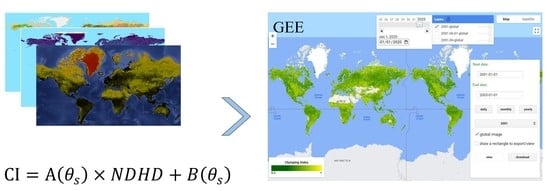
Real-Time Software for the Efficient Generation of the Clumping Index and Its Application Based on the Google Earth Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Retrieval Software Design
2.1. Materials
2.2. CI Retrieval Method
2.3. Software Design
3. Results
3.1. GEE-Based Software to Retrieve and Download CI
3.2. Temporal Variation of CI
4. Discussion
4.1. Contribution of the Study
4.2. Applicability of the Software
4.3. Retrieval of CI in the GEE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Code Availability
Appendix A

References
- Chen, J.M.; Black, T.A. Foliage area and architecture of plant canopies from sunfleck size distributions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1992, 60, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilson, T. A theoretical analysis of the frequency of gaps in plant stands. Agric. Meteorol. 1971, 8, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lu, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, H.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, F.; Arain, M.A.; Chen, J.; et al. Evaluation of clumping effects on the estimation of global terrestrial evapotranspiration. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.E.; Cescatti, A.; Baldocchi, D.D. Leaf area distribution and radiative transfer in open-canopy forests: Implications for mass and energy exchange. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B.; Yu, W.; Lin, S.; Hu, Z. Estimating fractional vegetation cover from leaf area index and clumping index based on the gap probability theory. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 90, 102112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Canopy clumping index (CI): A review of methods, characteristics, and applications. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 303, 108374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni-Meister, W.; Yang, W.; Kiang, N.Y. A clumped-foliage canopy radiative transfer model for a global dynamic terrestrial ecosystem model. I: Theory. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Mo, G.; Pisek, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, F.; Ishizawa, M.; Chan, D. Effects of foliage clumping on the estimation of global terrestrial gross primary productivity. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, GB1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Cao, B.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Song, L.; Fan, W.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q. A robust inversion algorithm for surface leaf and soil temperatures using the vegetation clumping index. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Harley, P.C. Scaling carbon dioxide and water vapour exchange from leaf to canopy in a deciduous forest. II. Model testing and application. Plant Cell Environ. 1995, 18, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M. 3.06-remote sensing emote sensing of leaf area index and clumping index. In Comprehensive Remote Sensing; Liang, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 53–77. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Baret, F.; Plummer, S.; Schaepman-Strub, G. An overview of global leaf area index (LAI): Methods, products, validation, and applications. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 739–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghiere, R.K.; Quaife, T.; Black, E.; Ryu, Y.; Chen, Q.; De Kauwe, M.G.; Baldocchi, D. Influence of sun zenith angle on canopy clumping and the resulting impacts on photosynthesis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Menges, C.H.; Leblanc, S.G. Global mapping of foliage clumping index using multi-angular satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Fang, H. Estimation of canopy clumping index from MISR and MODIS sensors using the normalized difference hotspot and darkspot (NDHD) method: The influence of BRDF models and solar zenith angle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, H.L. Estimation of LAI with the LiDAR technology: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.W. Stand structure and light penetration. I. Analysis by point quadrats. J. Appl. Ecol. 1965, 2, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Fang, H.; Schaaf, C.B.; He, L.; Chen, J.M. Global 500 m clumping index product derived from MODIS BRDF data (2001–2017). Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, J.M.; Pisek, J.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. Global clumping index map derived from the MODIS BRDF product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Schaaf, C.B.; Chen, J.M.; Román, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ding, A.; Erb, A.; Hill, M.J.; et al. An algorithm for the retrieval of the clumping index (CI) from the MODIS BRDF product using an adjusted version of the kernel-driven BRDF model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.-J.; Hung, C.-L.; Tang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.-L. Cloud computing service framework for bioinformatics tools. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine-Medical Informatics and Decision Making, Washington, DC, USA, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 1509–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.N.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.L. The application analysis of cloud computation technology into electronic information system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronics Engineering and Computing Technology (ICMECT), Shanghai, China, 9–10 April 2014; pp. 5552–5555. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google earth engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, W. Characterising three decades of evolution of forest spatial pattern in a major coal-energy province in northern China using annual landsat time series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 95, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B., 3rd. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google earth engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, R.; Yang, Z.; Gorelick, N.; Braaten, J.; Cavalcante, L.; Cohen, W.; Healey, S. Implementation of the LandTrendr algorithm on google earth engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wan, W.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Hong, Y. A Google earth engine-enabled software for efficiently generating high-quality user-ready landsat mosaic images. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 112, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, B.G.; Cohen, S.; Lucey, R.; Munasinghe, D.; Raney, A.; Brakenridge, G.R. Google earth engine implementation of the floodwater depth estimation tool (FwDET-GEE) for rapid and large scale flood analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, W.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. An algorithm for the retrieval of albedo from space using semiempirical BRDF models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanner, W.; Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. On the derivation of kernels for kernel-driven models of bidirectional reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 21077–21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.L.; Leroy, M.; Deschamps, P.Y. A bidirectional reflectance model of the Earth's surface for the correction of remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 20455–20468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. Geometric-optical bidirectional reflectance modeling of the discrete crown vegetation canopy: Effect of crown shape and mutual shadowing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, E.; Sinoquet, H. Botanical determinants of foliage clumping and light interception in two-year-old coppice poplar canopies: Assessment from 3-D plant mock-ups. Ann. For. Sci. 2007, 64, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisek, J.; Reznickova, L.; Adamson, K.; Ellsworth, D.S. Leaf inclination angle and foliage clumping in an evergreen broadleaf Eucalyptus forest under elevated atmospheric CO2. Aust. J. Bot. 2021, 69, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Román, M.O.; Schaaf, C.B.; Hutley, L.; Brannstrom, C.; Etter, A.; Hanan, N.P. Characterizing vegetation cover in global savannas with an annual foliage clumping index derived from the MODIS BRDF product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2008–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, A.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Near real-time vegetation monitoring at global scale. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipponi, F.; Valentini, E.; Nguyen Xuan, A.; Guerra, C.A.; Wolf, F.; Andrzejak, M.; Taramelli, A. Global MODIS fraction of green vegetation cover for monitoring abrupt and gradual vegetation changes. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Name | Usage | Description | Available Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCD43A1.v6 | Red band BRDF coefficients ) | Daily, 500 m | Available in GEE |
| MCD43A2.v6 | Quality indicator of red band BRDF product | Daily, 500 m | Available in GEE |
| MCD43A4.v6 | Nadir BRDF-adjusted reflectance to derive NDVI | Daily, 500 m | Available in GEE |
| MOD09A1.v6 | SZA when Terra over pass | 8 days, 500 m | Available in GEE |
| MYD09A1.v6 | SZA when Aqua over pass | 8 days, 500 m | Available in GEE |
| GEOV fCover.v2 | Vegetation cover fraction to confine SZA | Monthly, 1 km | https://land.copernicus.vgt.vito.be/ (accessed on 12 January 2022) |
| GLC2000 landcover | Vegetation type for determination of coefficients (A,B) | Once, 1 km | https://forobs.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 12 January 2022) |
| , | ||||
| 0° | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10° | 0.0121 | −0.0288 | 0.0156 | −0.4552 |
| 20° | 0.0504 | −0.0876 | 0.0682 | −0.9125 |
| 30° | 0.1215 | −0.1342 | 0.1786 | −1.3094 |
| 40° | 0.2398 | −0.1228 | 0.3986 | −1.6108 |
| 50° | 0.4364 | 0.0042 | 0.8645 | −2.1114 |
| 60° | 0.7853 | 0.3424 | 1.9999 | −2.9999 |
| Image | Setting |
|---|---|
| Name | Named by corresponding date |
| Bands | Band 1:CI, band 2: QA (0: main inversion; 2: magnitude inversion; and 255: filled value) |
| Format | GeoTIFF |
| Scaled | Band 1: 1000; band2: none |
| Projection | WGS-84 |
| Spatial resolution | 500 m |
| File size | ~845 M (global image) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Fang, H. Real-Time Software for the Efficient Generation of the Clumping Index and Its Application Based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153837
Li Y, Fang H. Real-Time Software for the Efficient Generation of the Clumping Index and Its Application Based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153837
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu, and Hongliang Fang. 2022. "Real-Time Software for the Efficient Generation of the Clumping Index and Its Application Based on the Google Earth Engine" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153837
APA StyleLi, Y., & Fang, H. (2022). Real-Time Software for the Efficient Generation of the Clumping Index and Its Application Based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153837