Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
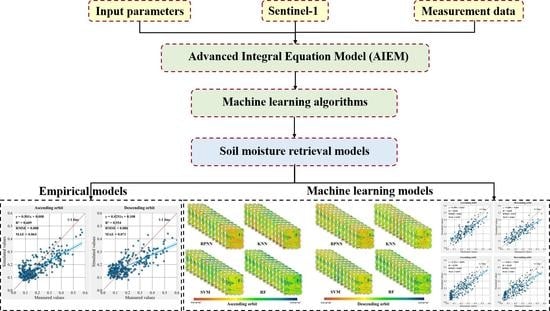
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Moisture Monitoring Networks
2.1.1. Naqu Soil Moisture Monitoring Network
2.1.2. Maqu Soil Moisture Monitoring Network
2.1.3. Tianjun Soil Moisture Monitoring Network
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Advanced Integral Equation Model (AIEM)
2.3.2. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.3.3. Establishment of Surface Microwave Scattering Database with AIEM
2.3.4. Construction of Empirical Model
3. Results
3.1. Soil Moisture Retrieval Using the Empirical Model
3.2. Soil Moisture Retrieval Using Machine Learning Algorithms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koster, R.D.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Guo, Z.; Bonan, G.; Chan, E.; Cox, P.; Gordon, C.T.; Kanae, S.; Kowalczyk, E.; Lawrence, D.; et al. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 2004, 305, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Cho, S.; Jeong, J.; Choi, M. A D-vine copula quantile regression approach for soil moisture retrieval from dual polarimetric SAR Sentinel-1 over vegetated terrains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Wagner, W.; Hasenauer, S.; Hahn, S. Assimilation of surface- and root-zone ASCAT soil moisture products into rainfall-runoff modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2012, 50, 2542–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharssi, I.; Bovis, K.J.; Macpherson, B.; Jones, d.C.P. Operational assimilation of ASCAT surface soil wetness at the Met Office. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2729–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Wagner, W.; Naeimi, V.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S. Improving runoff prediction through the assimilation of the ASCAT soil moisture product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; Elrayes, M.A. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil-part II_ dielectric-mixing models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1985, 23, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Entekhabi, D. Integration of microwave data from SMAP and AMSR2 for soil moisture monitoring in Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 212, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Bi, H.; Qiu, J.; Zou, P. Evaluation of remotely sensed and reanalysis soil moisture products over the Tibetan Plateau using in-situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaadi, N.; Jarlan, L.; Ezzahar, J.; Zribi, M.; Khabba, S.; Bouras, E.; Bousbih, S.; Frison, P.L. Monitoring of wheat crops using the backscattering coefficient and the interferometric coherence derived from Sentinel-1 in semi-arid areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyliger, A.M.; Muzalevskiy, K.V.; Zinchenko, E.V.; Ermolaeva, O.S. Field test of the surface soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1 radar data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Duan, Q.; Wang, W. A comprehensive evaluation of microwave emissivity and brightness temperature sensitivities to soil parameters using qualitative and quantitative sensitivity analyses. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2017, 55, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y. Quantitative retrieval of soil moisture content and surface roughness from multipolarized radar observations of bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2004, 42, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, P.C.; Zyl, J.v.; Engman, T. Measuring soil moisture with imaging radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1995, 33, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K.; Wigneron, J.P.; Chanzy, A. A parameterized multifrequency-polarization surface emission model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2005, 43, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K. Microwave Scattering and Emission Models for Users; Artech House Inc.: Boston, MA, USA; Artech House Inc.: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, A.K. Microwave Scattering and Emission Model and Their Applications; Artech House Inc.: Boston, MA, USA; Artech House Inc.: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive, Vol. III from Theory to Applications; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, A.K.; Li, Z.; Chen, K. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.S.; Wu, T.-D.; Tsay, M.-K.; Fung, A.K. A note on the multiple scattering in an IEM model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2000, 38, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Gherboudj, I.; Zribi, M.; Sahebi, M.; King, C.; Bonn, F. Semi-empirical calibration of the IEM backscattering model using radar images and moisture and roughness field measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 3593–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Baghdadi, N.; Ludwig, R. Validation of the AIEM through correlation length parameterization at field scale using radar imagery in a semi-arid environment. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 10, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zribi, M.; Ciarletti, V.; Taconet, O. Validation of a rough surface model based on Fractional Brownian Geometry with SIRC and ERASME radar data over Orgeval. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Vernieuwe, H.; Alvarez-Mozos, J.; Baets, B.D.; Verhoest, N.E. Error in radar-derived soil moisture due to roughness parameterization: An analysis based on synthetical surface profiles. Sensors 2009, 9, 1067–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Santi, E.; Notarnicola, C.; Pasolli, L.; Reppucci, A. Soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1 images: Algorithm and preliminary validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolassa, J.; Reichle, R.H.; Liu, Q.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Gentine, P.; Aida, K.; Asanuma, J.; Bircher, S.; Caldwell, T.; Colliander, A.; et al. Estimating surface soil moisture from SMAP observations using a Neural Network technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Bai, J. A new approach for soil moisture downscaling in the presence of seasonal difference. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowarda, A.S.; Bai, L.; Zhang, C.; Long, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q. Generating surface soil moisture at 30 m spatial resolution using both data fusion and machine learning toward better water resources management at the field scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Nguyen, C.T.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Bui, X.T.; Hoang, N.B. A low-cost approach for soil moisture prediction using multi-sensor data and machine learning algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Cui, Q.; Lu, H.; La, Z.; Han, M.; Tang, W. Evaluation of SMAP, SMOS, and AMSR2 soil moisture retrievals against observations from two networks on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5780–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ye, B.; Zhou, D.; Wu, B.; Foken, T.; Qin, J.; Zhou, Z. Response of hydrological cycle to recent climate changes in the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Han, M.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Lv, N.; Ding, B.; et al. A multiscale soil moisture and freeze-thaw monitoring network on the Third Pole. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wen, J.; Dente, L.; van der Velde, R.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; Hu, Z. The Tibetan Plateau observatory of plateau scale soil moisture and soil temperature (Tibet-Obs) for quantifying uncertainties in coarse resolution satellite and model products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 988–999. [Google Scholar]
- Dibike, Y.B.; Velickov, S.; Solomatine, D.; Abbott, M.B. Model induction with support vector machines: Introduction and applications. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2001, 15, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devroye, L.; Gyorfy, L.; Krzyzak, A.; Lugosi, G. On the strong universal consistency of nearest neighbor regression function estimates. Ann. Stat. 1994, 22, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, Y.; Sarabandi, K.; Ulaby, F.T. Semi-empirical model of the ensemble-averaged differential mueller matrix for microwave 569 backscattering from bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2002, 40, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Hsu, A.Y.; O’Neill, P.E.; Engman, E.T. Estimation of bare surface soil moisture and surface roughness parameter using L-band SAR image data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1997, 35, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Dechambre, M. A new empirical model to retrieve soil moisture and roughness from C-band radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 84, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Musial, J.; Malinska, A.; Budzynska, M.; Gurdak, R.; Kiryla, W.; Bartold, M.; Grzybowski, P. Soil 634 moisture in the Biebrza Wetlands retrieved from Sentinel-1 imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Xing, M.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Shang, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, M. Estimating soil moisture over winter wheat fields during growing season using machine-learning methods. IEEE J. Stars 2021, 14, 3706–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Gupta, D.K.; Kumar, P.; Prasad, R.; Pandey, D.K.; Das, A.K.; Gupta, M. Machine learning algorithms for soil moisture estimation using Sentinel-1: Model development and implementation. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, K.; Bi, H.; Zhao, T.; Yang, X. A comprehensive analysis of rough soil surface scattering and emission predicted by AIEM with comparison to numerical simulations and experimental measurements. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote 2017, 55, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T. Radar measurement of soil moisture content. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1974, 22, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruckler, L.; Witono, H.; Stengel, P. Near surface soil moisture estimation from microwave measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 26, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| R² | RMSE | MAE | Bias | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | SVM | Mean | 0.634 | 0.057 | 0.046 | 0.015 |
| Std | 0.025 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.008 | ||
| BPNN | Mean | 0.614 | 0.058 | 0.047 | 0.018 | |
| Std | 0.029 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.009 | ||
| KNN | Mean | 0.699 | 0.051 | 0.041 | 0.006 | |
| Std | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.004 | ||
| RF | Mean | 0.753 | 0.045 | 0.034 | 0.004 | |
| Std | 0.018 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | ||
| Descending | SVM | Mean | 0.548 | 0.060 | 0.052 | 0.021 |
| Std | 0.027 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.010 | ||
| BPNN | Mean | 0.561 | 0.056 | 0.048 | 0.016 | |
| Std | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.008 | ||
| KNN | Mean | 0.616 | 0.053 | 0.042 | 0.007 | |
| Std | 0.023 | 0.005 | 0.044 | 0.007 | ||
| RF | Mean | 0.671 | 0.049 | 0.038 | 0.006 | |
| Std | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.; Wang, W.; Jin, R.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Y. Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010153
Dong L, Wang W, Jin R, Xu F, Zhang Y. Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(1):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010153
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Leilei, Weizhen Wang, Rui Jin, Feinan Xu, and Yang Zhang. 2023. "Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Machine Learning Algorithms" Remote Sensing 15, no. 1: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010153
APA StyleDong, L., Wang, W., Jin, R., Xu, F., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Data and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010153