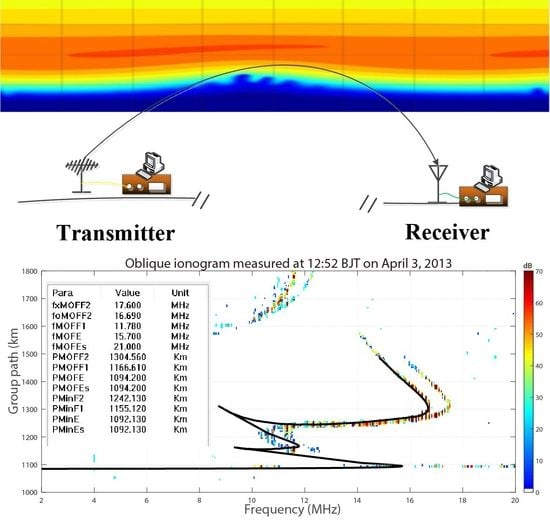
A Method for Automatic Inversion of Oblique Ionograms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Automatic Scaling Key Parameters from Measured Oblique Ionograms
2.2. Synthesizing Oblique Ionogram through the QPS Model
2.3. Matching Measured Oblique Ionograms with Synthesized Oblique Traces
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reinisch, B.W.; Galkin, I.A.; Khmyrov, G.M.; Kozlov, A.V.; Bibl, K.; Lisysyan, I.A.; Cheney, G.P.; Huang, X.; Kitrosser, D.F.; Paznukhov, V.V.; et al. New Digisonde for research and monitoring applications. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, RS0A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, M.T.; Wright, J.W.; Zabotin, N.; Pitteway, M.L.V. The Tromsø dynasonde. Polar Sci. 2008, 2, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDougall, J.W.; Grant, I.F.; Shen, X. The Canadian advanced digital ionosonde: Design and results. In Report UAG-14: Ionospheric Networks and Stations, World Data Center A for Solar-Terrestrial Physics; UAG-104, Ionosonde Network Advisory Group: Lowell, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zuccheretti, E.; Tutone, G.; Sciacca, U.; Bianchi, C.; Arokiasamy, B.J. The new AIS-INGV digital ionosonde. Ann. Geophys. Italy 2003, 46, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yang, G.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Wuhan Ionospheric Oblique Backscattering Sounding System and Its Applications—A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinisch, B.W.; Huang, X. Automatic calculation of electron density profiles from digital ionograms: 3. Processing of bottomside ionograms. Radio Sci. 1983, 18, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabotin, N.A.; Wright, J.W.; Zhbankov, G.A. NeXtYZ: Three-dimensional electron density inversion for dynasonde ionograms. Radio Sci. 2006, 41, RS6S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillat, V.G.; Guimaraes, L.N.F.; Fagundes, P.R.; da Silva, J.D.S. A computational tool for ionosonde CADI’s ionogram analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto, C.; Pezzopane, M. A software for automatic scaling of foF2 and MUF(3000)F2 from ionograms. In Proceedings of the URSI 2002, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 17–24 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, P.; Lan, T.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Software for scaling and analysis of vertical incidence ionograms-ionoScaler. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.S. The calculation of ionospheric profiles from data given on oblique incidence ionograms. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1970, 32, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bennett, J.A.; Dyson, P.L. Synthesis of oblique ionograms from vertical ionograms using quasi-parabolic segment models of the ionosphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1992, 54, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanivong, B.; Chen, J.; Dyson, P.L.; Bennett, J.A. Inversion of oblique ionograms including the earth’s magnetic field. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1995, 57, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Reinisch, B.W.; Kuklinski, W.S. Mid-point electron density profiles from oblique ionograms. Ann. Geophys. Italy 1996, 49, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, N.J. Image understanding of oblique ionograms: The autoscaling problem. In Proceedings of the IEEE Australian and New Zealand Conference on Intelligent Information Systems, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 18–20 November 1996; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Lu, Z.; Jiao, P. The intelligentized recognition of oblique propagation modes. Chin. J. Radio Sci. 2009, 24, 528. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settimi, A.; Pezzopane, M.; Pietrella, M.; Bianchi, C.; Scotto, C.; Zuccheretti, E.; Makris, J. Testing the IONORT-ISP system: A comparison between synthesized and measured oblique ionograms. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, A.; Scotto, C.; Francis, M.; Settimi, A.; Cesaronl, C. Automatic interpretation of oblique ionograms. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, A.J.; Gardiner-Garden, R.S. A robust feature extraction and parameterized fitting algorithm for bottom-side oblique and vertical incidence ionograms. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zou, X. An automatic scaling method for obtaining the trace and parameters from oblique ionogram based on hybrid genetic algorithm. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 1838–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, T.A.; Hoogasian, H. Exact ray calculations in a quasi-parabolic ionosphere with no magnetic field. Radio Sci. 1968, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, P.L.; Bennett, J.A. A model of the vertical distribution of the electron concentration in the ionosphere and its application to oblique propagation studies. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1988, 50, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethinga, P.J.D.; Maliphant, R.G. Unz’s application of Schlomilch’s integral equation to oblique incidence observations. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1967, 29, 599–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, M.; Kolesar, J. A method for real height analysis of oblique ionograms. Radio Sci. 1989, 24, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Sun, H. An automatic scaling technique for obtaining F2 parameters and F1 critical frequency from vertical incidence ionograms. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Sun, H.; Zhou, C. A method for the automatic calculation of electron density profiles from vertical incidence ionograms. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2014, 107, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilitza, D.; Altadill, D.; Truhlik, V.; Shubin, V.; Galkin, I.; Reinisch, B.; Huang, X. International Reference Ionosphere 2016: From ionospheric climate to real-time weather predictions. Soc. Work. 2017, 15, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, B.; Coisson, P.; Radicella, S.M. A new version of the NeQuick ionosphere electron density model. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, K.J.W. Histogram-based ionogram displays and their application to autoscaling. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, A.; Scotto, C.; Sabbagh, D.; Sgrigna, V.; Maher, P. A procedure for the reliability improvement of the oblique ionograms automatic scaling algorithm. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Item | fxMOFF2 | foMOFF2 | PminF2 | fMOFE | PminE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptable values | 96.34% | 91.98% | 86.41% | 60.05% | 96.75% |
| Total number of oblique ionograms | 795 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Z. A Method for Automatic Inversion of Oblique Ionograms. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071671
Jiang C, Zhao C, Zhang X, Liu T, Chen Z, Yang G, Zhao Z. A Method for Automatic Inversion of Oblique Ionograms. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071671
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Chunhua, Cong Zhao, Xuhui Zhang, Tongxin Liu, Ziwei Chen, Guobin Yang, and Zhengyu Zhao. 2022. "A Method for Automatic Inversion of Oblique Ionograms" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071671
APA StyleJiang, C., Zhao, C., Zhang, X., Liu, T., Chen, Z., Yang, G., & Zhao, Z. (2022). A Method for Automatic Inversion of Oblique Ionograms. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071671