A Novel Historical Landslide Detection Approach Based on LiDAR and Lightweight Attention U-Net
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.3. Historical Landslides Data
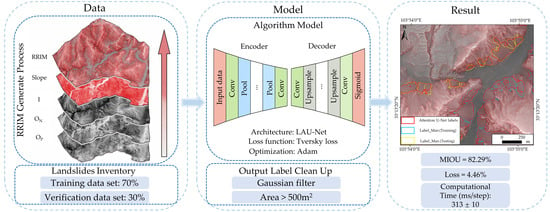
3. Detection Approach
3.1. U-Net
3.2. Attention Gate
3.3. Lightweight Attention U-Net
3.4. Optimization
3.5. Experiment
- -
- 3.7 GHz intel Xeon W2255 with 64 GB of RAM;
- -
- graphic processing unit (GPU), NVIDIA GeForce GTX 3090 card with 24 GB of RAM and reproducibility under NVIDIA Toolkit 11.0.2.
4. Results
4.1. Model Validation and Comparison
4.2. Identification Effect Analysis of Different Data Types
5. Discussion
5.1. Scale Parameter Analysis of Attention U-Net
5.2. Considerations on Multiple Sources
5.3. Historical Landslides in Jiuzhaigou
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sassa, K.; Canuti, P. Landslides-Disaster Risk Reduction; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.Q.; Fan, X.M. The landslide story. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Ngai, Y.Y. Landslide risk assessment and management: An overview. Eng. Geol. 2002, 64, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Lucieer, A.; de Jong, S.M. Time Series Analysis of Landslide Dynamics Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). Remote Sens 2015, 7, 1736–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrom, G.; Stark, C.P. Simple Scaling of Catastrophic Landslide Dynamics. Science 2013, 339, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzone, F.; Cardinali, M.; Carrara, A.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P. Impact of mapping errors on the reliability of landslide hazard maps. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakan, T.; Luigi, L. Completeness Index for Earthquake-Induced Landslide Inventories. Eng. Geol. 2020, 264, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, P.; Kirschbaum, D.; Stanley, T.; Tanyas, H. Landslide mapping using object-based image analysis and open source tools. Eng. Geol. 2021, 282, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, P.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Nuremanguli, T.; Ma, H.J.I.J.o.R.S. Landslide mapping with remote sensing: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 1555–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z. Remote sensing of landslides—A review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, B.; Dwivedi, R. Review on remote sensing methods for landslide detection using machine and deep learning. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 32, e3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Raspini, F.; Barra, A.; Bianchini, S.; Confuorto, P.; Casagli, N.; Crosetto, M. Review of Satellite Interferometry for Landslide Detection in Italy. Remote Sens 2020, 12, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.M.; Li, Y.; Cui, P.; Liang, L.; Pirasteh, S.; Marcato, J.; Goncalves, W.N.; Li, J. Landslide Detection of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data Based on Deep Learning with Constrains. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 5047–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, F.J.L. Landslide detection by deep learning of non-nadiral and crowdsourced optical images. Landslides 2021, 18, 1025–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.J.R.S. Landslide detection from open satellite imagery using distant domain transfer learning. Remote Sens 2021, 13, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Shahabi, H.; Crivellari, A.; Homayouni, S.; Blaschke, T.; Ghamisi, P.J.L. Landslide detection using deep learning and object-based image analysis. Landslides 2022, 19, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, A.C.; Guzzetti, F.; Chang, K.T.; Monserrat, O.; Martha, T.R.; Manconi, A. Landslide failures detection and mapping using Synthetic Aperture Radar: Past, present and future. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Cigna, F.; Bianchini, S.; Hölbling, D.; Füreder, P.; Righini, G.; Del Conte, S.; Friedl, B.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Iasio, C.; et al. Landslide mapping and monitoring by using radar and optical remote sensing: Examples from the EC-FP7 project SAFER. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneberg, W.C.; Creighton, A.L.; Medley, E.W.; Jonas, D.A. Use of LiDAR to assess slope hazards at the Lihir gold mine, Papua New Guinea. In Proceedings of the Proceedings, International Conference on Landslide Risk Management, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 31 May–3 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, N.F.; Streutker, D.R.; Chadwick, D.J.; Thackray, G.D.; Dorsch, S.J. Analysis of LiDAR-derived topographic information for characterizing and differentiating landslide morphology and activity. Geomorphology 2006, 73, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W.H. Landslide susceptibility revealed by LIDAR imagery and historical records, Seattle, Washington. Eng. Geol. 2007, 89, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigira, M.; Duan, F.J.; Yagi, H.; Furuya, T. Using an airborne laser scanner for the identification of shallow landslides and susceptibility assessment in an area of ignimbrite overlain by permeable pyroclastics. Landslides 2004, 1, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłuszek, K.; Marczak, S.; Borkowski, A.; Tarolli, P. Multi-aspect analysis of object-oriented landslide detection based on an extended set of LiDAR-derived terrain features. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsevski, P.V.; Brown, M.K.; Panter, K.; Onasch, C.M.; Simic, A.; Snyder, J. Landslide detection and susceptibility mapping using LiDAR and an artificial neural network approach: A case study in the Cuyahoga Valley National Park, Ohio. Landslides 2016, 13, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Oppikofer, T.; Abellan, A.; Derron, M.H.; Loye, A.; Metzger, R.; Pedrazzini, A. Use of LIDAR in landslide investigations: A review. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Seeni, M.I.; Nampak, H. Integration of LiDAR and QuickBird data for automatic landslide detection using object-based analysis and random forests. In Laser Scanning Applications in Landslide Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Eeckhaut, M.V.D.; Poesen, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Vanacker, V.; Nyssen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Vandekerckhove, L. Use of LIDAR-derived images for mapping old landslides under forest. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2007, 32, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorum, T. Landslide recognition and mapping in a mixed forest environment from airborne LiDAR data. Eng. Geol. 2019, 258, 105155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Merghadi, A.; Shirzadi, A.; Nguyen, H.; Hussain, Y.; Avtar, R.; Chen, Y.; Pham, B.T.; Yamagishi, H. Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.C.; Wang, M.; Peng, L.; Hong, H.Y. Comparative study of landslide susceptibility mapping with different recurrent neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 138, 104445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditian, A.; Kubota, T.; Shinohara, Y. Comparison of GIS-based landslide susceptibility models using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network in a tertiary region of Ambon, Indonesia. Geomorphology 2018, 318, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghadi, A.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Whiteley, J.; ThaiPham, B.; Bui, D.T.; Avtar, R.; Abderrahmane, B. Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: A comparative overview of algorithm performance. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Tien Bui, D.; Merghadi, A.; Sahana, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, C.W.; Khosravi, K.; Yang, Y.; Pham, B.T. Assessment of advanced random forest and decision tree algorithms for modeling rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan. Sci Total Environ. 2019, 662, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Palombi, L.; Raimondi, V. Data–driven classification of landslide types at a national scale by using Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, S.R.; Soares, L.P.; Grohmann, C.H.; van Westen, C.; Bhuyan, K.; Singh, R.P.; Floris, M.; Catani, F.J.L. Landslide detection in the Himalayas using machine learning algorithms and U-Net. Landslides 2022, 19, 1209–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T.; Gholamnia, K.; Meena, S.R.; Tiede, D.; Aryal, J. Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Methods and Deep-Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Landslide Detection. Remote Sens 2019, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli Piralilou, S.; Shahabi, H.; Jarihani, B.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T.; Gholamnia, K.; Meena, S.; Aryal, J. Landslide Detection Using Multi-Scale Image Segmentation and Different Machine Learning Models in the Higher Himalayas. Remote Sens 2019, 11, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Zhang, L.M.; Yin, K.S.; Luo, H.Y.; Li, J.H. Landslide identification using machine learning. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Cheng, X.W.; Chen, W.T.; Chen, G.; Liu, S.W. Identification of Forested Landslides Using LiDar Data, Object-based Image Analysis, and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens 2015, 7, 9705–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhong, H.; Ju, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. MILL: Channel Attention–based Deep Multiple Instance Learning for Landslide Recognition. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2021, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragagnolo, L.; Rezende, L.R.; da Silva, R.V.; Grzybowski, J.M.V. Convolutional neural networks applied to semantic segmentation of landslide scars. Catena 2021, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jin, S.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Guo, Q. Automatic Object Detection of Loess Landslide Based on Deep Learning. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Chen, G.; Pan, L.; Kou, R.; Wang, L.J.I.G.; Letters, R.S. GAN-based siamese framework for landslide inventory mapping using bi-temporal optical remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jin, S.; Li, W.; Su, Y.; Dong, X.; Guo, Q.J.R.S. Loess Landslide Detection Using Object Detection Algorithms in Northwest China. Remote Sens 2022, 14, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, W.C.; Jia, H.H.; Zhang, J.Q. Landslide susceptibility mapping using multiscale sampling strategy and convolutional neural network: A case study in Jiuzhaigou region. Catena 2020, 195, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Scaringi, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhan, W.; Dai, L.; Li, Y.; Pei, X.; Yang, Q.; Huang, R. Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake (Sichuan, China): Factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification. Landslides 2018, 15, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fan, X.; Yunus, A.P.; Siva Subramanian, S.; Alonso-Rodriguez, A.; Dai, L.; Xu, Q.; Huang, R. Coseismic landslides triggered by the 2018 Hokkaido, Japan (Mw 6.6), earthquake: Spatial distribution, controlling factors, and possible failure mechanism. Landslides 2019, 16, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.G.; Lombardo, L.; van Westen, C.; Pei, X.J.; Huang, R.Q. From scenario-based seismic hazard to scenario-based landslide hazard: Rewinding to the past via statistical simulations. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.N.; Li, C.C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.B.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.Y.; Li, W.Y.; Bai, Y.Q.; et al. Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; She, J. Error assessment of grid-based terrain shading algorithms for solar radiation modeling over complex terrain. Trans. GIS 2019, 24, 230–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Kaneta, S.I.; Suzuki, Y. Red relief image map: New visualization method for three dimensional data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda, H.; Chiba, T. Stereopaired Morphometric Protection Index Red Relief Image Maps (Stereo MPI-RRIMs): Effective Visualization of High-Resolution Digital Elevation Models for Interpreting and Mapping Small Tectonic Geomorphic FeaturesStereo MPI-RRIMs: Effective Visualization of High-Resolution Digital Elevation Models. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 109, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N.; Prabhat. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, L.F.; Du, B. Deep Learning for Remote Sensing Data A technical tutorial on the state of the art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, B.A.; Bolch, T.; MacDonell, S.; Holbling, D.; Rastner, P.; Schaffer, N. Automated detection of rock glaciers using deep learning and object-based image analysis. Remote Sens. Env. 2020, 250, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Ye, Y.X.; Yin, G.F.; Johnson, B.A. Deep learning in remote sensing applications: A meta-analysis and review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, T.; Mai, D.; Bensch, R.; Cicek, O.; Abdulkadir, A.; Marrakchi, Y.; Bohm, A.; Deubner, J.; Jackel, Z.; Seiwald, K.; et al. U-Net: Deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.J.a.p.a. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. Comput. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Luo, Z.M.; Zhong, Z.; Lin, X.; Su, S.Z.; Li, S.Z. Attention guided U-Net for accurate iris segmentation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 56, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Liu, J. CapsNet, CNN, FCN: Comparative Performance Evaluation for Image Classification. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2019, 9, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.S.M.; Erdogmus, D.; Gholipour, A. Tversky loss function for image segmentation using 3D fully convolutional deep networks. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10 September 2017; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Wei, M.; Yang, W.; Xu, C.; Ma, C. Automatic mapping of landslides by the ResU-net. Remote Sens 2020, 12, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, N. Pulmonary vessel segmentation based on orthogonal fused u-net++ of chest CT images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.05537. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Daquan, Z.; Maoqi, X. An approach to mass movements in the Jiuzhaigou catchment. Nat. Hazards 1993, 8, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Methods | Loss (%) | Accuracy (%) | F1 (%) | MIOU (%) | Computational Time (s/Epochs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResU-Net | 5.53 | 93.86 | 84.11 | 79.15 | 789 ± 9 |
| LU-Net | 4.76 | 93.91 | 86.50 | 81.45 | 335 ± 15 |
| DeepLabv3 | 4.61 | 94.27 | 86.67 | 81.57 | 470 ± 12 |
| U-Net++ | 4.54 | 94.43 | 86.90 | 81.76 | 670 ± 10 |
| R2U-Net | 4.50 | 94.61 | 87.15 | 81.85 | 808 ± 7 |
| SwinU-Net | 4.45 | 95.08 | 87.37 | 82.25 | 1207 ± 20 |
| LAU-Net | 4.46 | 95.17 | 87.45 | 82.29 | 313 ± 10 |
| Date Type | Loss (%) | Accuracy (%) | F1 (%) | MIOU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAV | 11.28 | 80.56 | 70.28 | 65.2 |
| DEM | 10.37 | 84.41 | 73.37 | 69.56 |
| Hillshade | 8.21 | 87.12 | 79.92 | 76.17 |
| RRIM | 4.46 | 95.17 | 87.45 | 82.29 |
| LAU-Net | TAU-Net | |
|---|---|---|
| Loss (%) | 4.45 | 4.46 |
| Accuracy (%) | 95.20 | 95.17 |
| F1 (%) | 87.48 | 87.45 |
| MIOU (%) | 82.31 | 82.29 |
| Computational Time (s/epochs) | 710 ± 10 | 313 ± 10 |
| Model Parameters | 7.98 × 106 | 1.98 × 106 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.; Fan, X.; Zhong, H.; Lombardo, L.; Tanyas, H.; Wang, X. A Novel Historical Landslide Detection Approach Based on LiDAR and Lightweight Attention U-Net. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174357
Fang C, Fan X, Zhong H, Lombardo L, Tanyas H, Wang X. A Novel Historical Landslide Detection Approach Based on LiDAR and Lightweight Attention U-Net. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174357
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Chengyong, Xuanmei Fan, Hao Zhong, Luigi Lombardo, Hakan Tanyas, and Xin Wang. 2022. "A Novel Historical Landslide Detection Approach Based on LiDAR and Lightweight Attention U-Net" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174357
APA StyleFang, C., Fan, X., Zhong, H., Lombardo, L., Tanyas, H., & Wang, X. (2022). A Novel Historical Landslide Detection Approach Based on LiDAR and Lightweight Attention U-Net. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174357