Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Yangtze Main Stream Based on Sentinel-2 MSI Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
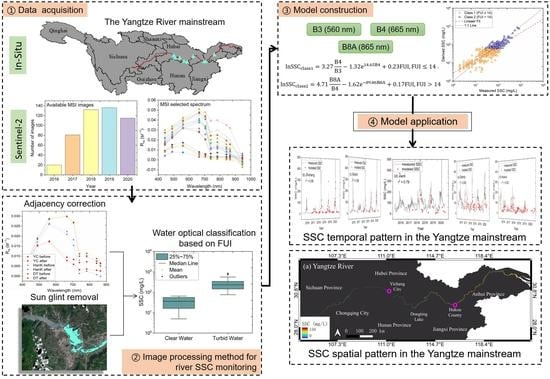
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Gauging Stations Data
2.3. Sentinel-2 Image Processing
2.4. Water Optical Classification
2.5. Model Construction
2.6. Accuracy Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Sentinel-2 MSI Rrs
3.2. Validation of the SSC Retrieval Model
3.3. Temporal Characteristics of SSC
3.4. Spatial Distribution of SSC
3.5. Case Study
3.5.1. Yibin Reach
3.5.2. Three Gorges Reservoir
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparisons of Various SSC Retrieved Models
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halfman, J.D.; Scholz, C.A. Suspended Sediments in Lake Malawi, Africa: A Reconnaissance Study. J. Great Lakes Res. 1993, 19, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems; Gulf Professional Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schild, R.; Prochnow, D. Coupling of biomass production and sedimentation of suspended sediments in eutrophic rivers. Ecol. Model. 2001, 145, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.R.; King, S.L. Spatial dynamics of overbank sedimentation in floodplain systems. Geomorphology 2008, 100, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.W.; Schaffranek, R.W.; Noe, G.B.; Larsen, L.G.; Nowacki, D.J.; O’Connor, B.L. Hydroecological factors governing surface water flow on a low-gradient floodplain. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juez, C.; Schärer, C.; Jenny, H.; Schleiss, A.; Franca, M. Floodplain land cover and flow hydrodynamic control of overbank sedimentation in compound channel flows. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9072–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maren, D.; Hoekstra, P. Dispersal of suspended sediments in the turbid and highly stratified Red River plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Shi, X.; Zhu, A.; Liu, Y.; Bi, N.; Fang, X.; Yang, G. Distribution and transport of suspended sediments off the Yellow River (Huanghe) mouth and the nearby Bohai Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, G.; Camenen, B.; Jodeau, M.; Némery, J.; Esteves, M. Downstream erosion and deposition dynamics of fine suspended sediments due to dam flushing. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Jin, Y.Q.; Yun, C.X. Suspended sediment concentrations in the Yangtze River estuary retrieved from the CMODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4329–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Kumar, A. Continuous measurement of suspended sediment concentration: Technological advancement and future outlook. Measurement 2015, 76, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Hamshaw, S.D.; Lee, B.S.; Rizzo, D.M. Multivariate event time series analysis using hydrological and suspended sediment data. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Qing, S.; Diao, R.; Hao, Y. Remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in optically complex estuarine and inland waters based on optical classification. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 102, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, M.; Wang, R. Numerical simulation of Donghu Lake hydrodynamics and water quality based on remote sensing and MIKE 21. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Pappenberger, F.; Matgen, P. Flood hazard mapping combining hydrodynamic modeling and multi annual remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14200–14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtarelli, M.; Ogashawara, I.; Alcântara, E.; Stech, J. Coupling remote sensing bio-optical and three-dimensional hydrodynamic modeling to study the phytoplankton dynamics in a tropical hydroelectric reservoir. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, H.; Song, K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Remote chlorophyll-a estimates for inland waters based on a cluster-based classification. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Lu, X.X.; Liew, S.C.; Zhou, Y. Retrieval of suspended sediment concentrations in large turbid rivers using Landsat ETM+: An example from the Yangtze River, China. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2009, 34, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Lu, X. Estimation of suspended sediment concentrations using Terra MODIS: An example from the Lower Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.-L.; Sun, X.-M.; Wong, D.W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, L.-X. A semi-analytical model for remote sensing retrieval of suspended sediment concentration in the Gulf of Bohai, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5373–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavora, J.; Boss, E.; Doxaran, D.; Hill, P. An algorithm to estimate suspended particulate matter concentrations and associated uncertainties from remote sensing reflectance in coastal environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuru, N.; Martin, P.; Sanwlani, N.; Mujahid, A.; Müller, M. A semi-analytical optical remote sensing model to estimate suspended sediment and dissolved organic carbon in tropical coastal waters influenced by peatland-draining river discharges off Sarawak, Borneo. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, N.; do Carmo, A.; Park, E.; Alcântara, E. Retrieval of suspended particulate matter in inland waters with widely differing optical properties using a semi-analytical scheme. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, S.; Doxaran, D.; Ody, A.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Lafon, V.; Lubac, B.; Gernez, P. Atmospheric corrections and multi-conditional algorithm for multi-sensor remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in low-to-high turbidity levels coastal waters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Chen, J.; Pan, D.; Tao, B.; Zhu, Q. A regional remote sensing algorithm for total suspended matter in the East China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petus, C.; Chust, G.; Gohin, F.; Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Sagarminaga, Y. Estimating turbidity and total suspended matter in the Adour River plume (South Bay of Biscay) using MODIS 250-m imagery. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jally, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Balabantaray, S. Retrieval of suspended sediment concentration of the Chilika Lake, India using Landsat-8 OLI satellite data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.R.; Harmel, T.; Martinez, J.-M.; Filizola Junior, N.P. Spatiotemporal dynamics of suspended sediments in the negro river, amazon basin, from in situ and sentinel-2 remote sensing data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Kupssinskü, L.; Thomassim Guimarães, T.; Menezes de Souza, E.; Zanotta, D.C.; Roberto Veronez, M.; Gonzaga, L., Jr.; Mauad, F.F. A method for chlorophyll-a and suspended solids prediction through remote sensing and machine learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.D.; Simic Milas, A.; Vincent, R.K.; Evans, J.E. Landsat 8 monitoring of multi-depth suspended sediment concentrations in Lake Erie’s Maumee River using machine learning. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4064–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.T.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Cox, A.L.; Martinez, M. Suspended sediment concentration estimation from landsat imagery along the lower missouri and middle Mississippi Rivers using an extreme learning machine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Bryère, P.; Ouillon, S.; Dessailly, D.; Xing, Q.; Zhu, J. Development of a semi-analytical algorithm for the retrieval of suspended particulate matter from remote sensing over clear to very turbid waters. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.V.; Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Binding, C.; Schalles, J.; Loisel, H.; Gurlin, D.; Greb, S.; Alikas, K.; Randla, M. Robust algorithm for estimating total suspended solids (TSS) in inland and nearshore coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forel, F.A. Une nouvelle forme de la gamme de couleur pour l’étude de l’eau des lacs. Arch. Des. Sci. Phys. Nat. Société Phys. D’histoire Nat. Genève 1890, 6, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Ule, W. Die bestimmung der Wasserfarbe in den Seen. Kleinere Mittheilungen. Dr. A. Petermanns Mitth. Aus Justus Perthes Geogr. Anst. 1892, 38, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Kimball, J.S.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Guo, P. Evaluation of trophic state for inland waters through combining Forel-Ule Index and inherent optical properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Qiu, Y.; Fei, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Using remotely sensed suspended sediment concentration variation to improve management of Poyang Lake, China. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2013, 29, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, E.; Grippa, M.; Kergoat, L.; Pinet, S.; Gal, L.; Cochonneau, G.; Martinez, J.-M. Monitoring water turbidity and surface suspended sediment concentration of the Bagre Reservoir (Burkina Faso) using MODIS and field reflectance data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zha, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M. A Landsat 8 OLI-based, semianalytical model for estimating the total suspended matter concentration in the slightly turbid Xin’anjiang Reservoir (China). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, Q.; Cui, T.; Xue, C.; Zhang, S. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River estuary from Landsat TM and ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 146, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Tang, S.; Zhan, H. Spatio-temporal variation of the suspended sediment concentration in the Pearl River Estuary observed by MODIS during 2003–2015. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 172, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; D’Sa, E.; Cui, T.; Zhang, X. A semi-analytical total suspended sediment retrieval model in turbid coastal waters: A case study in Changjiang River Estuary. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 13018–13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Verhoef, W.; Zhou, Y.; Salama, M.; Liu, X. Satellite estimates of wide-range suspended sediment concentrations in Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary using MERIS data. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, W. A total suspended sediment retrieval model for multiple estuaries and coasts by Landsat imageries. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Guangzhou, China, 4–6 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Sokoletsky, L.; Yang, X.; Shen, F. MODIS-based retrieval of suspended sediment concentration and diffuse attenuation coefficient in Chinese estuarine and coastal waters. In Ocean Remote Sensing and Monitoring from Space; SPIE: Beijing, China, 2014; p. 926119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Du, C. Landsat-based long-term monitoring of total suspended matter concentration pattern change in the wet season for Dongting Lake, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13975–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cui, L.; He, J.; Duan, H.; Fei, T.; Liu, Y. Comparison of MODIS-based models for retrieving suspended particulate matter concentrations in Poyang Lake, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 24, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Dai, J. Investigation of chlorophyll-a and total suspended matter concentrations using Landsat ETM and field spectral measurement in Taihu Lake, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2779–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, C.; Cavalli, R.M.; Pignatti, S.; Santini, F. Evaluation of adjacency effect for MIVIS airborne images. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere XII, SPIE, Florence, Italy, 17–19 September 2007; pp. 384–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, H.; Zhanghua, W. Yangtze River of China: Historical analysis of discharge variability and sediment flux. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.; Kotchenova, S. Second simulation of a satellite signal in the solar spectrum-vector (6SV). 6s User Guide Version 2006, 3, 675–686. [Google Scholar]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y. MCD19A2 MODIS/Terra+ Aqua Land Aerosol Optical Depth Daily L2G Global 1km SIN Grid V006 [Data Set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC. 2018. Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/MCD19A2 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Platnick, S.; King, M.; Meyer, K.; Wind, G.; Amarasinghe, N.; Marchant, B.; Arnold, G.; Zhang, Z.; Hubanks, P.; Ridgway, B. MODIS Atmosphere L3 Monthly Product; NASA MODIS Adaptive Processing System; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Leetmaa, A.; Reynolds, R.; Jenne, R.; Josepht, D. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, W.J.; Sterckx, S.; Montes, M.J.; De Keukelaere, L.; Knaeps, E. Atmospheric correction for inland waters. In Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhang, X.; Shang, G. Quantification of the adjacency effect on measurements in the thermal infrared region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9674–9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R.; Louis, J.; Müller-Wilm, U. [L2A-ATBD] Sentinel-2 Level-2A Products Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. Version 2.0. 2012, pp. 1–72. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/c/document_library/get_file?folderId=349490&name=DLFE-4518.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Kristollari, V.; Karathanassi, V. Artificial neural networks for cloud masking of Sentinel-2 ocean images with noise and sunglint. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4102–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Pflug, B.; Main-Knorn, M.; Bieniarz, J.; Mueller-Wilm, U.; Cadau, E.; Gascon, F. Sentinel-2 Sen2Cor: L2A processor for users. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tian, L.; Song, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Wei, A. A near-infrared band-based algorithm for suspended sediment estimation for turbid waters using the experimental Tiangong 2 moderate resolution wide-wavelength imager. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Lee, Z.; Spyrakos, E.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L. Changes of water clarity in large lakes and reservoirs across China observed from long-term MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, K.; Ouyang, C.; Duan, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Ma, J.; An, H.; Zhou, S. Reflections on the catastrophic 2020 Yangtze River Basin flooding in southern China. Innovation 2020, 1, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Li, J. Retrieval and Spatio-Temporal Variations Analysis of Yangtze River Water Clarity from 2017 to 2020 Based on Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Dong, Z.; Duan, C.; Ni, X.; Zhu, Z. Ecological reservoir operation based on DFM and improved PA-DDS algorithm: A case study in Jinsha river, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 1723–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, X.X.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Lin, L. Sediment load responses to climate variation and cascade reservoirs in the Yangtze River: A case study of the Jinsha River. Geomorphology 2018, 322, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changjiang Sediment Bulletin; Yangtze River Committee of the Ministry of Water Resources: Wuhan, China, 2012.
- Changjiang Sediment Bulletin; Yangtze River Committee of the Ministry of Water Resources: Wuhan, China, 2013.
- Huang, Z.; Wu, B. Three Gorges Dam; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Zhong, Z.; Zou, Q.; Ding, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, X. Study on Countermeasures for Risks of Flood Resources Utilization in the Three Gorges Project. In Flood Resources Utilization in the Yangtze River Basin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 325–345. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Lu, Y.; Fan, H.; Lu, Y. Spatial-temporal distribution of sediment phosphorus with sediment transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A. The Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River in China. Geography 2004, 89, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Tang, D.; Levy, G.; Liu, D. Remote sensing of the impacts of construction in coastal waters on suspended particulate matter concentration–the case of the Yangtze River delta, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2132–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Shi, K. Fifteen-year monitoring of the turbidity dynamics in large lakes and reservoirs in the middle and lower basin of the Yangtze River, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, H.-J.; Inoue, T.; Schmetz, J. NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Comparison of a split-window and a multi-spectral cloud classification for MODIS observations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2003, 81, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Feng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.; Huang, J.; Xiao, T. An automated method for extracting rivers and lakes from Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5067–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonecker, E.T.; Jones, D.K.; Pellerin, B.A. The new Landsat 8 potential for remote sensing of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Y. Retrieval of suspended sediment concentrations in the turbid water of the Upper Yangtze River using Landsat ETM+. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Jacinthe, P.-A.; Wang, X.; Lyu, L.; Tao, H.; Ma, Y.; Duan, H.; Shang, Y. Remote sensing of total suspended matter concentration in lakes across China using Landsat images and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Station | Number | Max (mg/L) | Min (mg/L) | Mean (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yichang | 36 | 443 | 2 | 44.42 |
| Zhicheng | 68 | 712 | 3 | 45.77 |
| Shashi | 28 | 850 | 5 | 72.00 |
| Jianli | 26 | 779 | 24 | 130.5 |
| Luoshan | 28 | 233 | 35 | 76.61 |
| Hankou | 91 | 409 | 28 | 85.92 |
| Jiujiang | 38 | 238 | 33 | 85.35 |
| Datong | 64 | 363 | 23 | 91.15 |
| Hukou | 109 | 240 | 10 | 44.16 |
| Total | 488 | 850 | 2 | 69.51 |
| Water Type | Calibration Dataset | Validation Dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | RMSE | MRE (%) | Number | RMSE | MRE (%) | |
| Clear water | 268 | 24.12 | 53.55 | 69 | 20.76 | 54.04 |
| Turbid water | 122 | 52.70 | 33.72 | 29 | 49.72 | 30.82 |
| Total | 390 | 35.62 | 47.35 | 98 | 24.87 | 51.91 |
| Name | SSC Range (mg/L) | Recalibrated Model | MRE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cai model | About 100–800 | 146.09% | 32.68 | |
| Hou model | 1–300 | 123.60% | 30.97 | |
| Yue model | 1.5–2301 | 54.25% | 26.44 | |
| SOLID | About 1–1000 | - | 59.44% | 33.63 |
| Our model | 2–850 | 51.91% | 24.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y. Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Yangtze Main Stream Based on Sentinel-2 MSI Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184446
Zhang C, Liu Y, Chen X, Gao Y. Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Yangtze Main Stream Based on Sentinel-2 MSI Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184446
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenlu, Yongxin Liu, Xiuwan Chen, and Yu Gao. 2022. "Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Yangtze Main Stream Based on Sentinel-2 MSI Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184446
APA StyleZhang, C., Liu, Y., Chen, X., & Gao, Y. (2022). Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Yangtze Main Stream Based on Sentinel-2 MSI Data. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184446