Organic Matter Retrieval in Black Soil Based on Oblique Extremum Signatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Pre-Process
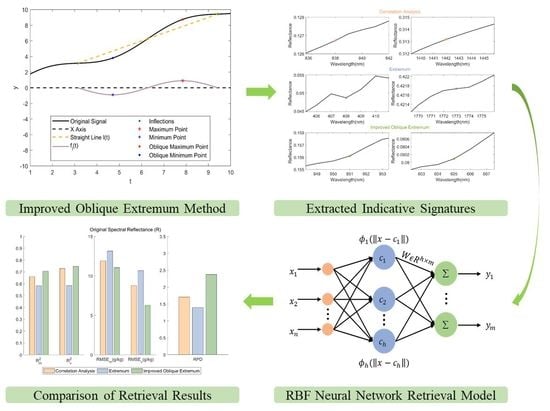
2.3. Indicative Signature Extraction
2.3.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis
2.3.2. Extremum Method
2.3.3. Oblique Extremum Method and Improved Oblique Extremum Method
| Algorithm 1 Improved algorithm to extract oblique extremum points. |
| 1. Calculate the second-order derivative of original hyperspectral signal Step 1. concave interval Step 2. , and .
Step 4. and construct a set 3. Extract the oblique minimum points of the signal. Step 1. convex interval Step 2. , and .
Step 4. and construct a set |
2.4. Retrieval Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Spectral Characteristics Analysis
3.2. Extraction Results of Indicative Signatures for SOM
3.2.1. Correlation Analysis between the SOM Contents and the Spectral Reflectance and Their Different Transformations
3.2.2. Indicative Signatures Extracted by Extremum Method
3.2.3. Indicative Signatures Extracted by Improved Oblique Extremum Method
3.3. The Retrieval Results Analysis with Different Indicative Signature Extraction Methods
3.3.1. The Retrieval Results Based on Indicative Signatures with Correlation Analysis
3.3.2. The Retrieval Results Based on Indicative Signatures with Extremum Method
3.3.3. The Retrieval Results Based on Indicative Signatures with Improved Oblique Extremum Method
3.3.4. Comparison of Retrieval Results with Different Indicative Signature Extraction Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, H.; Meng, D.; Li, X.; Zhu, F. Soil Degradation and Food Security Coupled with Global Climate Change in Northeastern China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Sui, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Herbert, S.J.; Ding, G. Soil Degradation: A Problem Threatening the Sustainable Development of Agriculture in Northeast China. Plant Soil Environ. 2010, 56, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolton, D.K.; Friedl, M.A. Forecasting Crop Yield Using Remotely Sensed Vegetation Indices and Crop Phenology Metrics. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 173, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Tirfessa, D.; Baudron, F. Soil Organic Matter Underlies Crop Nutritional Quality and Productivity in Smallholder Agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 266, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.-X.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.-C.; Yang, W.-D.; Ding, G.-W.; Sun, H.; Liang, Z.-Y.; Shi, C.-C. Hyperspectral Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Different Spectral Preprocessing Techniques. Spectrosc. Lett. 2017, 50, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Gao, M.; Yan, J.; Li, Z.-L.; Leng, P.; Yang, Q.; Duan, S.-B. Hyperspectral Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Content Using Different Spectral Preprocessing Techniques and PLSR Method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.-L.; Pan, X.-Z.; Sun, B. Visible and Near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Prediction of Soil Properties near a Copper Smelter. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, K.; Ding, L. Research on Estimation Models of the Spectral Characteristics of Soil Organic Matter Based on the Soil Particle Size. Spectrochim. Acta Part Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 260, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Lu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Estimation of Heavy Metal (Loid) Contents in Agricultural Soil of the Suzi River Basin Using Optimal Spectral Indices. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašát, R.; Kodešová, R.; Klement, A.; Borůvka, L. Simple but Efficient Signal Pre-Processing in Soil Organic Carbon Spectroscopic Estimation. Geoderma 2017, 298, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Borůvka, L.; Saberioon, M.M.; Kozák, J.; Vašát, R.; Němeček, K. Comparing Different Data Preprocessing Methods for Monitoring Soil Heavy Metals Based on Soil Spectral Features. Soil Water Res. 2016, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ji, J.; Gong, P.; Liao, Q.; Tian, Q.; Ma, H. A Mechanism Study of Reflectance Spectroscopy for Investigating Heavy Metals in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 2007, 71, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Xia, K.; Zhang, S.; Kong, C.; Hu, Q.; Yang, S. Hyperspectral Indirect Inversion of Heavy-Metal Copper in Reclaimed Soil of Iron Ore Area. Spectrochim. Acta Part Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Guo, K. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Inversion and Monitoring of Organic Matter in Black Soil Based on Dynamic Fitness Inertia Weight Particle Swarm Optimization Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Feasibility of Using Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy to Monitor Heavy Metal Contaminants in Urban Lake Sediment. Catena 2018, 162, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, X. Estimating Soil Zinc Concentrations Using Reflectance Spectroscopy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Ju, X.; Ding, N.; Dong, Y.; et al. Wavelength Selection for Estimating Soil Organic Matter Contents Through the Radiative Transfer Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 176286–176293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, G. Estimation of Arsenic in Agricultural Soils Using Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices of Rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Fei, T.; Chen, Y.; Wu, G. Comparison of Multivariate Methods for Estimating Soil Total Nitrogen with Visible/near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Plant Soil 2012, 366, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Tian, Q.; Ji, J.; Qin, Z. Possibilities of Reflectance Spectroscopy for the Assessment of Contaminant Elements in Suburban Soils. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, R. Exploring Appropriate Preprocessing Techniques for Hyperspectral Soil Organic Matter Content Estimation in Black Soil Area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Tian, S. Rapid Inversion of Heavy Metal Concentration in Karst Grain Producing Areas Based on Hyperspectral Bands Associated with Soil Components. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardane, N.K.; Ge, Y.; Morgan, C.L.S. Moisture Insensitive Prediction of Soil Properties from VNIR Reflectance Spectra Based on External Parameter Orthogonalization. Geoderma 2016, 267, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Q.; Nie, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. Hyperspectral Inversion of Heavy Metal Content in Reclaimed Soil from a Mining Wasteland Based on Different Spectral Transformation and Modeling Methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 211, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Qing, C. An Oblique-Extrema-Based Approach for Empirical Mode Decomposition. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinier, J.; Termonia, Y.; Deltour, J. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Square Procedure. Anal. Chem. 1972, 44, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Min, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, N. Retrieval of Farmland Surface Soil Moisture Based on Feature Optimization and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S. Least Squares Quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 1982, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Deng, Y. Determine the Number of Unknown Targets in Open World Based on Elbow Method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 29, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; Behrens, T. Using Data Mining to Model and Interpret Soil Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Li, R.; Li, S. Visible and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Chemometrics Are Able to Predict Soil Physical and Chemical Properties. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2749–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B.; Rossel, R.A.V. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for High-Resolution Soil Sensing. In Proximal Soil Sensing; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Hu, C.; Yan, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Ju, X. Semi-Empirical Soil Organic Matter Retrieval Model with Spectral Reflectance. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 134164–134172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R. Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy-Principal Components Regression Analyses of Soil Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Dataset | Number of Samples | Minimum (g/kg) | Maximum (g/kg) | Mean (g/kg) | SD 1 (g/kg) | CV 2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total dataset | 68 | 7.651 | 133.678 | 40.055 | 19.226 | 2.083 |
| Modeling dataset | 51 | 7.651 | 133.678 | 40.431 | 20.579 | 1.965 |
| Validation dataset | 17 | 12.408 | 76.433 | 38.929 | 14.923 | 2.609 |
| Spectral Transformation | Indicative Bands (nm) | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|---|
| 838 | −0.607 | |
| 1142 | −0.573 | |
| 537 | −0.546 | |
| 1442 | −0.521 | |
| 762 | 0.643 | |
| 838 | 0.642 | |
| 697 | 0.638 | |
| 838 | 0.629 | |
| 683 | 0.616 | |
| 1003 | 0.608 | |
| 929 | −0.584 | |
| 1280 | −0.541 | |
| 574 | −0.519 | |
| 1042 | −0.563 | |
| 941 | −0.558 | |
| 1145 | −0.552 | |
| 838 | −0.619 | |
| 1141 | −0.576 | |
| 537 | −0.562 |
| Spectral Transformation | Indicative Bands (nm) | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|---|
| 408 | −0.477 | |
| 1773 | −0.467 | |
| 998 | −0.595 | |
| 2354 | 0.474 | |
| 463 | 0.544 | |
| 1002 | 0.612 | |
| 2354 | 0.463 | |
| 463 | 0.533 | |
| 1002 | 0.607 | |
| 408 | −0.464 | |
| 1773 | −0.461 | |
| 998 | −0.579 | |
| 408 | −0.441 | |
| 1773 | −0.453 | |
| 998 | −0.559 | |
| 408 | −0.478 | |
| 1773 | −0.469 | |
| 998 | −0.601 |
| Spectral Transformation | Indicative Signatures Kind | Bands (nm) | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oblique Minimum | 841 | −0.607 | |
| 951 | −0.601 | ||
| 605 | −0.567 | ||
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 841 | −0.607 | |
| 951 | −0.601 | ||
| 701 | −0.588 | ||
| 605 | −0.567 | ||
| Oblique Minimum | 863 | 0.636 | |
| 703 | 0.637 | ||
| 941 | 0.624 | ||
| 557 | 0.605 | ||
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 863 | 0.636 | |
| 1587 | 0.494 | ||
| 557 | 0.605 | ||
| Oblique Minimum | 863 | 0.624 | |
| 703 | 0.617 | ||
| 941 | 0.617 | ||
| 557 | 0.583 | ||
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 863 | 0.624 | |
| 1587 | 0.494 | ||
| Oblique Minimum | 841 | −0.577 | |
| 415 | −0.486 | ||
| 1516 | −0.503 | ||
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 841 | −0.577 | |
| 605 | −0.525 | ||
| 1516 | −0.503 | ||
| 1677 | −0.474 | ||
| Oblique Minimum | 841 | −0.542 | |
| 419 | −0.470 | ||
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 841 | −0.542 | |
| 951 | −0.558 | ||
| 605 | −0.476 | ||
| 701 | −0.503 | ||
| Oblique Minimum | 841 | −0.618 | |
| 951 | −0.609 | ||
| 605 | −0.584 | ||
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 841 | −0.618 | |
| 951 | −0.609 | ||
| 701 | −0.604 |
| Spectral Transformation | Modeling Dataset | Validation Dataset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPD | |||||
| 0.659 | 11.900 | 0.730 | 8.755 | 1.705 | |
| 0.534 | 13.908 | 0.639 | 8.025 | 1.860 | |
| 0.653 | 12.004 | 0.602 | 7.919 | 1.885 | |
| 0.579 | 13.219 | 0.725 | 8.126 | 1.836 | |
| 0.527 | 14.025 | 0.751 | 8.452 | 1.766 | |
| 0.638 | 12.258 | 0.562 | 8.773 | 1.701 | |
| Spectral Transformation | Modeling Dataset | Validation Dataset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPD | |||||
| 0.583 | 13.163 | 0.586 | 10.679 | 1.397 | |
| 0.498 | 14.441 | 0.432 | 9.785 | 1.525 | |
| 0.518 | 14.145 | 0.337 | 11.726 | 1.273 | |
| 0.550 | 13.663 | 0.702 | 9.085 | 1.643 | |
| 0.465 | 14.898 | 0.742 | 8.208 | 1.818 | |
| 0.599 | 12.896 | 0.541 | 11.934 | 1.251 | |
| Spectral Transformation | Indicative Signatures Kind | Modeling Dataset | Validation Dataset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPD | ||||||
| Oblique Minimum | 0.642 | 12.185 | 0.660 | 8.692 | 1.717 | |
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 0.706 | 11.046 | 0.747 | 6.280 | 2.376 | |
| Oblique Minimum | 0.624 | 12.502 | 0.736 | 7.715 | 1.934 | |
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 0.598 | 12.916 | 0.745 | 6.751 | 2.211 | |
| Oblique Minimum | 0.622 | 12.532 | 0.501 | 9.440 | 1.581 | |
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 0.550 | 13.662 | 0.591 | 7.677 | 1.944 | |
| Oblique Minimum | 0.560 | 13.512 | 0.738 | 10.625 | 1.405 | |
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 0.614 | 12.655 | 0.842 | 6.652 | 2.243 | |
| Oblique Minimum | 0.416 | 15.577 | 0.515 | 10.096 | 1.478 | |
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 0.547 | 13.721 | 0.744 | 8.639 | 1.727 | |
| Oblique Minimum | 0.656 | 11.946 | 0.668 | 8.382 | 1.780 | |
| Oblique Minimum Without Local Minimum | 0.671 | 11.685 | 0.772 | 6.642 | 2.247 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, W. Organic Matter Retrieval in Black Soil Based on Oblique Extremum Signatures. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102508
Zhang M, Wang M, Wang D, Wang S, Xu W. Organic Matter Retrieval in Black Soil Based on Oblique Extremum Signatures. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102508
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mingyue, Maozhi Wang, Daming Wang, Shangkun Wang, and Wenxi Xu. 2023. "Organic Matter Retrieval in Black Soil Based on Oblique Extremum Signatures" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102508
APA StyleZhang, M., Wang, M., Wang, D., Wang, S., & Xu, W. (2023). Organic Matter Retrieval in Black Soil Based on Oblique Extremum Signatures. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102508