Comparative Study on Potential Landslide Identification with ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1A Data in Heavy Forest Reach, Upstream of the Jinsha River
Abstract
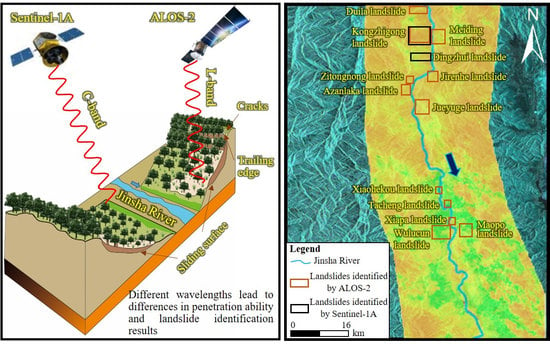
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. SBAS-InSAR Technology
2.4. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Potential Landslides
3.2. On-Site Investigation and Mechanism Analysis of Typical Landslides
3.2.1. Old Landslide Deformation Features
3.2.2. Integral Deforming Landslides
3.3. Deformation Results of KZG Landslide Based on SAR Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Ge, D.; Liang, R.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Identifying Potential Landslides by Stacking-InSAR in Southwestern China and Its Performance Comparison with SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, J. Mechanism of the catastrophic June 2017 landslide at Xinmo Village, Songping River, Sichuan Province, China. Landslides 2018, 15, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Comparisons of several methods for landslide susceptibility mapping: Case of the Benzilan and Waka Towns, Southwest China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Han, X.; Chen, J.; Bao, Y.; Peng, W. Numerical simulation of the Qulong Paleolandslide Dam event in the late pleistocene using the finite volume type shallow water model. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, I.J.; Montgomery, D.R. Landslide erosion coupled to tectonics and river incision. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, F.; Li, Z.; Mehmood, Q. Stability evaluation and potential damage of a giant paleo-landslide deposit at the East Himalayan Tectonic Junction on the Southeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 2117–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Chen, N.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Rahman, M. New insights into the occurrence of the Baige landslide along the Jinsha River in Tibet. Landslides 2020, 17, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.M.; Lan, H.X.; Li, L.P.; Cao, Y.M.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhou, C.D. Characteristics of a rapid landsliding area along Jinsha River revealed by multi-temporal remote sensing and its risks to Sichuan-Tibet railway. Landslides 2022, 19, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dai, F.; Lv, T.; Cui, Z. Holocene landslide-dammed lake deposits in the Upper Jinsha River, SE Tibetan Plateau and their ages. Quat. Int. 2013, 298, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Bao, Y.; et al. Numerical simulation of the Rongcharong paleolandslide river-blocking event: Implication for the longevity of the landslide dam. Landslides 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.S.G.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, N.; Ahmed, B.; Rabbi, M.F.; Rahman, R.M. Improving Spatial Agreement in Machine Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Xu, P.; Cao, C.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, X. Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, C.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, X.; Du, Y. Characteristics of the Residual Surface Deformation of Multiple Abandoned Mined-Out Areas Based on a Field Investigation and SBAS-InSAR: A Case Study in Jilin, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlacchini, S.; Ballabio, C.; Blahut, J.; Masetti, M.; Sorichetta, A. Spatial agreement of predicted patterns in landslide susceptibility maps. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Ardizzone, F.; Cardinali, M.; Galli, M. Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Mondini, A.C.; Peruccacci, S. Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; de la Fuente, J. Large-area landslide detection and monitoring with ALOS/PALSAR imagery data over Northern California and Southern Oregon, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Gong, W.; Gao, L.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z. An Interpretation Approach of Ascending-Descending SAR Data for Landslide Identification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Gong, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Xue, A.; Liao, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, L.; et al. Understanding Uneven Land Subsidence in Beijing, China, Using a Novel Combination of Geophysical Prospecting and InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Elliott, J.R.; Craig, T.J.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T.J. Improving the Resolving Power of InSAR for Earthquakes Using Time Series: A Case Study in Iran. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Xie, C.; Tian, B. Movement estimate of the Dongkemadi Glacier on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau using L-band and C-band spaceborne SAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6911–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Wetzel, H.-U.; Roessner, S.; Kaufmann, H. A TerraSAR-X InSAR study of landslides in southern Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, F.; Farina, P.; Moretti, S.; Nico, G.; Strozzi, T. On the application of SAR interferometry to geomorphological studies: Estimation of landform attributes and mass movements. Geomorphology 2005, 66, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Du, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, C. Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring subsidence induced by longwall mining activity using Radarsat-2, Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 61, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.H.T.; Tran, Q.C.; Pham, Q.N.; Dang, T.T.; Nguyen, D.A.; El-Moussawi, I.; Toan, T.L. Measuring Ground Subsidence in Ha Noi Through the Radar Interferometry Technique Using TerraSAR-X and Cosmos SkyMed Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3874–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F.; Weckwerth, T.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Klees, R. High-resolution water vapor mapping from interferometric radar measurements. Science 1999, 283, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; White, L.; Banks, S.; Behnamian, A.; Montpetit, B.; Pasher, J.; Duffe, J.; Bernard, D. Characterizing marsh wetlands in the Great Lakes Basin with C-band InSAR observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Shan, B.; Song, S.; Zhan, J. Quantitative estimation of debris flow source materials by integrating multi-source data: A case study. Eng. Geol. 2021, 291, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, Y.; Kankaku, Y.; Saruwatari, H.; Hatooka, Y.; Suzuki, S. ALOS-2 launch and initial checkout status. In Proceedings of the Conference on Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites XVIII, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22–25 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, N.; Kaiser, M.; Koch, M.; Gaber, A. Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Jiang, L.; Paloscia, S.; Santi, E.; Pettinato, S.; Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Liao, W. The Potential of ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Data for Soil Moisture Retrieval With High Spatial Resolution Over Agroforestry Areas, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekertekin, A.; Marangoz, A.M.; Abdikan, S. ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1 SAR data sensitivity analysis to surface soil moisture over bare and vegetated agricultural fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 171, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Feng, G.; Feng, Z.; Miao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Luo, S. Pre- and post-failure spatial-temporal deformation pattern of the Baige landslide retrieved from multiple radar and optical satellite images. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Liao, M.; Gong, J.; Luo, H. Measuring precursory movements of the recent Xinmo landslide in Mao County, China with Sentinel-1-and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 datasets. Landslides 2018, 15, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayik, C.; Abdikan, S.; Ozdemir, A.; ArIkan, M.; Sanli, F.B.; Dogan, U. Investigation of the landslides in Beylikduzu-Esenyurt Districts of Istanbul from InSAR and GNSS observations. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 1201–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, Q.; Hu, J. Quantitatively Estimating of InSAR Decorrelation Based on Landsat-Derived NDVI. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, S.; Soosani, J.; Adeli, K.; Fadaei, H.; Naghavi, H.; Pham, T.D.; Bui, D.T. Improving Accuracy Estimation of Forest Aboveground Biomass Based on Incorporation of ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-2A Imagery and Machine Learning: A Case Study of the Hyrcanian Forest Area (Iran). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A Small-Baseline Approach for Investigating Deformations on Full-Resolution Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, E.A.; Pradhan, B.; Gokceoglu, C. Manifestation of an adaptive neuro-fuzzy model on landslide susceptibility mapping: Klang valley, Malaysia. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 8208–8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xie, S.; Fan, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Liu, G.; et al. Detection of Active Landslides in Southwest China using Sentinel-1A and ALOS-2 Data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 181, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holah, N.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Bruand, A.; King, C. Potential of ASAR/ENVISAT for the characterization of soil surface parameters over bare agricultural fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.; Hu, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, Y. Numerical simulations of kinetic formation mechanism of Tangjiashan landslide. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 4, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, J.; ML, X.; HJ, C.; Tao, L.; Fan, B.; Bing, L. Physical model studies on fill embankment slope deformation mechanism under rainfall condition. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 39, 2933–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skempton, A.W. Long-Term Stability of Clay Slopes. Géotechnique 1964, 14, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shuzui, H. Process of slip-surface development and formation of slip-surface clay in landslides in Tertiary volcanic rocks, Japan. Eng. Geol. 2001, 61, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Huang, R.; CJ, Z.; XJ, P. Types and formation law of structural planes of Emeishan basalt in Sichuan, China. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 2015, 42, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Satellite | ALOS-2 | Sentinel-1A |
|---|---|---|
| Orbital direction | Ascending | Ascending |
| Temporal coverage | 6 October 2014–25 May 2020 | 18 March 2017–21 November 2020 |
| Level | L1.1 | L1.1 |
| Band | L-band | C-band |
| Wavelength | 23.5 cm | 5.6 cm |
| Resolution | 10 m | 5 × 20 m |
| Average angle of incidence | 36.28° | 33.91° |
| Polarization | HH | VV |
| Landslide | NDVI | Slope (°) | Landslide | NDVI | Slope (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duila | 0.058 | 31 | Jueyuge | 0.090 | 24.5 |
| Kongzhigong | 0.060 | 28.8 | Xiaohekou | 0.252 | 39.4 |
| Meiding | 0.099 | 37.4 | Tacheng | 0.413 | 37.9 |
| Dingzhui | 0.068 | 31.4 | Xiapa | 0.223 | 31.9 |
| Jirenhe | 0.074 | 26.9 | Maopo | 0.214 | 23.8 |
| Zitongnong | 0.083 | 36 | Wulucun | 0.304 | 20.7 |
| Azanlaka | 0.089 | 27.9 | / | / | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, C.; Zhu, K.; Song, T.; Bai, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Song, S. Comparative Study on Potential Landslide Identification with ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1A Data in Heavy Forest Reach, Upstream of the Jinsha River. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091962
Cao C, Zhu K, Song T, Bai J, Zhang W, Chen J, Song S. Comparative Study on Potential Landslide Identification with ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1A Data in Heavy Forest Reach, Upstream of the Jinsha River. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091962
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Chen, Kuanxing Zhu, Tianhao Song, Ji Bai, Wen Zhang, Jianping Chen, and Shengyuan Song. 2022. "Comparative Study on Potential Landslide Identification with ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1A Data in Heavy Forest Reach, Upstream of the Jinsha River" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091962
APA StyleCao, C., Zhu, K., Song, T., Bai, J., Zhang, W., Chen, J., & Song, S. (2022). Comparative Study on Potential Landslide Identification with ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1A Data in Heavy Forest Reach, Upstream of the Jinsha River. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091962