Combining Deep Semantic Edge and Object Segmentation for Large-Scale Roof-Part Polygon Extraction from Ultrahigh-Resolution Aerial Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
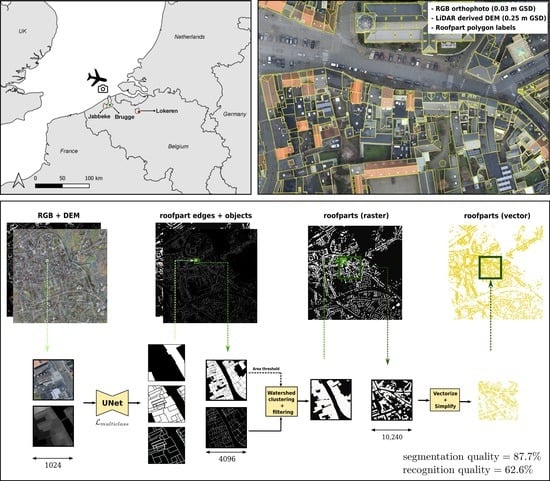
2.1. Study Area and Dataset
2.2. Workflow Overview
2.3. Semantic Edge and Object Segmentation
2.3.1. FCN Architectures
2.3.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3.3. FCN Training
2.3.4. Validation
2.4. Closed Shape Extraction
2.5. Vectorization
2.6. Evaluation
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Influence of Ground Truth and Loss Weighting
3.2. Influence of Patch Size and Object Mask Usage
3.3. Influence of the Modelling Approach and Input Sources
3.4. Influence of the FCN Architecture
3.5. Visual Examples of the Optimized Workflow
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AT | Area threshold |
| CCE | Categorical cross-entropy |
| CRS | Coordinate reference system |
| CSE | Closed shape extraction |
| DEM | Digital elevation model |
| DV | Direct vectorization |
| EO | Earth observation |
| FCN | Fully convolutional network |
| GSD | Ground sampling distance |
| IoU | Intersection over union |
| PQ | Panoptic quality |
| PS | Patch size |
| RQ | Recognition quality |
| SQ | Segmentation quality |
| UHR | Ultrahigh resolution |
| WM | Watershed mask |
References
- Wu, A.N.; Biljecki, F. Roofpedia: Automatic mapping of green and solar roofs for an open roofscape registry and evaluation of urban sustainability. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 214, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeser, T.; Kuenzer, C. Object Detection and Image Segmentation with Deep Learning on Earth Observation Data: A Review—Part I: Evolution and Recent Trends. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeser, T.; Bachofer, F.; Kuenzer, C. Object Detection and Image Segmentation with Deep Learning on Earth Observation Data: A Review—Part II: Applications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P. Automatic building extraction from high-resolution aerial images and LiDAR data using gated residual refinement network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, D.; Matuk, O.; Bielecka, E. Polish Cadastre Modernization with Remotely Extracted Buildings from High-Resolution Aerial Orthoimagery and Airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Wu, R.; Huang, Y. Plane segmentation for a building roof combining deep learning and the RANSAC method from a 3D point cloud. J. Electron. Imaging 2021, 30, 053022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochem, A.; Höfle, B.; Rutzinger, M.; Pfeifer, N. Automatic Roof Plane Detection and Analysis in Airborne Lidar Point Clouds for Solar Potential Assessment. Sensors 2009, 9, 5241–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohle-Fröhlich, R.; Bohm, A.; Korb, M.; Goebbels, S. Roof Segmentation based on Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and ComputerGraphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), Prague, Czech Republic, 25–27 February 2019; pp. 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ji, S. Roof Plane Segmentation from LiDAR Point Cloud Data Using Region Expansion Based L0Gradient Minimization and Graph Cut. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10101–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, J. Automated residential building detection from airborne LiDAR data with deep neural networks. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 36, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISPRS WGII/4. 2D Semantic Labeling—Vaihingen Data, 2013. Available online: https://www2.isprs.org/commissions/comm2/wg4/benchmark/2d-sem-label-vaihingen/ (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P. Can Semantic Labeling Methods Generalize to Any City? The Inria Aerial Image Labeling Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Roscher, R.; Volpi, M.; Mallet, C.; Drees, L.; Wegner, J.D.; Dirk, J.; Semcity, W.; Roscher, R.; Volpi, M.; Mallet, C.; et al. SemCity Toulouse: A benchmark for building instance segmentation in satellite images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 5, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirko, W.; Kashubin, S.; Ritter, M.; Annkah, A.; Bouchareb, Y.S.E.; Dauphin, Y.; Keysers, D.; Neumann, M.; Cisse, M.; Quinn, J. Continental-Scale Building Detection from High Resolution Satellite Imagery. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.12283. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; He, C.; Fang, J.; Zheng, J.; Fu, H.; Yu, L. Semantic Segmentation-Based Building Footprint Extraction Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Images and Multi-Source GIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, M.; Yan, Q.; Awrangjeb, M.; Sirmacek, B.; Demir, N. Precise Extraction of Buildings from High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Images Based on Semantic Edges and Segmentation. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 42, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmanis, D.; Schindler, K.; Wegner, J.D.; Galliani, S.; Datcu, M.; Stilla, U. Classification with an edge: Improving semantic image segmentation with boundary detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Guo, Z.; Shi, X.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Y.; Shibasaki, R.; Shao, X. A Boundary Regulated Network for Accurate Roof Segmentation and Outline Extraction. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResUNet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, H.; Samadzadegan, F.; Javan, F.D. A Novel Boundary Loss Function in Deep Convolutional Networks to Improve the Buildings Extraction From High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4437–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Mou, L.; Hua, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jin, P.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Instance segmentation of buildings using keypoints. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xin, Q.; Sun, Y.; Cao, M. A deep learning-based framework for automated extraction of building footprint polygons from very high-resolution aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Waslander, S.L.; Liu, X. An end-to-end shape modeling framework for vectorized building outline generation from aerial images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 170, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelmans, L.; Janssen, L.; Hambsch, L. Landgebruik en Ruimtebeslag in Vlaanderen, Toestand 2019, Uitgevoerd in Opdracht van het Vlaams Planbureau voor Omgeving; Vlaams Planbureau voor Omgeving: Brussel, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2015, 9, 16591–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 10691–10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei-Fei, L.; Deng, J.; Li, K. ImageNet: Constructing a large-scale image database. J. Vis. 2010, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.G.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C. Recalibrating Fully Convolutional Networks with Spatial and Channel ‘Squeeze & Excitation’ Blocks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubovskiy, P. Segmentation Models Pytorch. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/qubvel/segmentation_models.pytorch (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. NeurIPS 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Carlinet, E.; Chazalon, J.; Mallet, C.; Dumenieu, B.; Perret, J. Vectorization of historical maps using deep edge filtering and closed shape extraction. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR’21), Lausanne, Switzerland, 5–10 September 2021; pp. 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. scikit-image: Image processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Cheung, C.K. Performance Evaluation of Line Simplification Algorithms for Vector Generalization. Cartogr. J. 2006, 43, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Rother, C.; Dollar, P. Panoptic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9396–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Informatie Vlaanderen. Large-Scale Reference Database (LRD). 2021. Available online: https://overheid.vlaanderen.be/en/producten-diensten/large-scale-reference-database-lrd (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. (ECCV) 2018, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Ma-net: A multi-scale attention network for liver and tumor segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179656–179665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2018, BMVC 2018, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6230–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: Redesigning Skip Connections to Exploit Multiscale Features in Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Partition | Location | Total Area [km] | Roof Parts | Roof-Part Area [km] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Brugge | 0.72 | 26,984 | 0.34 |
| Validation | Jabbeke | 0.18 | 1629 | 0.04 |
| Test | Lokeren | 3.65 | 27,303 | 0.68 |
| Dilation [pix] | Smoothing | Loss Weight | Edge IoU [%] | PQ [%] | SQ [%] | RQ [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | - | + | 24.87 | 34.67 | 83.89 | 41.33 |
| 5 | √ | + | 24.72 | 36.19 | 84.26 | 42.95 |
| 5 | - | ++ | 17.88 | 37.27 | 84.26 | 44.23 |
| 5 | √ | ++ | 18.02 | 37.20 | 84.48 | 44.04 |
| 11 | - | + | 39.80 | 37.84 | 84.55 | 44.75 |
| 11 | √ | + | 39.64 | 37.84 | 84.55 | 44.75 |
| 11 | - | ++ | 32.01 | 37.84 | 84.54 | 44.75 |
| 11 | √ | ++ | 31.22 | 36.93 | 83.98 | 43.97 |
| Model Type | Input | IoU [%] | Roof Mask Usage | PQ [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Edge | Object | Edge | ||||
| double | D 1 | D | 49.4 | 16.2 | WM 3 | 10.6 | |
| AT 4 | 22.2 | ||||||
| RGB | RGB | 68.3 | 31.7 | WM | 37.8 | ||
| AT | 47.1 | ||||||
| RGB-LRD2 | RGB | 83.5 | 31.7 | WM | 44.3 | ||
| AT | 45.8 | ||||||
| RGB + D | RGB + D | 71.9 | 34.4 | WM | 35.6 | ||
| AT | 46.6 | ||||||
| Single multilabel | RGB | 67.2 | 23.5 | AT | 43.3 | ||
| RGB + D | 74.0 | 25.4 | AT | 46.6 | |||
| Single multiclass | RGB | 67.2 | 31.0 | DV 5 | 40.3 | ||
| AT | 47.0 | ||||||
| RGB + D | 70.4 | 31.3 | DV | 42.4 | |||
| AT | 50.0 | ||||||
| Model | Decoder Parameters | PQ [%] |
|---|---|---|
| DeepLabV3+ | 46.7 | |
| FPN | 47.9 | |
| MAnet | 49.7 | |
| PAN | 45.2 | |
| PSPNet | 32.4 | |
| UNet | 50.0 | |
| UNet++ | 49.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van den Broeck, W.A.J.; Goedemé, T. Combining Deep Semantic Edge and Object Segmentation for Large-Scale Roof-Part Polygon Extraction from Ultrahigh-Resolution Aerial Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194722
Van den Broeck WAJ, Goedemé T. Combining Deep Semantic Edge and Object Segmentation for Large-Scale Roof-Part Polygon Extraction from Ultrahigh-Resolution Aerial Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194722
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan den Broeck, Wouter A. J., and Toon Goedemé. 2022. "Combining Deep Semantic Edge and Object Segmentation for Large-Scale Roof-Part Polygon Extraction from Ultrahigh-Resolution Aerial Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194722
APA StyleVan den Broeck, W. A. J., & Goedemé, T. (2022). Combining Deep Semantic Edge and Object Segmentation for Large-Scale Roof-Part Polygon Extraction from Ultrahigh-Resolution Aerial Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194722