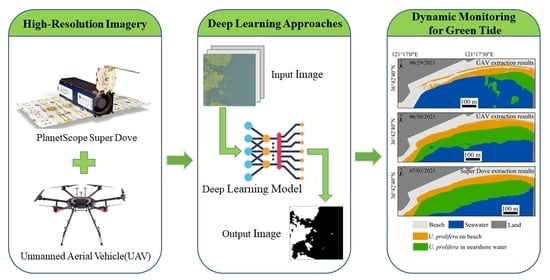
Monitoring Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using High-Resolution Imagery and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data Preparations
2.2.1. PlanetScope Super Dove Data
2.2.2. UAV Data
2.3. U. prolifera Extraction and Quantification Workflow
2.3.1. U. prolifera Extraction Workflow
2.3.2. The Construction of the VGGUnet Model
Model Architecture
Training and Accuracy Evaluation of the VGGUnet Model
2.3.3. U. prolifera Coverage Area and Biomass Density Quantification
3. Results
3.1. U. prolifera Extraction Performance from the Super Dove and UAV Images
3.2. The Spatiotemporal Change Analysis of U. prolifera on the Beach and in Nearshore Water
3.3. Results of Monitoring U. prolifera Using the Super Dove Images Combined with the UAV Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Weaknesses of the VGGUnet Model for U. prolifera Extraction
4.2. The VGGUnet Model Application for U. prolifera near Real-Time Monitoring and Tracking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valiela, I.; McClelland, J.; Hauxwell, J.; Behr, P.J.; Hersh, D.; Foreman, K. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merceron, M.; Antoine, V.; Auby, I.; Morand, P. In situ growth potential of the subtidal part of green tide forming Ulva spp. stocks. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; Xing, Q.; Shi, P. World’s largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ju, L.; Chen, M. Interannual variability of Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4099–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; Dong, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Di, B.; Shi, Y.; Fearns, P.; Shi, P. Recurrence of the world’s largest green-tide in 2009 in Yellow Sea, China: Porphyra yezoensis aquaculture rafts confirmed as nursery for macroalgal blooms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D.; Fearns, P.; Garcia, R. Inter- and intra-annual patterns of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007-2009, their origin and relationship to the expansion of coastal seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, M.; Yu, K.; Chen, Q.; He, Q.; He, P. Green algae blooms caused by Ulva prolifera in the southern Yellow Sea: Identification of the original bloom location and evaluation of biological processes occurring during the early northward floating period. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 2206–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, K.; Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, R.; He, P. The origin of the Ulva macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea in 2013. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X. Cruise observation of Ulva prolifera bloom in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.G. Tracing floating green algae blooms in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using GOCI satellite data and Lagrangian transport simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yi, Y. An early forecasting method for the drift path of green tides: A case study in the Yellow Sea, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 71, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, C.; He, M. Remote estimation of biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae in the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zeng, K.; Hu, C.; He, M. On the remote estimation of Ulva prolifera areal coverage and biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Liang, X. Remote sensing estimation of the biomass of floating Ulva prolifera and analysis of the main factors driving the interannual variability of the biomass in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Liang, C.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Xing, Q.; Shang, S. Long-term trend of Ulva prolifera blooms in the western Yellow Sea. Harmful Algae 2016, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Cui, X.; Liang, J.; Song, X. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Morphological Characteristics of Ulva prolifera Distribution in the Yellow Sea, China in 2016–2018. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Gao, S.; Huo, Y.; Cui, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, G.; He, P. Annual patterns of macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea during 2007–2017. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Meng, J. Satellite monitoring of massive green macroalgae bloom (GMB): Imaging ability comparison of multi-source data and drifting velocity estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Min, J.E.; Ryu, J.H. Detecting Massive Green Algae (Ulva prolifera) Blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Ocean Sci. J. 2012, 47, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T. High-precision extraction of nearshore green tides using satellite remote sensing data of the Yellow Sea, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1626–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.W.; Liang, X.J.; Gong, J.L.; Tong, C.; Xiao, Y.F.; Liu, R.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Assessing and refining the satellite-derived massive green macro-algal coverage in the Yellow Sea with high resolution images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Automatic Extraction of Sargassum Features From Sentinel-2 MSI Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 2579–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Song, D. Analysis of environmental factors affecting the large-scale long-term sequence of green tide outbreaks in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F. Research on the dissipation of green tide and its influencing factors in the Yellow Sea based on Google Earth Engine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Analysis of the reasons for the outbreak of Yellow Sea green tide in 2021 based on long-term multi-source data. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 178, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, P.; Lazuardi, W. Assessment of PlanetScope images for benthic habitat and seagrass species mapping in a complex optically shallow water environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5739–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, H.; Sakuma, A.; Harii, S. Coral-spawn slicks: Reflectance spectra and detection using optical satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikaki, A.; Karantzalos, K.; Power, C.A.; Raitsos, D.E. Remotely Sensing the Source and Transport of Marine Plastic Debris in Bay Islands of Honduras (Caribbean Sea). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Satellite remote sensing of pelagic Sargassum macroalgae: The power of high resolution and deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Glamore, W.; Tamburic, B.; Morrow, A.; Johnson, F. Remote sensing to detect harmful algal blooms in inland waterbodies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.S.; Jo, Y.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Khim, B.K.; Kim, S.M. High Spatial-Resolution Red Tide Detection in the Southern Coast of Korea Using U-Net from PlanetScope Imagery. Sensors 2021, 21, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Gao, M.; Gao, Z. A novel index to detect green-tide using UAV-based RGB imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 245, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Shang, W.; Xu, F. Remote sensing methods for biomass estimation of green algae attached to nursery-nets and raft rope. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Qu, L.; Yu, C.; Sun, Y.; Gao, F.; Dong, J. Accurate Ulva prolifera regions extraction of UAV images with superpixel and CNNs for ocean environment monitoring. Neurocomputing 2019, 348, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In 3rd Earth Resources Technology Satellite-1 Symposium; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Ge, J.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Liu, J.; Yu, F.; He, M. On the recurrent Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C05017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Green macroalgae blooms in the Yellow Sea during the spring and summer of 2008. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114, C12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zheng, G.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F. Deep-learning-based information mining from ocean remote-sensing imagery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1584–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Deng, C.; Huang, G.; Zhao, B. Compressed-Domain Ship Detection on Spaceborne Optical Image Using Deep Neural Network and Extreme Learning Machine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep learning in remote sensing applications: A meta-analysis and review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, H. Development of a Dual-Attention U-Net Model for Sea Ice and Open Water Classification on SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano-Verdejo, J.; Lazcano-Hernandez, H.E.; Cabanillas-Teran, N. ERISNet: Deep neural network for Sargassum detection along the coastline of the Mexican Caribbean. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Li, X.; Kong, F.; Yu, R.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y. AlgaeNet: A Deep-Learning Framework to Detect Floating Green Algae From Optical and SAR Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2782–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir, I.; Alexey, S. Ternausnet: U-net with vgg11 encoder pre-trained on imagenet for image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.05746. [Google Scholar]
- Karen, S.; Andrew, Z. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Iglovikov, V.; Mushinskiy, S.; Osin, V. Satellite imagery feature detection using deep convolutional neural network: A kaggle competition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06169. [Google Scholar]
- Loffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, B.C.; Torralba, A.; Murphy, K.P.; Freeman, W.T. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minar, M.R.; Naher, J. Recent advances in deep learning: An overview. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.08169. [Google Scholar]
- Woebbecke, D.M.; Meyer, G.E.; Vonbargen, K.; Mortensen, D.A. Color Indices for Weed Identification Under Various Soil, Residue, and Lighting Conditions. Trans. ASAE 1995, 38, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 117, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification: Benchmark and State of the Art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Shang, S.; Wilson, C. Floating Algae Blooms in the East China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11501–11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.M.; Espeseth, M.M.; Borch, N. Large-Scale Detection and Categorization of Oil Spills from SAR Images with Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M. Acute toxicity of live and decomposing green alga Ulva (Enteromorpha) prolifera to abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M. Effects of the decomposing green macroalga Ulva (Enteromorpha) prolifera on the growth of four red-tide species. Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Shi, X.; Su, R.; et al. Ulva prolifera green-tide outbreaks and their environmental impact in the Yellow Sea, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]











| Sensor | Band | Wavelength (nm) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Revisit Cycle (day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super Dove | Blue | 465–515 | 3 | 1 |
| Green | 547–585 | |||
| Red | 650–680 | |||
| NIR | 845–885 |
| Data | Super Dove | UAV |
|---|---|---|
| Number of training datasets | 3540 | 3136 |
| Batch size | 32 | 32 |
| Number of epochs | 200 | 200 |
| Average running time per epoch (s) | 78 | 65 |
| Model training time (h) | 4.3 | 3.6 |
| Input Data | Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super Dove | NDVI | 91.32 | 87.26 | 79.35 | 0.83 |
| U-net | 95.14 | 91.13 | 90.16 | 0.91 | |
| VGGUnet | 98.05 | 94.01 | 92.26 | 0.93 | |
| UAV | EXG | 90.16 | 85.21 | 80.43 | 0.82 |
| U-net | 93.26 | 90.12 | 89.82 | 0.90 | |
| VGGUnet | 96.43 | 93.57 | 90.53 | 0.92 |
| Data | Super Dove | UAV |
|---|---|---|
| The average time required to process each image | 126 s | 182 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, W.; Gao, Z.; Gao, M.; Jiang, X. Monitoring Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using High-Resolution Imagery and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041101
Shang W, Gao Z, Gao M, Jiang X. Monitoring Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using High-Resolution Imagery and Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(4):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041101
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Weitao, Zhiqiang Gao, Meng Gao, and Xiaopeng Jiang. 2023. "Monitoring Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using High-Resolution Imagery and Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 4: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041101
APA StyleShang, W., Gao, Z., Gao, M., & Jiang, X. (2023). Monitoring Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using High-Resolution Imagery and Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 15(4), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041101