A High-Precision Water Body Extraction Method Based on Improved Lightweight U-Net
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Improved Network Structure
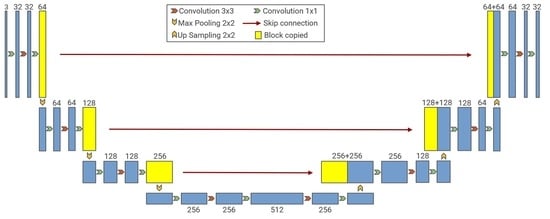
2.1.1. Architecture of the Proposed Network
2.1.2. Architecture of the Proposed Network
2.1.3. DownBottleneck and UpBottleneck
2.1.4. Implementation Details of the Network
2.2. Comparison Method
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Data and Experiments
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Extraction Results of BU-Net
3.4. Comparative Experiment Using Different Parameters
3.5. Comparative Experiment of Different Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Fan, R.S.; Yang, X.C.; Wang, J.X.; Latif, A. Extraction of Urban Water Bodies from High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Imagery Using Deep Learning. Water 2018, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Wu, B.; Chen, B.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y. Review of water body information extraction based on satellite remote sensing. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, Z. Extraction of water information based on China-made GF-1 remote sense image. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, H. Comparison and Analysis of Several Common Water Extraction Methods Based on TM Image. Remote Sens. Inf. 2012, 27, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Frazier, P.S.; Page, K.J. Water body detection and delineation with Landsat TM data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Minghua, Z. Extracting Water—Body Infonmtion with Improved Model of Spectal Relationship in a Higher Mountain Area. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2008, 24, 14. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Tateishi, R. A water index for rapid mapping of shoreline changes of five East African Rift Valley lakes: An empirical analysis using Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3153–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Meng, L.; Fan, Z.; Hu, W.; Xie, W. Applicability of the water information extraction method based on GF-1 image. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2015, 27, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.J.; Zhang, C.Y. Summary of water body extraction methods based on ZY-3 satellite. In Proceedings of the 1st International Global on Renewable Energy and Development (IGRED), Singapore, 22–25 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Water extraction technique in mountainous areas from satellite images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 46002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Wu, P.H.; Wang, B.; Park, H.; Hui, Y.; Wu, Y.L. A Deep Learning Method of Water Body Extraction From High Resolution Remote Sensing Images With Multisensors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3120–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wu, Y.; Xie, D.; Liu, L. Water Body Extraction from High-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing Images Based on Deep Learning. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 35, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Isikdogan, F.; Bovik, A.C.; Passalacqua, P. Surface Water Mapping by Deep Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.R.; Liu, W.J.; Yang, L.; Sun, S.H.; Hu, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, W. DeepUNet: A Deep Fully Convolutional Network for Pixel-Level Sea-Land Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.D.; Li, Z.W.; Zeng, C.; Xia, G.S.; Shen, H.F. An Urban Water Extraction Method Combining Deep Learning and Google Earth Engine. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.W.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J.M. UNet plus plus: Redesigning Skip Connections to Exploit Multiscale Features in Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.S.; Shi, J.P.; Qi, X.J.; Wang, X.G.; Jia, J.Y. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6230–6239. [Google Scholar]
- Jegou, S.; Drozdzal, M.; Vazquez, D.; Romero, A.; Bengio, Y. The One Hundred Layers Tiramisu: Fully Convolutional DenseNets for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1175–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q.K.; Shen, H.F.; Li, S.Y.; You, S.C.; Zhang, L.P. Land-cover classification with high-resolution remote sensing images using transferable deep models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Satellite Parameters | GF-2 Multispectral Imagery |
|---|---|
| Product level | 1A |
| Number of bands | 4 |
| Wavelength (μm) | Blue (0.42–0.52) Green (0.52–0.59) Red (0.63–0.69) Near-infrared (0.77–0.89) |
| Size | 6800 × 7200 |
| Spatial resolution (m) | 0.8 m pan/3.24 m MS |
| Test Images | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All images | 98.31 | 98.89 | 97.81 |
| Image1 | 99.52 | 99.73 | 99.46 |
| Image2 | 97.89 | 98.71 | 97.45 |
| Image3 | 97.51 | 98.39 | 96.83 |
| Image4 | 98.00 | 97.91 | 95.90 |
| Image5 | 98.93 | 98.93 | 97.89 |
| Image6 | 99.62 | 99.77 | 99.54 |
| Image7 | 97.72 | 98.56 | 97.15 |
| Image8 | 99.23 | 99.59 | 99.17 |
| Image9 | 97.93 | 98.69 | 97.42 |
| Image10 | 96.78 | 98.00 | 96.07 |
| Methods | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BU-Net (2.16) | 90.21 | 93.92 | 88.54 |
| BU-Net (2.32) | 98.31 | 98.89 | 97.81 |
| BU-Net (2.64) | 96.14 | 97.46 | 95.05 |
| BU-Net (2.128) | 93.55 | 95.91 | 92.14 |
| BU-Net (4.16) | 92.71 | 95.40 | 91.21 |
| BU-Net (4.32) | 98.18 | 98.81 | 97.64 |
| BU-Net (4.64) | 96.10 | 97.48 | 95.09 |
| BU-Net (4.128) | 96.38 | 97.67 | 95.45 |
| Methods | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BU-Net | 98.31 | 98.89 | 97.81 |
| U-Net | 91.00 | 94.40 | 89.39 |
| SegNet | 95.69 | 97.24 | 94.63 |
| ResNet | 98.29 | 98.88 | 97.78 |
| DenseNet | 89.57 | 93.58 | 87.93 |
| PSPNet | 94.01 | 96.19 | 92.67 |
| NDWI | 89.04 | 92.44 | 85.94 |
| Methods | OA (%) | Number of Parameters (MB) | PB * | Prediction Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BU-Net | 98.31 | 33.3 | 0.2625 | 41 |
| U-Net | 91.00 | 355.0 | 0.0040 | 67 |
| SegNet | 95.69 | 364.0 | 0.0168 | 65 |
| ResNet | 98.29 | 377.0 | 0.0231 | 64 |
| DenseNet | 89.57 | 15.9 | 0.0000 | 934 |
| PSPNet | 94.01 | 45.9 | 0.0967 | 53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, S.; Rui, X. A High-Precision Water Body Extraction Method Based on Improved Lightweight U-Net. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174127
An S, Rui X. A High-Precision Water Body Extraction Method Based on Improved Lightweight U-Net. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174127
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Shihao, and Xiaoping Rui. 2022. "A High-Precision Water Body Extraction Method Based on Improved Lightweight U-Net" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174127
APA StyleAn, S., & Rui, X. (2022). A High-Precision Water Body Extraction Method Based on Improved Lightweight U-Net. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174127