Mapping Impervious Surface Using Phenology-Integrated and Fisher Transformed Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology
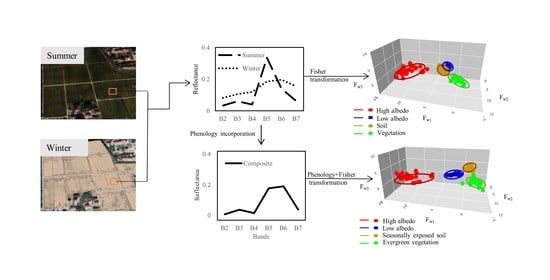
2.2.1. Workflow
2.2.2. Image Pre-Processing
2.2.3. Endmember Model and Phenological Information Integration
2.2.4. Endmember Selection
2.2.5. Spectral Transformation Using Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis
2.2.6. Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis in Fisher Feature Space
2.2.7. Validation
3. Results
3.1. Endmember Discrimination by Phenology Integration and Fisher Transformation
3.2. Endmember Fractions and Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Phenology Combined with Fisher Transformation to Enhance the ISA Extraction
4.2. Advantages and Limitation Compared with Other ISA Products
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, J.O.; Song, X.-P.; Huang, C.; Channan, S.; Baker, M.E.; Townshend, J.R. Urban growth of the Washington, DC–Baltimore, MD metropolitan region from 1984 to 2010 by annual, Landsat-based estimates of impervious cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Zong, J.; Xiao, X. Assessing spatial-temporal dynamics of urban expansion, vegetation greenness and photosynthesis in megacity Shanghai, China during 2000–2016. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Berry, J. Tracking spatial-temporal landscape changes of impervious surface areas, bare lands, and inundation areas in China during 2001–2017. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious Surface Coverage: The Emergence of a Key Environmental Indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, G.; Fatichi, S.; Schläpfer, M.; Yu, K.; Crowther, T.W.; Meili, N.; Burlando, P.; Katul, G.G.; Bou-Zeid, E. Magnitude of urban heat islands largely explained by climate and population. Nature 2019, 573, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzat, A.; Fischer, L.K.; Kowarik, I. Unexploited opportunities in understanding liveable and biodiverse cities. A review on urban biodiversity perception and valuation. Glob. Environ. Change 2016, 39, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Li, X.; Dewals, B. Experimental modelling of urban flooding: A review. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sattar, A.; Goswami, A.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Emmer, A. Lake Evolution, Hydrodynamic Outburst Flood Modeling and Sensitivity Analysis in the Central Himalaya: A Case Study. Water 2020, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schinasi, L.H.; Benmarhnia, T.; De Roos, A. Modification of the association between high ambient temperature and health by urban microclimate indicators: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ning, G.; Xu, B. Production of global daily seamless data cubes and quantification of global land cover change from 1985 to 2020-iMap World 1.0. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Johnson, P.E. Spectral mixture modeling: A new analysis of rock and soil types at the Viking Lander 1 site. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 8098–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R.O. Mapping chaparral in the Santa Monica Mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, Z.; Deng, J.; Gan, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, K. Mapping Impervious Surfaces in Town–Rural Transition Belts Using China’s GF-2 Imagery and Object-Based Deep CNNs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Gong, P. An “exclusion-inclusion” framework for extracting human settlements in rapidly developing regions of China from Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Qi, S.; Tao, S.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y. An efficient approach to capture continuous impervious surface dynamics using spatial-temporal rules and dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, R.; Burazerovic, D.; Scheunders, P. Non-Linear Spectral Unmixing by Geodesic Simplex Volume Maximization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitraka, Z.; Del Frate, F.; Carbone, F. Nonlinear Spectral Unmixing of Landsat Imagery for Urban Surface Cover Mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3340–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridd, M.K. Exploring a V-I-S (vegetation-impervious surface-soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: Comparative anatomy for cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2165–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhu, Z. Continuous subpixel monitoring of urban impervious surface using Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 110929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, C.; Cao, L.; Zhu, F.; Meng, X.; Wu, J. Impacts of landscape structure on surface urban heat islands: A case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3249–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Normalized spectral mixture analysis for monitoring urban composition using ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Murray, A.T. Estimating impervious surface distribution by spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Asner, G.P.; Tits, L.; Coppin, P. Endmember variability in Spectral Mixture Analysis: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rivard, B.; Sánchez-Azofeifa, A.; Castro-Esau, K. Intra- and inter-class spectral variability of tropical tree species at La Selva, Costa Rica: Implications for species identification using HYDICE imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C. Spectral mixture analysis for subpixel vegetation fractions in the urban environment: How to incorporate endmember variability? Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, C. A spatially adaptive spectral mixture analysis for mapping subpixel urban impervious surface distribution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Delalieux, S.; Verstraeten, W.W.; van Aardt, J.A.N.; Albrigo, G.L.; Coppin, P. An automated waveband selection technique for optimized hyperspectral mixture analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5549–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rivard, B.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, A. Derivative spectral unmixing of hyperspectral data applied to mixtures of lichen and rock. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsoi, R.; Imbiriba, T.; Bermudez, J.C.; Richard, C.; Chanussot, J.; Drumetz, L.; Tourneret, J.-Y.; Zare, A.; Jutten, C. Spectral variability in hyperspectral data unmixing: A comprehensive review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 9, 223–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X. Medium Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery for Estimating and Mapping Urban Impervious Surfaces Using LSMA and ANN. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. A Novel Approach Based on Fisher Discriminant Null Space for Decomposition of Mixed Pixels in Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Somers, B. Mapping impervious surface fractions using automated Fisher transformed unmixing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. Multisensor Characterization of Urban Morphology and Network Structure. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T.; Yang, W. Temporal mixture analysis for estimating impervious surface area from multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data in Japan. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 72, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Wu, C. Phenology-based temporal mixture analysis for estimating large-scale impervious surface distributions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Shi, Q.; Tao, H.; Zheng, J.; Li, Q. An improved temporal mixture analysis unmixing method for estimating impervious surface area based on MODIS and DMSP-OLS data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Urbanization diversifies land surface phenology in arid environments: Interactions among vegetation, climatic variation, and land use pattern in the Phoenix metropolitan region, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Li, J. Impacts of urbanization on vegetation phenology over the past three decades in Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Li, J. Deriving Annual Double-Season Cropland Phenology Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, S.M.S. Shanghai Statistical Yearbook 2016; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ciais, P.; Lin, P.; Gong, K.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chen, A.; et al. High-spatiotemporal-resolution mapping of global urban change from 1985 to 2015. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Kuang, S.; He, Y.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Song, C.; Anderson, P.; Łowicki, D. Plant Diversity Along the Urban–Rural Gradient and Its Relationship with Urbanization Degree in Shanghai, China. Forests 2020, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Sha, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, L. Modeling the impacts of alternative fertilization methods on nitrogen loading in rice production in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Joseph Hughes, M.; Laue, B. Cloud detection algorithm comparison and validation for operational Landsat data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H. A study on information extraction of water body with the modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2006, 5, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, G.; Shi, H.; Dewitz, J.; Wu, Z. Performances of WorldView 3, Sentinel 2, and Landsat 8 data in mapping impervious surface. Remote Sens. Appl. 2019, 15, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, K.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y.; Du, P. Comparison of surface water extraction performances of different classic water indices using OLI and TM imageries in different situations. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 18, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Zortea, M.; Plaza, A.; Asner, G.P. Automated extraction of image-based endmember bundles for improved spectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tompkins, S. Optimization of endmembers for spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Lu, D. Extracting impervious surfaces from medium spatial resolution multispectral and hyperspectral imagery: A comparison. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3209–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Li, C.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, W.; Xi, L. Subpixel urban impervious surface mapping: The impact of input Landsat images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.L.; Younan, N.H. Pixel Unmixing via Information of Neighboring Pixels. GIScience Remote Sens. 2006, 43, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degerickx, J.; Okujeni, A.; Iordache, M.-D.; Hermy, M.; van der Linden, S.; Somers, B. A Novel Spectral Library Pruning Technique for Spectral Unmixing of Urban Land Cover. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, C. Automated construction of multiple regional libraries for neighborhoodwise local multiple endmember unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4232–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Qi, H. Endmember Extraction from Highly Mixed Data Using Minimum Volume Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, T.; Weeks, J.R.; Roberts, D.; Rogan, J.; Powell, R. Measuring the physical composition of urban morphology using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. An Orthogonal Fisher Transformation-Based Unmixing Method Toward Estimating Fractional Vegetation Cover in Semiarid Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, Q.; Lu, H.; Ma, S. Solving the small sample size problem of LDA. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 August 2002; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; Song, C.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal pattern of urbanization in Shanghai, China between 1989 and 2005. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1545–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.O.; Johnson, P.E.; Adams, J.B. Quantitative determination of mineral types and abundances from reflectance spectra using principal components analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.Y.; Li, M.-H. Considering plant phenology for improving the accuracy of urban impervious surface mapping in a subtropical climate regions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Luo, H.; Yao, Y. Optimizing Subpixel Impervious Surface Area Mapping Through Adaptive Integration of Spectral, Phenological, and Spatial Features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, B. Development of a global 30-m impervious surface map using multi-source and multi-temporal remote sensing datasets with the Google Earth Engine platform. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Use of impervious surface in urban land-use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Deng, Y. Enhancing endmember selection in multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (MESMA) for urban impervious surface area mapping using spectral angle and spectral distance parameters. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Liang, L. A 30-year (1984–2013) record of annual urban dynamics of Beijing City derived from Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 166, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reba, M.; Seto, K.C. A systematic review and assessment of algorithms to detect, characterize, and monitor urban land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Date | Image ID in GEE |
|---|---|
| 08/03/2015 | LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_SR/LC08_118038_20150803 |
| 08/03/2015 | LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_SR/LC08_118039_20150803 |
| 02/27/2016 | LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_SR/LC08_118038_20160227 |
| 02/27/2016 | LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_SR/LC08_118039_20160227 |
| w1 | w2 | w3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue (Summer image) | 0.006049 | −0.00178 | 0.006383 |
| Green (Summer image) | −0.00804 | 0.014469 | −0.01551 |
| Red (Summer image) | 0.00883 | −0.01271 | 0.009168 |
| NIR (Winter image) | −0.00344 | 0.002205 | 0.003375 |
| SWIR1 (Winter image) | −0.00038 | 0.000429 | −0.0046 |
| SWIR2 (Summer image) | 0.000697 | 0.001588 | 0.001412 |
| Proportion of trace | 0.8287 | 0.1601 | 0.0112 |
| w1 | w2 | w3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue (Winter image) | 0.000997 | 0.003179 | 0.003115 |
| Green (Winter image) | 0.002031 | −0.00903 | 0.00438 |
| Red (Winter image) | 0.001651 | 0.00643 | −0.00301 |
| NIR (Winter image) | −0.00339 | −0.00252 | 0.000207 |
| SWIR1 (Winter image) | 0.000964 | 0.000778 | −0.0025 |
| SWIR2 (Winter image) | 0.000206 | −0.00172 | −0.00056 |
| Proportion of trace | 0.7117 | 0.2574 | 0.0309 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, L.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, J.; Song, C.; Yu, Q.; Haase, D. Mapping Impervious Surface Using Phenology-Integrated and Fisher Transformed Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071673
Ouyang L, Wu C, Li J, Liu Y, Wang M, Han J, Song C, Yu Q, Haase D. Mapping Impervious Surface Using Phenology-Integrated and Fisher Transformed Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071673
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Linke, Caiyan Wu, Junxiang Li, Yuhan Liu, Meng Wang, Ji Han, Conghe Song, Qian Yu, and Dagmar Haase. 2022. "Mapping Impervious Surface Using Phenology-Integrated and Fisher Transformed Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071673
APA StyleOuyang, L., Wu, C., Li, J., Liu, Y., Wang, M., Han, J., Song, C., Yu, Q., & Haase, D. (2022). Mapping Impervious Surface Using Phenology-Integrated and Fisher Transformed Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071673