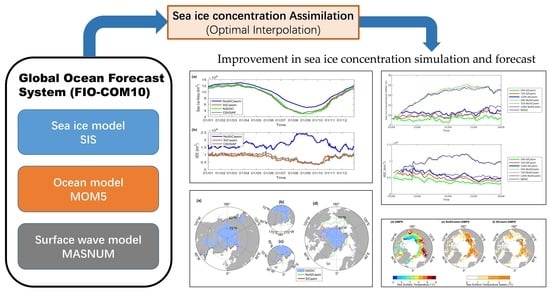
Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Assimilation in an Operational Global 1/10° Ocean Forecast System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Sea Ice Data Assimilation Method
2.3. Data
2.3.1. Sea Ice Concentration
2.3.2. SST Dataset
2.4. Numerical Experiments of Sea Ice Concentration Assimilation
2.5. Real-Time Forecast of 2021
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Sea Ice Assimilation
3.2. Impact on SST
3.3. Impacts on Real-Time Sea Ice Forecasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979–2010. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comiso, J.C.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gersten, R.; Stock, L. Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, F.; He, S.; Sandven, S.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lohmann, K.; Keenlyside, N.; Furevik, T.; et al. Arctic sea ice and Eurasian climate: A review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landrum, L.; Holland, M.M. Extremes become routine in an emerging new Arctic. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.N.; Perovich, D.; Farrell, S.; Haas, C.; Hendricks, S.; Petty, A.A.; Webster, M.; Divine, D.; Gerland, S.; Kaleschke, L.; et al. Sea Ice. NOAA Technical Report OAR ARC. 2021. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/34474 (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Hebert, D.A.; Allard, R.A.; Metzger, E.J.; Posey, P.G.; Preller, R.H.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Phelps, M.W.; Smedstad, O.M. Short-term sea ice forecasting: An assessment of ice concentration and ice drift forecasts using the U.S. Navy’s Arctic Cap Nowcast/Forecast System. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 8327–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, L.; Liang, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zheng, F. Arctic Ice Ocean Prediction System: Evaluating sea-ice forecasts during Xuelong’s first trans-Arctic Passage in summer 2017. J. Glaciol. 2019, 65, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Cavalieri, D.J. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979–2006. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C07003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, Q.; Qiao, F.; Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yin, X.; Song, Y. Arctic sea ice concentration and thickness data assimilation in the FIO-ESM climate forecast system. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Curry, J.A.; Wang, H.; Song, M.; Horton, R.M. Impact of declining Arctic sea ice on winter snowfall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4074–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, M.; Watanabe, M.; Shiogama, H.; Inoue, J.; Kimoto, M. Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, E.J.; Helber, R.W.; Hogan, P.J.; Posey, P.G.; Thoppil, P.G.; Townsend, T.L.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Smedstad, O.M.; Franklin, D.S.; Zamudo-Lopez, L.; et al. Global Ocean Forecast System 3.1 Validation Test; NRL/MR/7320–17-9722; Stennis Space Center: Hancock, MS, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.C.; Roy, F.; Reszka, M.; Surcel Colan, D.; He, Z.; Deacu, D.; Belanger, J.-M.; Skachko, S.; Liu, Y.; Dupont, F.; et al. Sea ice forecast verification in the Canadian Global Ice Ocean Prediction System. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, N.; Metzger, E.J.; Reynolds, C.A.; Ruston, B.; Rowley, C.; Smedstad, O.M.; Ridout, J.A.; Wallcraft, A.; Frolov, S.; Hogan, P.; et al. The Navy’s Earth System Prediction Capability: A New Global Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Sea Ice Prediction System Designed for Daily to Subseasonal Forecasting. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Q.; Nerger, L.; Spreen, G.; Horton, R.; et al. Towards reliable Arctic sea ice prediction using multivariate data assimilation. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Thomas, D.R.; Rothrock, D.A.; Lindsay, R.W.; Yu, Y.; Kwok, R. Assimilation of ice motion observations and comparisons with submarine ice thickness data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, J.D.; Ridley, J.; Martin, M.; Hines, A. Sea ice concentration and motion assimilation in a sea ice−ocean model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C05S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Debernard, J.B.; Sperrevik, A.K.; Isachsen, P.E.; Lavergne, T. A combined optimal interpolation and nudging scheme to assimilate OSISAF sea-ice concentration into ROMS. Ann. Glaciol. 2013, 54, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, R.W.; Zhang, J. Assimilation of Ice Concentration in an Ice–Ocean Model. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Perrie, W.; Qiao, F.; Wang, G. Intercomparisons of High-Resolution Global Ocean Analyses: Evaluation of A New Synthesis in Tropical Oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffies, S.M. Elements of the Modular Ocean Model (MOM) (2012 Release with Updates); NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 614–627. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, F.; Zhao, W.; Yin, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Shu, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; et al. A Highly Effective Global Surface Wave Numerical Simulation with Ultra-High Resolution. In Proceedings of the SC16: International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 13–18 November 2016; pp. 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Winton, M. A Reformulated Three-Layer Sea Ice Model. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, G.; Yeager, S.G. Diurnal to Decadal Global Forcing for Ocean and Sea-Ice Models: The Data Sets and Flux Climatologies (No. NCAR/TN-460+STR); University Corporation for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004; Available online: https://opensky.ucar.edu/islandora/object/technotes:434 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Qiao, F.; Yang, Y.; Xia, C.; Yuan, Y. The role of surface waves in the ocean mixed layer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2008, 27, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, F.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, J.; Dai, D.; Song, Z. Wave–turbulence interaction-induced vertical mixing and its effects in ocean and climate models. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, F.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Xia, C.; Ma, J. Wave-induced mixing in the upper ocean: Distribution and application to a global ocean circulation model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Qiao, F.; Shu, Q. Using ensemble adjustment Kalman filter to assimilate Argo profiles in a global OGCM. Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavelle, J.; Tonboe, R.; Tian, T.; Pfeiffer, R.-H.; Howe, E. Product User Manual for the OSI SAF AMSR-2 Global Sea Ice Concentration; Product OSI-408; Danish Meteorological Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gloersen, P.; Zwally, H.J.; DiGirolamo, N. Sea Ice Concentrations from Nimbus-7 SMMR and DMSP SSM/I-SSMIS Passive Microwave Data; Version 2 [NSIDC-0051]; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Germain, K.M.S.; Swift, C.T. Reduction of weather effects in the calculation of sea-ice concentration with the DMSP SSM/I. J. Glaciol. 1995, 41, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Crawford, J.; Drinkwater, M.; Emery, W.J.; Eppler, D.T.; Farmer, L.D.; Goodberlet, M.; Jentz, R.; Milman, A.; Morris, C.; et al. NASA Sea Ice Validation Program for the DMSP SSM/I: Final Report; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, W.N.; Fetterer, F.; Stewart, J.S.; Helfrich, S. How do sea-ice concentrations from operational data compare with passive microwave estimates? Implications for improved model evaluations and forecasting. Ann. Glaciol. 2015, 56, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonboe, R.; Nielsen, E. Global Sea Ice Concentration Reprocessing Validation Report; European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) Ocean and Sea Ice Satellite Application Facility: Darmstadt/Boulder, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, N.; Pedersen, L.T.; Tonboe, R.T.; Kern, S.; Heygster, G.; Lavergne, T.; Sørensen, A.; Saldo, R.; Dybkjær, G.; Brucker, L.; et al. Inter-comparison and evaluation of sea ice algorithms: Towards further identification of challenges and optimal approach using passive microwave observations. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 1797–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisæter, K.A.; Rosanova, J.; Evensen, G. Assimilation of ice concentration in a coupled ice–ocean model, using the Ensemble Kalman filter. Ocean Dyn. 2003, 53, 368–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, C. Atmospheric influence on Arctic marginal ice zone position and width in the Atlantic sector, February–April 1979–2010. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Losa, S.N.; Losch, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Nerger, L.; Yang, H. Assimilating summer sea-ice concentration into a coupled ice–ocean model using a LSEIK filter. Ann. Glaciol. 2015, 56, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goessling, H.F.; Tietsche, S.; Day, J.J.; Hawkins, E.; Jung, T. Predictability of the Arctic sea ice edge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikolajewicz, U.; Sein, D.V.; Jacob, D.; Königk, T.; Podzun, R.; Semmler, T. Simulating Arctic sea ice variability with a coupled regional atmosphere-ocean-sea ice model. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadhams, P. Arctic sea ice extent and thickness. In The Arctic and Environmental Change; Dowdeswell, J.A., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Losch, M.; Nerger, L.; Mu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C. Using Sea Surface Temperature Observations to Constrain Upper Ocean Properties in an Arctic Sea Ice-Ocean Data Assimilation System. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 4727–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Dash, P.; Ignatov, A.; Banzon, V.; Beggs, H.; Brasnett, B.; Cayula, J.-F.; Cummings, J.; Donlon, C.; Gentemann, C.; et al. Group for High Resolution Sea Surface temperature (GHRSST) analysis fields inter-comparisons. Part 1: A GHRSST multi-product ensemble (GMPE). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 77–80, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- While, J.; Martin, M.J. Variational bias correction of satellite sea-surface temperature data incorporating observations of the bias. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 2733–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E.; Armour, K.C.; Bitz, C.M.; DeWeaver, E. Persistence and Inherent Predictability of Arctic Sea Ice in a GCM Ensemble and Observations. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, S.; Bishop, C.H.; Holt, T.; Cummings, J.; Kuhl, D. Facilitating Strongly Coupled Ocean–Atmosphere Data Assimilation with an Interface Solver. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Model Components | Model Parameters/Schemes | Values/Configurations |
|---|---|---|
| Surface wave model MASNUM | Horizontal resolution | 1/10° × 1/10° |
| Spectral discretization | 24 directions, 25 wave numbers | |
| Spatial coverage | global ocean | |
| Ocean model MOM5 | Horizontal resolution | 1/10° × 1/10° |
| Vertical levels | 54 levels (min: 2 m) | |
| Spatial coverage | global ocean | |
| Horizontal grid | Tri-polar grid with bi-polar region set to north of 65°N | |
| Vertical grid | Z* coordinate configured with bottom partial cells | |
| Horizontal diffusivity | Bi-harmonic, diffusive velocities of 1.96 cm/s for momentum and 0.65 cm/s for tracers | |
| Vertical diffusivity | KPP + Bv | |
| Air-sea fluxes | NCEP/Bulk formula | |
| Model topography | ETOPO1 | |
| Sea ice model SIS | Ice thickness categories | 5 |
| Ice bulk salinity | 0.005 PSU | |
| Snow albedo | 0.85 | |
| Ice albedo | 0.72 | |
| Ice/ocean drag coefficient | ||
| Ice surface roughness length |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Q.; Shu, Q.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Qiao, F. Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Assimilation in an Operational Global 1/10° Ocean Forecast System. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051274
Shao Q, Shu Q, Xiao B, Zhang L, Yin X, Qiao F. Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Assimilation in an Operational Global 1/10° Ocean Forecast System. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051274
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Qiuli, Qi Shu, Bin Xiao, Lujun Zhang, Xunqiang Yin, and Fangli Qiao. 2023. "Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Assimilation in an Operational Global 1/10° Ocean Forecast System" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051274
APA StyleShao, Q., Shu, Q., Xiao, B., Zhang, L., Yin, X., & Qiao, F. (2023). Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Assimilation in an Operational Global 1/10° Ocean Forecast System. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051274