Study on the Backscatter Differential Phase Characteristics of X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar and its Processing Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
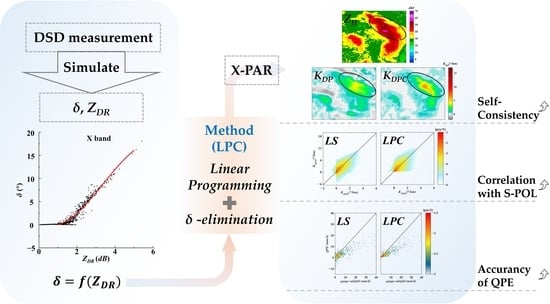
2.1. Simulation and Correction Methods Based on DSD Data
- Firstly, based on the local DSD data, the fitted relationship between δ and ZDR was calculated.
- Based on this relationship, the threshold of ZDR for δ correction was determined; i.e., δ was only calculated when ZDR was larger than this threshold.
- The elimination of δ from the filtered ΦDP was carried out:
2.2. The X-PAR Data
2.3. KDP Calculation Methods
2.3.1. KDP Calculation Based on Low-Pass Filtering and Least Squares (LS)
2.3.2. KDP Calculation Based on SG Smoothing Filters and LP Method
2.3.3. KDP Calculation Schemes for X-PAR
3. Results
3.1. The Relationship of δ with Raindrops’ Size and Temperature
3.2. The δ-Correction Effect Based on Simulated Data
3.2.1. Simulating the Effects of δ on ФDP and KDP
3.2.2. The Effects of δ on Attenuation Correction
3.2.3. The Effects of δ-Elimination on KDP Calculation
3.3. The Effect of δ Correction on X-PAR KDP Calculation
3.3.1. Case Analysis on Radial Data
3.3.2. Case Analysis on PPI
3.3.3. Statistical Analysis
3.3.4. QPE Test
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| X-PAR | X-band dual-polarization phased-array weather radar |
| S-POL | S-band dual-polarization Doppler weather radar |
| DSD | raindrop size distribution |
| δ | backscatter differential phase |
| KDP | specific differential propagation phase |
| Z | reflectivity |
| ΦDP | differential propagation phase |
| ZDR | differential reflectivity factor |
| ρHV | correlation coefficient |
| QPE | quantitative precipitation estimation |
| PIA | path integral attenuation |
| LP | Linear Programming |
| LS | Least Squares |
References
- Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.N. Error structure of multiparameter radar and surface measurements of rainfall. Part iii: Specific differential phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1988, 5, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zrnić, D.S. Comparison of dual-polarization radar estimators of rain. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Kropfli, R.A.; Reinking, R.F.; Martner, B.E. Prospects for measuring rainfall using propagation differential phase in x- and ka-radar bands. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 38, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Clark, K.A.; Martner, B.E.; Tokay, A. X-band polarimetric radar measurements of rainfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M. A variational approach for retrieving raindrop size distribution from polarimetric radar measurements in the presence of attenuation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Ushio, T.; Matsuda, T. A bayesian approach for integrated raindrop size distribution (dsd) retrieval on an x-band dual-polarization radar network. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 33, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Maki, M.; Lee, D.-I. Retrieval of three-dimensional raindrop size distribution using x-band polarimetric radar data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1265–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besic, N.; Figueras i Ventura, J.; Grazioli, J.; Gabella, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Hydrometeor classification through statistical clustering of polarimetric radar measurements: A semi-supervised approach. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4425–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorgucci, E.; Scarchilli, G.; Chandrasekar, V. Specific differential phase estimation in the presence of nonuniform rainfall medium along the path. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 16, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M. Effect of nonuniform beam filling on the propagation of radar signals at x-band frequencies. Part ii: Examination of differential phase shift. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Bouar, E.L.; OBligis, E.; Ali-Mehenni, M. The rain profiling algorithm applied to polarimetric weather radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 332–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trömel, S.; Kumjian, M.R.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Simmer, C.; Diederich, M. Backscatter differential phase—Estimation and variability. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2529–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubbert, J.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.N.; Meischner, P. Processing and interpretation of coherent dual-polarized radar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1993, 10, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, J.; Bringi, V.N. An iterative filtering technique for the analysis of copolar differential phase and dual-frequency radar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneebeli, M.; Berne, A. An extended kalman filter framework for polarimetric x-band weather radar data processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 29, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Fox, N.; Market, P. A gaussian mixture method for specific differential phase retrieval at x-band frequency. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5613–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinoso-Rondinel, R.; Unal, C.; Russchenberg, H. Adaptive and high-resolution estimation of specific differential phase for polarimetric x-band weather radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, S.E.; Mcgraw, R.; Lei, L. An application of linear programming to polarimetric radar differential phase processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1716–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, K.; Giangrande, S. A hybrid method to estimate specific differential phase and rainfall with linear programming and physics constraints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, M.; Li, S.; Yang, M. Application of linear programming on quality control of differential propagation phase shift data for x-band dual linear polarimetric doppler weather radar. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2019, 77, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimel, K.; Kumjian, M. Evaluation of kdp estimation algorithm performance in rain using a known-truth framework. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 38, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmus, J.; Collis, S. The python arm radar toolkit (py-art), a library for working with weather radar data in the python programming language. J. Open Res. Softw. 2016, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarchilli, G.; Goroucci, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Seliga, T.A. Rainfall estimation using polarimetric techniques at c-band frequencies. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1993, 32, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Russchenberg, H.W.J. Estimation of specific differential phase and differential backscatter phase from polarimetric weather radar measurements of rain. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. IEEE 2011, 8, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, X.; Huang, H. Research on Quantitative Comparison and Observation Precision of Dual Polarization Phased Array Radar and Operational Radar. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; ISBN 9780521623841. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, P.; Yeh, C. Scattering of electromagnetic waves by arbitrarily shaped dielectric bodies. Appl. Opt. 1975, 14, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Tibetan Plateau and southern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Petersen, W.A.; Gatlin, P.; Wingo, M. Comparison of raindrop size distribution measurements by collocated disdrometers. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1672–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrain, J.; Berne, A. Experimental quantification of the sampling uncertainty associated with measurements from parsivel disdrometers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V. The quantitative precipitation estimation system for dallas-fort worth (dfw) urban remote sensing network. J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diederich, M.; Ryzhkov, A.; Simmer, C.; Zhang, P.; Troemel, S. Use of specific attenuation for rainfall measurement at x-band radar wavelengths. Part II: Rainfall Estimates and Comparison with Rain Gauges. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Radar Parameters | X-PAR | Shenzhen S-POL |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 9.3~9.5 GHz | 2.8 GHz |
| Peak power | 256 W | ≥650 kW |
| Update time | 92 s | 360 s |
| Range coverage | 42 km | 230 km |
| Range resolution | 30 m | 250 m |
| Elevation scan range | 0.9°~20.7° with 1.8° step | 0.5~19.5°, 9 layers |
| Beamwidths | Horizontal: 3.6°; vertical: 1.8° | Horizontal: <1°; vertical: <1° |
| Array plane normal angle | 15° | / |
| Scan mode | Volume range height indicator scan | Volume plan position indicator scan |
| S-POL Test | Self-Consistency Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | MAE | RMSE | CC | R2 | RMSE |
| Exp1 | 0.74 | 1.14 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.96 |
| Exp2 | 0.71 | 1.11 | 0.75 | 0.64 | 0.94 |
| Exp3 | 0.73 | 1.16 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 0.95 |
| Exp4 | 0.71 | 1.13 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.92 |
| Test | MAE (mm/h) | RMSE (mm/h) | RMAE (%) | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All cases | Exp1 | 4.51 | 7.02 | 59.18 | 0.78 |
| Exp2 | 4.51 | 6.98 | 59.19 | 0.79 | |
| Exp3 | 3.61 | 6.32 | 47.37 | 0.89 | |
| Exp4 | 3.60 | 6.27 | 47.19 | 0.89 | |
| Rainfall ≤5 mm/h | Exp1 | 2.20 | 3.35 | 96.44 | 0.31 |
| Exp2 | 2.19 | 3.33 | 96.22 | 0.32 | |
| Exp3 | 0.98 | 1.33 | 43.12 | 0.58 | |
| Exp4 | 0.97 | 1.31 | 42.57 | 0.59 | |
| Rainfall >5 mm/h | Exp1 | 7.50 | 9.92 | 51.65 | 0.77 |
| Exp2 | 7.51 | 9.86 | 51.70 | 0.78 | |
| Exp3 | 7.00 | 9.44 | 48.23 | 0.82 | |
| Exp4 | 6.99 | 9.37 | 48.12 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, F.; Liu, L. Study on the Backscatter Differential Phase Characteristics of X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar and its Processing Methods. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051334
Geng F, Liu L. Study on the Backscatter Differential Phase Characteristics of X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar and its Processing Methods. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051334
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Fei, and Liping Liu. 2023. "Study on the Backscatter Differential Phase Characteristics of X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar and its Processing Methods" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051334
APA StyleGeng, F., & Liu, L. (2023). Study on the Backscatter Differential Phase Characteristics of X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar and its Processing Methods. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051334