Aircraft and Satellite Observations of Vortex Evolution and Surface Wind Asymmetry of Concentric Eyewalls in Hurricane Irma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dataset and Method
2.1. Aircraft Observations
2.2. C-Band SAR Wind Data
2.3. Model Approach and Validation
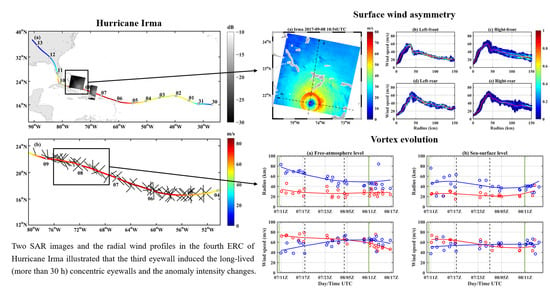
3. Results
3.1. ERC Process following the Classic ERC Theory
3.2. ERC Process in Contrast to the Classic ERC Theory
3.3. Asymmetric CE Surface Wind Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willoughby, H.E.; Clos, J.A.; Shoreibah, M.G. Concentric eye walls, secondary wind maxima, and the evolution of the hurricane vortex. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.L.; Willoughby, H.E. The concentric eyewall cycle of Hurricane Gilbert. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1992, 120, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkins, J.D.; Helveston, M. Tropical cyclone multiple eyewall characteristics. In Proceedings of the 26th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, Miami, FL, USA, 2–5 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, H.C.; Chang, C.P.; Yang, Y.T.; Jiang, H.J. Western North Pacific typhoons with concentric eyewalls. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2009, 137, 3758–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkowski, M.; Kossin, J.P.; Rozoff, C.M. Intensity and structure changes during hurricane eyewall replacement cycles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 3829–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, J.L.; Resio, D.T.; Ratcliff, J.J. The influence of storm size on hurricane surge. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Lane, P.; Emanuel, K.A.; Sullivan, R.M.; Donnelly, J.P. Heightened hurricane surge risk in northwest Florida revealed from climatological-hydrodynamic modeling and paleorecord reconstruction. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 8606–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kossin, J.P.; Sitkowski, M. Predicting hurricane intensity and structure changes associated with eyewall replacement cycles. Wea. Forecast. 2012, 27, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kossin, J.P.; DeMaria, M. Reducing operational hurricane intensity forecast errors during eyewall replacement cycles. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.J.; Willoughby, H.E. The response of balanced hurricanes to local sources of heat and momentum. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 3, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Kuo, H.C.; Hendricks, E.A.; Peng, M.S. Structural and intensity changes of concentric eyewall typhoons in the western North Pacific basin. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2632–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A., Jr.; Chen, S.S.; Smull, B.F.; Lee, W.C.; Bell, M.M. Hurricane intensity and eyewall replacement. Science 2007, 315, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozoff, C.M.; Nolan, D.S.; Kossin, J.P.; Zhang, F.; Fang, J. The roles of an expanding wind field and inertial stability in tropical cyclone secondary eyewall formation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 2621–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepert, J.D. How does the boundary layer contribute to eyewall replacement cycles in axisymmetric tropical cyclones? J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 2808–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhu, Z.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Black, R.; Marks, F.D.; Tallapragada, V.; Gao, C. Impact of subgrid-scale processes on eyewall replacement cycle of tropical cyclones in HWRF system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10027–10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhorn, E.W.; Klotz, B.W.; Vukicevic, T.; Reasor, P.D.; Rogers, R.F. Observed hurricane wind speed asymmetries and relationships to motion and environmental shear. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 1290–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.A.; Rogers, R.F.; Reasor, P.D.; Uhlhorn, E.W.; Marks, F.D., Jr. Asymmetric hurricane boundary layer structure from dropsonde composites in relation to the environmental vertical wind shear. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 3968–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didlake, A.C.; Houze, R.A. Dynamics of the stratiform sector of a tropical cyclone rainband. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1891–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didlake, A.C.; Reasor, P.D.; Rogers, R.F.; Lee, W.C. Dynamics of the transition from spiral rainbands to a secondary eyewall in Hurricane Earl (2010). J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 2909–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.S.; Rogers, R.F.; Reasor, P.D. The rapid intensification and eyewall replacement cycles of Hurricane Irma (2017). Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 981–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W. Cross-polarized synthetic aperture radar: A new potential measurement technique for hurricanes. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, J.A.; Uhlhorn, E.W.; He, Y. High resolution hurricane vector winds from C-band dual-polarization SAR observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouche, A.A.; Chapron, B.; Zhang, B.; Husson, R. Combined co- and cross-polarized SAR measurements under extreme wind conditions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6746–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Perrie, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.A. A hurricane morphology and sea surface wind vector estimation model based on C-band cross-polarization SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouche, A.A.; Chapron, B.; Knaff, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Combot, C. Copolarized and cross-polarized SAR measurements for high-resolution description of major hurricane wind structures: Application to Irma category 5 hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 3905–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Perrie, W. Effects of asymmetric secondary eyewall on tropical cyclone evolution in Hurricane Ike (2008). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 45, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Perrie, W. Symmetric double-eye structure in hurricane bertha (2008) imaged by SAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlhorn, E.W.; Black, P.G. Verification of remotely sensed sea surface winds in hurricanes. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, B.W.; Uhlhorn, E.W. Improved stepped frequency microwave radiometer tropical cyclone surface winds in heavy precipitation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 2392–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.L.; Black, M.L.; Valde, K. GPS dropwindsonde wind profiles in hurricanes and their operational implications. Weather Forecast. 2003, 18, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, G.J.; Belanger, J.I.; Fritz, A. A revised model for radial profiles of hurricane winds. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 4393–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, V.T.; White, L.W.; Willoughby, H.E.; Jorgensen, D.P. A new parametric tropical cyclone tangential wind profile model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 1884–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelton, A.T.; Hart, R.E. Hurricane Eyewall Slope as Determined from Airborne Radar Reflectivity Data: Composites and Case Studies. Weather Forecast. 2013, 28, 368–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNoldy, B.D. Triple eyewall in Hurricane Juliette. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Lin, Q.; Lee, W.-C.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, F. Doppler radar analysis of triple eyewalls in typhoon Usagi (2013). Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsujino, S.; Tsuboki, K.; Kuo, H. Structure and maintenance mechanism of long-lived concentric eyewalls associated with simulated Typhoon Bolaven (2012). J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 3609–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, K.; Bourassa, M.A.; Hart, R.E.; Zhang, J.A.; Rogers, R.F. Observed Kinematic and Thermodynamic Structure in the Hurricane Boundary Layer during Intensity Change. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 2765–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, K.; Hart, R.E.; Bourassa, M.A. Asymmetric Hurricane Boundary Layer Structure during Storm Decay. Part I: Formation of Descending Inflow. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 3851–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, J.A. Tropical cyclone winds and inflow angle asymmetry from SAR imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Perrie, W.; He, Y. Evaluation of Hurricane Wind Speed Retrieval from Cross-Dual-Pol SAR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Guan, C. Extreme Wind Speeds Retrieval Using Sentinel-1 IW Mode SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guan, C.; Sun, J.; Xie, L. A New Hurricane Wind Direction Retrieval Method for SAR Images without Hurricane Eye. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W. High Wind Speed Retrieval from Multi-Polarization SAR. In Hurricane Monitoring with Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar; Li, X., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 85–98. ISBN 978-981-10-2893-9. [Google Scholar]
- Benassai, G.; Migliaccio, M.; Montuori, A.; Ricchi, A. Wave Simulations Through Sar Cosmo-Skymed Wind Retrieval and Verification with Buoy Data. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 17–22 June 2012. [Google Scholar]

















| Hurricane | Year | Category | Approximate Start Time | Approximate End Time | Radial Legs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diana | 1984 | C4 | 03:00 UTC 11 September | 06:00 UTC 12 September | 80 |
| Erika | 1997 | C4 | 05:00 UTC 8 September | 16:30 UTC 9 September | 56 |
| Georges | 1998 | C3 | 17:30 UTC 19 September | 16:00 UTC 21 September | 54 |
| Floyd | 1999 | C4 | 06:00 UTC 11 September | 21:00 UTC 14 September | 60 |
| Isidore | 2002 | C3 | 17:30 UTC 19 September | 23:30 UTC 20 September | 26 |
| Isabel | 2003 | C5 | 17:00 UTC 15 September | 16:00 UTC 18 September | 52 |
| Irma | 2017 | C5 | 05:00 UTC 5 September | 00:00 UTC 9 September | 116 |
| Hurricane | Category | Sensor | Imaging Mode | Polarization | Acquisition Time (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irma | C5 | S1A | IW | VV + VH | 10:30 UTC 7 September 2017 |
| Irma | C5 | RS2 | SCW | VV + VH | 10:51 UTC 8 September 2017 |
| Jose | C4 | S1A | IW | VV + VH | 22:03 UTC 8 September 2017 |
| Michael | C5 | S1A | EW | VV + VH | 23:44 UTC 9 October 2018 |
| Michael | C5 | S1A | EW | VV + VH | 11:50 UTC 10 October 2018 |
| ERC Events | Starting Time | Ending Time | Duration in Three Phases |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERC01 | 09:00 UTC 4 September | 19:00 UTC 4 September | 2 h; 2 h; 6 h |
| ERC02 | 03:00 UTC 5 September | 13:00 UTC 5 September | 2 h; 3 h; 5 h |
| ERC03 | 22:45 UTC 5 September | 05:00 UTC 6 September | 2 h; 2 h; 2 h |
| ERC04 | 11:00 UTC 7 September | 17:00 UTC 8 September | 6 h; 12 h; 12 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G.; Perrie, W.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Aircraft and Satellite Observations of Vortex Evolution and Surface Wind Asymmetry of Concentric Eyewalls in Hurricane Irma. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092158
Hua H, Zhang B, Zhang G, Perrie W, Chen C, Li Y. Aircraft and Satellite Observations of Vortex Evolution and Surface Wind Asymmetry of Concentric Eyewalls in Hurricane Irma. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092158
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Han, Biao Zhang, Guosheng Zhang, William Perrie, Changlin Chen, and Yuanben Li. 2022. "Aircraft and Satellite Observations of Vortex Evolution and Surface Wind Asymmetry of Concentric Eyewalls in Hurricane Irma" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092158
APA StyleHua, H., Zhang, B., Zhang, G., Perrie, W., Chen, C., & Li, Y. (2022). Aircraft and Satellite Observations of Vortex Evolution and Surface Wind Asymmetry of Concentric Eyewalls in Hurricane Irma. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092158