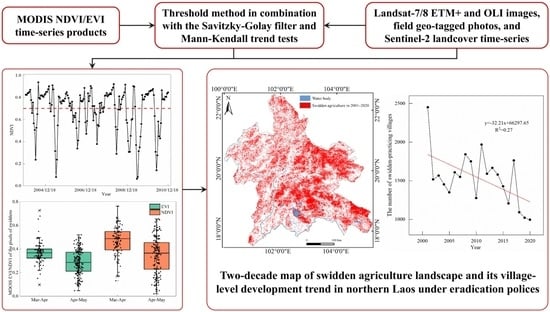
Swidden Agriculture Landscape Mapping Using MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series and Its Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Northern Laos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. MODIS Vegetation Indices Products and Preprocessing
3.2. Landsat-8 Surface Reflectance and Sampling Selection
3.3. Sentinel-2 10 m Land Use and Land Cover Products
3.4. Samples Selection of Swidden Agriculture Landscape Using the Mann-Kendall Trend Test
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Threshold Ranges of Vegetation Indices for Detecting Swidden Agriculture Landscape
4.2. Annual Changes in Swidden Agriculture Landscape in Northern Laos
4.3. Village-Level Changes in Swidden Agriculture Landscape in Northern Laos
5. Discussion
5.1. Potential and Limitations of MODIS Vegetation Indices in Mapping Swidden Agriculture Landscape
5.2. Enhancing Remote Sensing of Swidden Agriculture in Transition in the Tropics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Vliet, N.; Mertz, O.; Heinimann, A.; Langanke, T.; Pascual, U.; Schmook, B.; Adams, C.; Schmidt-Vogt, D.; Messerli, P.; Leisz, S.; et al. Trends, drivers and impacts of changes in swidden cultivation in tropical forest-agriculture frontiers: A global assessment. Glob. Environ. Change 2012, 22, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liao, C.; Zhang, J. A review of swidden agriculture in Southeast Asia. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1654–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinimann, A.; Mertz, O.; Frolking, S.; Egelund Christensen, A.; Hurni, K.; Sedano, F.; Parsons Chini, L.; Sahajpal, R.; Hansen, M.; Hurtt, G. A global view of shifting cultivation: Recent, current, and future extent. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e184479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dove, M.R. The view of swidden agriculture, by the early naturalists Linnaeus and Wallace. In Shifting Cultivation and Environmental Change: Indigenous People, Agriculture and Forest Conservation; Cairns, M.F., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- FAO Staff. Shifting cultivation. Unasylva 1957, 11, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Agenda 21. United Nations Conference on Environment & Development; United Nations: Rio de Janerio, Brazil, 1992; p. 351. [Google Scholar]
- Tomich, T.P.; Timmer, D.W.; Velarde, S.J.; Alegre, J.; Areskoug, V.; Cash, D.W.; Cattaneo, A.; Ericksen, P.; Joshi, L.; Kasyoki, J.; et al. Integrative science in practice: Process perspectives from ASB, the Partnership for the Tropical Forest Margins. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brady, N.C. Alternatives to slash-and-burn: A global imperative. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 58, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.R.; Challinor, A.J.; Henriksen, C.B.; Howden, S.M.; Martre, P.; Smith, P. Invited review: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, agriculture, and food-A case of shifting cultivation and history. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2518–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, R.; Dhyani, S.; Basu, M.; Kadaverugu, R.; Hashimoto, S.; Kumar, P.; Johnson, B.A.; Takahashi, Y.; Mitra, B.K.; Avtar, R.; et al. Exploring Indigenous and Local Knowledge and Practices (ILKPs) in Traditional Jhum Cultivation for Localizing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Case Study from Zunheboto District of Nagaland, India. Environ. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, O. Trends in shifting cultivation and the REDD mechanism. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2009, 1, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, J. Agroforestry and the search for alternatives to slash-and-burn cultivation: From technological optimism to a political economy of deforestation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiao, C.; Feng, Z. Swidden agriculture in transition and its roles in tropical forest loss and industrial plantation expansion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y. The Impact of the Financial Crisis on Developing Countries; License: CC BY 3.0 IGO; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/26129 (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Dressler, W.; Wilson, D.; Clendenning, J.; Cramb, R.; Mahanty, S.; Lasco, R.; Keenan, R.; To, P.; Gevana, D. Examining how long fallow swidden systems impact upon livelihood and ecosystem services outcomes compared with alternative land-uses in the uplands of Southeast Asia. J. Dev. Eff. 2015, 7, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reang, D.; Hazarika, A.; Sileshi, G.W.; Pandey, R.; Das, A.K.; Nath, A.J. Assessing tree diversity and carbon storage during land use transitioning from shifting cultivation to indigenous agroforestry systems: Implications for REDD+ initiatives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.M.N.; Carreiras, J.M.B.; Rosa, I.; Pereira, J.M.C. Greenhouse gas emissions from shifting cultivation in the tropics, including uncertainty and sensitivity analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borah, J.R.; Evans, K.L.; Edwards, D.P. Quantifying carbon stocks in shifting cultivation landscapes under divergent management scenarios relevant to REDD+. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutrieux, L.P.; Jakovac, C.C.; Latifah, S.H.; Kooistra, L. Reconstructing land use history from Landsat time-series: Case study of a swidden agriculture system in Brazil. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 47, 112–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mertz, O.; Padoch, C.; Fox, J.; Cramb, R.A.; Leisz, S.J.; Lam, N.T.; Vien, T.D. Swidden change in Southeast Asia: Understanding causes and consequences. Hum. Ecol. 2009, 37, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, N.; Mertz, O.; Birch-Thomsen, T.; Schmook, B. Is there a continuing rationale for swidden cultivation in the 21st century? Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottrup, C.; Rasmussen, M.S.; Eklundh, L.; Jönsson, P. Mapping fractional forest cover across the highlands of mainland Southeast Asia using MODIS data and regression tree modelling. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 28, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuyper, M.; Chávez, R.O.; Lohbeck, M.; Lastra, J.A.; Tsendbazar, N.; Hackländer, J.; Herold, M.; Vågen, T. Continuous monitoring of forest change dynamics with satellite time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, P.; Feng, Z. Remote sensing of swidden agriculture in the tropics: A review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2022, 112, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, A.R.; Karale, Y.; Cummings, G.R.; Hamer, E.; Moses, P.; Norman, Z.; Captain, V. UAV-derived data for mapping change on a swidden agriculture plot: Preliminary results from a pilot study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2066–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; De Leeuw, J.; Skidmore, A.K.; Prins, H.H.T.; Liu, Y. Comparison of MODIS and Landsat TM5 images for mapping tempo-spatial dynamics of Secchi disk depths in Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 2183–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky–Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Prasad, A.K.; El-Askary, H.; Lee, W.; Kwak, D.; Lee, S.; Kafatos, M. Application of the Savitzky-Golay filter to land cover classification using temporal MODIS vegetation indices. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2014, 80, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsalyuk, M.; Kelly, M.; Getz, W.M. Improving the prediction of African savanna vegetation variables using time series of MODIS products. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2017, 131, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. A simple method to improve the quality of NDVI time-series data by integrating spatiotemporal information with the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, K.; Hett, C.; Heinimann, A.; Messerli, P.; Wiesmann, U. Dynamics of shifting cultivation landscapes in northern Lao PDR between 2000 and 2009 based on an analysis of MODIS time series and Landsat images. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padoch, C.; Coffey, K.; Mertz, O.; Leisz, S.J.; Fox, J.; Wadley, R.L. The demise of swidden in Southeast Asia? Local realities and regional ambiguities. Geogr. Tidsskr.-Dan. J. Geogr. 2007, 107, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao Statistics Bureau. Vientiane Capital: Laos Statistical Information Service. In Statistical Yearbook 2021; Lao Statistics Bureau: Vientiane, Laos, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplot, V.; Khampaseuth, X.; Valentin, C.; Bissonnais, Y.L. Interrill erosion in the sloping lands of northern Laos subjected to shifting cultivation. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2007, 32, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, K.; Kontgis, C.; Statman-Weil, Z.; Mazzariello, J.C.; Mathis, M.; Brumby, S.P. Global land use/land cover with Sentinel 2 and deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; IEEE: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 4704–4707. [Google Scholar]
- Keonuchan, K. The Adoption of New Agricultural Practices in Northern Laos: A Political Ecology of Shifting Cultivation. Doctoral Dissertation; University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2000; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Lao PDR. National Poverty Eradication Programme (NPEP); Lao PDR: Vientiane, Laos, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- MAF. Framework of Strategic Vision on Forest Resources Management to the Year 2020; Ministère de l’Agriculture et des Forêts: Vientiane, Laos, 2000.
- Thanichanon, P.; Schmidt-Vogt, D.; Epprecht, M.; Heinimann, A.; Wiesmann, U. Balancing cash and food: The impacts of agrarian change on rural land use and wellbeing in Northern Laos. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e209166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemaru, K.; Muhammad, R.; Hirota, I. Analysis of Monsoon Climate Variability for Swidden Agriculture in Northern Laos. In Integrated Studies of Social and Natural Environmental Transition in Laos. Advances in Asian Human-Environmental Research; Yokoyama, S., Okamoto, K., Takenaka, C., Hirota, I., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, C.J. Remote sensing of leaf water content in the near infrared. Remote Sens. Environ. 1980, 10, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Liu, H.; van Leeuwen, W.J.D. The use of vegetation indices in forested regions: Issues of linearity and saturation. IGARSS’97. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings. Remote Sensing-A Scientific Vision for Sustainable Development, 3–8 August 1997, Singapore; IEEE: Singapore, 1997; Volume 4, pp. 1966–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Hollinger, D.; Aber, J.; Goltz, M.; Davidson, E.A.; Zhang, Q.; Moore, B. Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in an evergreen needleleaf forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.J.L.; Caselles, V. Mapping burns and natural reforestation using Thematic Mapper data. Geocarto Int. 1991, 6, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Dutta, S. Vegetation dynamics from denoised NDVI using empirical mode decomposition. J. Indian Soc. Remote 2013, 41, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Giglio, L.; Huang, H.; Zubkova, M.; Humber, M.L. Global validation of the collection 6 MODIS burned area product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liang, T.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z. Validation of MODIS snow cover products using Landsat and ground measurements during the 2001–2005 snow seasons over northern Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Seo, B.; Narantsetseg, A.; Han, Y. Estimating fractional green vegetation cover of Mongolian grasslands using digital camera images and MODIS satellite vegetation indices. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hett, C.; Castella, J.; Heinimann, A.; Messerli, P.; Pfund, J. A landscape mosaics approach for characterizing swidden systems from a REDD+ perspective. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mudi, S.; Behera, M.D.; Barik, S.K.; Mishra, D.R.; Roy, P.S. Automated mapping for long-term analysis of shifting cultivation in Northeast India. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, K.; Fensholt, R. Exploring patterns and effects of aerosol quantity flag anomalies in MODIS surface reflectance products in the tropics. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3495–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, Z. Extent and area of swidden in Montane Mainland Southeast Asia: Estimation by multi-step thresholds with Landsat-8 OLI data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dove, M.R. Swidden Agriculture in Indonesia: The Subsistence Strategies of the Kalimantan Kant’; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Carmenta, R.; Vermeylen, S.; Parry, L.; Barlow, J. Shifting cultivation and fire policy: Insights from the Brazilian Amazon. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Vogt, D.; Leisz, S.J.; Mertz, O.; Heinimann, A.; Thiha, T.; Messerli, P.; Epprecht, M.; Cu, P.V.; Chi, V.K.; Hardiono, M.; et al. An assessment of trends in the extent of swidden in Southeast Asia. Hum. Ecol. 2009, 37, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.J.; Reang, D.; Sileshi, G.W. The shifting cultivation juggernaut: An attribution problem. Glob. Chall. 2022, 6, 2200051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Robayo, K.J.; Méndez-López, M.E.; Molina-Villegas, A.; Juárez, L. What do we talk about when we talk about milpa? A conceptual approach to the significance, topics of research and impact of the mayan milpa system. J. Rural. Stud. 2020, 77, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D. The Politics of Swidden Farming: Environment and Development in Eastern India; Anthem Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]








| 2001–2010 | 2011–2020 | 2001–2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| March–April | April–May | March–April | April–May | March–April | April–May | |
| EVI | 0.3668 | 0.3055 | 0.3718 | 0.2709 | 0.3676 | 0.2892 |
| NDVI | 0.4558 | 0.3629 | 0.4940 | 0.3307 | 0.4683 | 0.3469 |
| Landsat Path/Row and Classes | NDVI-Based Mapping of SAL | EVI-Based Mapping of SAL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swidden | Non-Swidden | Total | Swidden | Non-Swidden | Total | ||
| 130/046 (2013) | Swidden | 123 | 0 | 123 | 66 | 0 | 66 |
| Non-swidden | 90 | 223 | 313 | 147 | 223 | 370 | |
| Total | 213 | 223 | 436 | 213 | 223 | 436 | |
| Overall accuracy | 79.36% | 66.28% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.58 | 0.31 | |||||
| 128/047 (2013) | Swidden | 114 | 0 | 114 | 108 | 0 | 108 |
| Non-swidden | 70 | 188 | 258 | 76 | 188 | 264 | |
| Total | 184 | 188 | 372 | 184 | 188 | 372 | |
| Overall accuracy | 81.18% | 79.57% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.62 | 0.59 | |||||
| 129/045 (2013) | Swidden | 78 | 0 | 78 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| Non-swidden | 48 | 108 | 156 | 76 | 108 | 184 | |
| Total | 126 | 108 | 234 | 126 | 108 | 234 | |
| Overall accuracy | 79.49% | 67.52% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.60 | 0.38 | |||||
| 129/046 (2003) | Swidden | 159 | 1 | 160 | 148 | 1 | 149 |
| Non-swidden | 104 | 249 | 353 | 115 | 249 | 364 | |
| Total | 263 | 250 | 513 | 263 | 250 | 513 | |
| Overall accuracy | 79.53% | 77.39% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.59 | 0.55 | |||||
| 129/046 (2008) | Swidden | 200 | 1 | 201 | 154 | 0 | 154 |
| Non-swidden | 133 | 320 | 453 | 179 | 321 | 500 | |
| Total | 333 | 321 | 654 | 333 | 321 | 654 | |
| Overall accuracy | 79.51% | 72.63% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.59 | 0.46 | |||||
| 129/046 (2012) | Swidden | 245 | 1 | 246 | 144 | 0 | 144 |
| Non-swidden | 185 | 423 | 608 | 286 | 424 | 710 | |
| Total | 430 | 424 | 854 | 430 | 424 | 854 | |
| Overall accuracy | 78.22% | 66.51% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.57 | 0.33 | |||||
| 129/046 (2016) | Swidden | 174 | 0 | 174 | 66 | 0 | 66 |
| Non-swidden | 124 | 299 | 423 | 232 | 299 | 531 | |
| Total | 298 | 299 | 597 | 298 | 299 | 597 | |
| Overall accuracy | 79.23% | 61.14% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.58 | 0.22 | |||||
| 129/046 (2020) | Swidden | 99 | 0 | 99 | 37 | 1 | 38 |
| Non-swidden | 69 | 153 | 222 | 131 | 152 | 283 | |
| Total | 168 | 153 | 321 | 168 | 153 | 321 | |
| Overall accuracy | 78.50% | 58.88% | |||||
| Kappa | 0.58 | 0.21 | |||||
| 2005 | 2010 | 2018–2020 | Swidden Agriculture Restart in 2011 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percent/% | Count | Percent/% | Count | Percent/% | Count | Percent/% | |
| Villages | 1350 | 55.08 | 1174 | 47.90 | 1318 | 53.77 | 735 | 62.61 |
| Districts | 2 | 2.02 | 3 | 3.03 | 4 | 4.04 | 3 | 100.00 |
| 0 | 1–5 Years | 5–10 Years | 10–20 Years | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percent/% | Count | Percent/% | Count | Percent/% | Count | Percent/% | |
| Villages | 957 | 38.57 | 110 | 4.43 | 300 | 12.09 | 1084 | 43.69 |
| Districts | 91 | 91.92 | 3 | 3.03 | 5 | 5.05 | 0 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Yang, Y. Swidden Agriculture Landscape Mapping Using MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series and Its Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Northern Laos. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236173
Li P, Yang Y. Swidden Agriculture Landscape Mapping Using MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series and Its Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Northern Laos. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236173
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peng, and Yin Yang. 2022. "Swidden Agriculture Landscape Mapping Using MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series and Its Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Northern Laos" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236173
APA StyleLi, P., & Yang, Y. (2022). Swidden Agriculture Landscape Mapping Using MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series and Its Spatio-Temporal Dynamics in Northern Laos. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236173