensing Data. Crop J. 2016, 4, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Jin, X.; Robin Bryant, C.; Senthilnath, J. Integrated Phenology and Climate in Rice Yields Prediction Using Machine Learning Methods. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.L.; Blackburn, G.A.; Carrasco, L.; Redhead, J.W.; Rowland, C.S. High Resolution Wheat Yield Mapping Using Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Resop, J.P.; Mueller, N.D.; Fleisher, D.H.; Yun, K.; Butler, E.E.; Timlin, D.J.; Shim, K.-M.; Gerber, J.S.; Reddy, V.R.; et al. Random Forests for Global and Regional Crop Yield Predictions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Ramos, A.P.; Prado Osco, L.; Elis Garcia Furuya, D.; Nunes Gonçalves, W.; Cordeiro Santana, D.; Pereira Ribeiro Teodoro, L.; Antonio da Silva Junior, C.; Fernando Capristo-Silva, G.; Li, J.; Henrique Rojo Baio, F.; et al. A Random Forest Ranking Approach to Predict Yield in Maize with Uav-Based Vegetation Spectral Indices. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnath, J.; Dokania, A.; Kandukuri, M.; Ramesh, K.N.; Anand, G.; Omkar, S.N.N. Detection of Tomatoes Using Spectral-Spatial Methods in Remotely Sensed RGB Images Captured by UAV. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 146, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beurs, K.M.; Henebry, G.M. Land Surface Phenology and Temperature Variation in the International Geosphere-Biosphere Program High-Latitude Transects. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Prediction of Crop Yield Using Phenological Information Extracted from Remote Sensing Vegetation Index. Sensors 2021, 21, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; d’Andrimont, R.; Vrieling, A.; Fasbender, D.; Lemoine, G.; Rembold, F.; Seguini, L.; Verhegghen, A. Comparing Land Surface Phenology of Major European Crops as Derived from SAR and Multispectral Data of Sentinel-1 and -2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.H.; Chen, S.; Robin Bryant, C.; Li, X.; Senthilnath, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; de Beurs, K. Integrating Spectral and Textural Information for Identifying the Tasseling Date of Summer Maize Using UAV Based RGB Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Shi, L.; Han, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, K. A near Real-Time Deep Learning Approach for Detecting Rice Phenology Based on UAV Images. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 287, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beurs, K.M.; Henebry, G.M. Spatio-Temporal Statistical Methods for Modelling Land Surface Phenology. In Phenological Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 177–208. [Google Scholar]
- Montazeaud, G.; Karatoğma, H.; Özturk, I.; Roumet, P.; Ecarnot, M.; Crossa, J.; Özer, E.; Özdemir, F.; Lopes, M.S. Predicting Wheat Maturity and Stay–Green Parameters by Modeling Spectral Reflectance Measurements and Their Contribution to Grain Yield under Rainfed Conditions. F. Crop. Res. 2016, 196, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psomiadis, E.; Dercas, N.; Dalezios, N.R.; Spiropoulos, N.V. Evaluation and Cross-Comparison of Vegetation Indices for Crop Monitoring from Sentinel-2 and Worldview-2 Images. In Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XIX; Neale, C.M., Maltese, A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Théau, J.; Sankey, T.T.; Weber, K.T. Multi-Sensor Analyses of Vegetation Indices in a Semi-Arid Environment. GISci. Remote Sens. 2010, 47, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoque, M.A.-A.; Phinn, S. Methods for Linking Drone and Field Hyperspectral Data to Satellite Data. In Fundamentals, Sensor Systems, Spectral Libraries, and Data Mining for Vegetation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 321–354. [Google Scholar]
- Emilien, A.-V.; Thomas, C.; Thomas, H. UAV & Satellite Synergies for Optical Remote Sensing Applications: A Literature Review. Sci. Remote Sens. 2021, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Pinzon, J.E.; Didan, K.; Morisette, J.T.; Tucker, C.J. Evaluation of the Consistency of Long-Term NDVI Time Series Derived from AVHRR, SPOT-Vegetation, SeaWiFS, MODIS, and Landsat ETM+ Sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, K.; Ji, L.; Reed, B.; Eidenshink, J.; Dwyer, J. Multi-Platform Comparisons of MODIS and AVHRR Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 99, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meroni, M.; Atzberger, C.; Vancutsem, C.; Gobron, N.; Baret, F.; Lacaze, R.; Eerens, H.; Leo, O. Evaluation of Agreement Between Space Remote Sensing SPOT-VEGETATION FAPAR Time Series. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Zhang, L.; Cen, Y.; Wu, T.; Huang, C.; Baig, M.H.A. Comparison of the Continuity of Vegetation Indices Derived from Landsat 8 OLI and Landsat 7 ETM+ Data among Different Vegetation Types. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13485–13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teillet, P.; Fedosejevs, G.; Barker, J.; Miskey, C.; Bannari, A. Spectral Simulations of Vegetation Indices in the Context of Landsat Data Continuity. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 1784–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Teillet, P.M.; Ren, X. Spectral Band Difference Effects on Vegetation Indices Derived from Multiple Satellite Sensor Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 34, 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Laliberte, A.S.; Goforth, M.A.; Steele, C.M.; Rango, A. Multispectral Remote Sensing from Unmanned Aircraft: Image Processing Workflows and Applications for Rangeland Environments. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2529–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Orr, B.J.; Marsh, S.E.; Herrmann, S.M. Multi-Sensor NDVI Data Continuity: Uncertainties and Implications for Vegetation Monitoring Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Jacquemoud, S.; Guyot, G.; Leprieur, C. Modeled Analysis of the Biophysical Nature of Spectral Shifts and Comparison with Information Content of Broad Bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT+SAIL Models: A Review of Use for Vegetation Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, K.; Atzberger, C.; Danner, M.; D’Urso, G.; Mauser, W.; Vuolo, F.; Hank, T.; D’Urso, G.; Mauser, W.; Vuolo, F.; et al. Evaluation of the PROSAIL Model Capabilities for Future Hyperspectral Model Environments: A Review Study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verrelst, J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Veroustraete, F.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Moreno, J. Optical Remote Sensing and the Retrieval of Terrestrial Vegetation Bio-Geophysical Properties—A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, M.D.; Miguez, F.E.; Heaton, E.A. The Older Plant Gets the Sun: Age-Related Changes in Miscanthus × Giganteus Phenology. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Senthilnath, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, H. Radiometric Calibration for Multispectral Camera of Different Imaging Conditions Mounted on a UAV Platform. Sustainability 2019, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datt, B. Remote Sensing of Water Content in Eucalyptus Leaves. Aust. J. Bot. 1999, 47, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Fujiwara, K.; Yamamoto, H. Inter-Comparison of ASTER and MODIS Surface Reflectance and Vegetation Index Products for Synergistic Applications to Natural Resource Monitoring. Sensors 2008, 8, 2480–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Merzlyak, M.N. Use of a Green Channel in Remote Sensing of Global Vegetation from EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripada, R.P.; Heiniger, R.W.; White, J.G.; Meijer, A.D. Aerial Color Infrared Photography for Determining Early In-Season Nitrogen Requirements in Corn. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A. Wide Dynamic Range Vegetation Index for Remote Quantification of Biophysical Characteristics of Vegetation. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tehada, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices and Novel Algorithms for Predicting Green LAI of Crop Canopies: Modeling and Validation in the Context of Precision Agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Merzlyak, M.N. Quantitative Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Using Reflectance Spectra: Experiments with Autumn Chestnut and Maple Leaves. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1994, 22, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Rondeaux, G.; Steven, M.; Baret, F. Optimization of Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Niu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Huang, W. Estimating Chlorophyll Content from Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices: Modeling and Validation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A. A Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinowski, S.; Krzyżak, J.; Clifton-Brown, J.; Jensen, E.; Mos, M.; Webster, R.; Sitko, K.; Pogrzeba, M. New Miscanthus Hybrids Cultivated at a Polish Metal-Contaminated Site Demonstrate High Stomatal Regulation and Reduced Shoot Pb and Cd Concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrego, J.P.F.; Huang, B.; Næss, J.S.; Hu, X.; Cherubini, F. Meta-Analysis of Leaf Area Index, Canopy Height and Root Depth of Three Bioenergy Crops and Their Effects on Land Surface Modeling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 306, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Meyer, H.; Obermeier, W.A.; Silva, B.; Regeling, B.; Bendix, J. Hyperspectral Data Analysis in R: The Hsdar Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781315370279. [Google Scholar]
- Nolè, A.; Rita, A.; Ferrara, A.M.S.; Borghetti, M. Effects of a Large-Scale Late Spring Frost on a Beech (Fagus Sylvatica L.) Dominated Mediterranean Mountain Forest Derived from the Spatio-Temporal Variations of NDVI. Ann. For. Sci. 2018, 75, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonucci, G.; Croci, M.; Miras-Moreno, B.; Fracasso, A.; Amaducci, S. Integration of Gas Exchange with Metabolomics: High-Throughput Phenotyping Methods for Screening Biostimulant-Elicited Beneficial Responses to Short-Term Water Deficit. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woźniak, G.; Dyderski, M.K.; Kompała-Bąba, A.; Jagodziński, A.M.; Pasierbiński, A.; Błońska, A.; Bierza, W.; Magurno, F.; Sierka, E.; Kompała-Bąba, A.; et al. Use of Remote Sensing to Track Postindustrial Vegetation Development. L. Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biecek, P. DALEX: MoDel Agnostic Language for Exploration and Explanation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2018, 19, 3245–3249. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Feng, H.; Xu, L.; Miao, M.; Long, H.; Yue, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Yang, X.; Fan, L. Estimation of Crop Growth Parameters Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Jiang, L.; Feng, Z. Cross-Comparison of Vegetation Indices Derived from Landsat-7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) and Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) Sensors. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Z.; Kerekes, J.P. Potential of Red Edge Spectral Bands in Future Landsat Satellites on Agroecosystem Canopy Green Leaf Area Index Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengarajan, R.; Schott, J. Evaluation of Sensor and Environmental Factors Impacting the Use of Multiple Sensor Data for Time-Series Applications. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Huete, A.; Miura, T.; Jiang, Z. Spectral Compatibility of Vegetation Indices across Sensors: Band Decomposition Analysis with Hyperion Data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 043520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaescusa-Nadal, J.L.; Franch, B.; Roger, J.-C.; Vermote, E.F.; Skakun, S.; Justice, C. Spectral Adjustment Model’s Analysis and Application to Remote Sensing Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen-Climent, M.L.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Villalobos, F.J. Estimating Radiation Interception in Heterogeneous Orchards Using High Spatial Resolution Airborne Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, H.; Feng, H.; Xu, L.; Miao, M.; Yang, G.; Yang, X.; Fan, L. Estimation of the Yield and Plant Height of Winter Wheat Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Images. Sensors 2020, 20, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.H.; Angel, Y.; Houborg, R.; Ali, S.; McCabe, M.F. A Random Forest Machine Learning Approach for the Retrieval of Leaf Chlorophyll Content in Wheat. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillack, A.; Clasen, A.; Kleinschmit, B.; Förster, M. Estimation of the Seasonal Leaf Area Index in an Alluvial Forest Using High-Resolution Satellite-Based Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, L.; Pinto, F.; González-Pérez, L.; Thompson, I.G.; Borém, A.; Reynolds, M.; Gérard, B.; Molero, G.; Rodrigues, F.A. High Throughput Field Phenotyping for Plant Height Using UAV-Based RGB Imagery in Wheat Breeding Lines: Feasibility and Validation. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.R.; Patel, N.R.; Danodia, A. Cotton Yield Estimation Using Phenological Metrics Derived from Long-Term MODIS Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 2597–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Location | UAV | Multispectral Camera Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Band | Centre (nm) | FWHM (nm) | ||
| PAC 1 | DJI M210 RTK | MicaSense RedEdge-Mx | Blue | 475 | 32 |
| Green | 560 | 27 | |||
| Red | 668 | 14 | |||
| Red edge | 717 | 12 | |||
| Near-infrared | 840 | 57 | |||
| TWS 1 | DJI M210 | SlantRange 4P | Blue | 470 | 100 |
| Green | 550 | 100 | |||
| Red | 650 | 40 | |||
| Red edge | 710 | 20 | |||
| Near-infrared | 850 | 100 | |||
| VIs | Equation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Datt1 | [66] | |
| EVI2 | [67] | |
| GNDVI | [68] | |
| GOSAVI | [69] | |
| greenWDRVI | [70] | |
| MSAVI | [71] | |
| MTVI1 | [72] | |
| MTVI2 | [72] | |
| NDRE | [73] | |
| NDVI | [74] | |
| OSAVI | [75] | |
| OSAVI2 | [76] | |
| rededgeWDRVI | [70] | |
| SAVI | [77] | |
| WDRVI | [70] |
| Parameter | Abbreviation | Unit | Values (Step) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | Structure parameter | N | Unitless | 1–2 (1) |
| Chlorophyll content | LCC | µg cm−2 | 10–80 (10) | |
| Relative equivalent water thickness | Cwr | % | 20–80 (20) | |
| Dry matter content | Cm | g cm−2 | 0.01–0.025 (0.005) | |
| Canopy | Leaf area index | LAI | m2 m−2 | 1–8 (1) |
| Leaf inclination distribution | LIDF | Spherical | ||
| Hotspot parameter | hot | m m−1 | 0.05–0.45 (0.2) | |
| Solar zenith angle | tts | deg | 20–80 (10) | |
| Observer zenith angle | tto | deg | 5–10 (5) | |
| Relative azimuth angle | psi | deg | 180–220 (10) | |
| Structure parameter | N | Unitless | 1–2 (1) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Impollonia, G.; Croci, M.; Ferrarini, A.; Brook, J.; Martani, E.; Blandinières, H.; Marcone, A.; Awty-Carroll, D.; Ashman, C.; Kam, J.; et al. UAV Remote Sensing for High-Throughput Phenotyping and for Yield Prediction of Miscanthus by Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122927
Impollonia G, Croci M, Ferrarini A, Brook J, Martani E, Blandinières H, Marcone A, Awty-Carroll D, Ashman C, Kam J, et al. UAV Remote Sensing for High-Throughput Phenotyping and for Yield Prediction of Miscanthus by Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122927
Chicago/Turabian StyleImpollonia, Giorgio, Michele Croci, Andrea Ferrarini, Jason Brook, Enrico Martani, Henri Blandinières, Andrea Marcone, Danny Awty-Carroll, Chris Ashman, Jason Kam, and et al. 2022. "UAV Remote Sensing for High-Throughput Phenotyping and for Yield Prediction of Miscanthus by Machine Learning Techniques" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122927
APA StyleImpollonia, G., Croci, M., Ferrarini, A., Brook, J., Martani, E., Blandinières, H., Marcone, A., Awty-Carroll, D., Ashman, C., Kam, J., Kiesel, A., Trindade, L. M., Boschetti, M., Clifton-Brown, J., & Amaducci, S. (2022). UAV Remote Sensing for High-Throughput Phenotyping and for Yield Prediction of Miscanthus by Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122927