Analysis of Atmospheric Elements in Near Space Based on Meteorological-Rocket Soundings over the East China Sea
Abstract
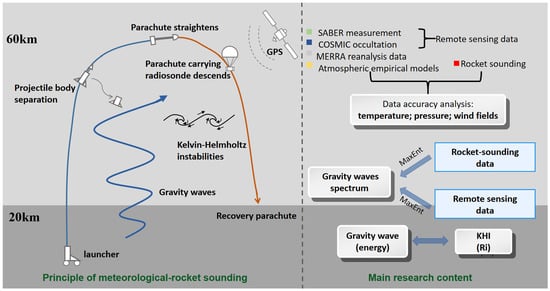
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Detection Principle of the Meteorological Rocket
2.2. Atmospheric Empirical Model
2.3. Satellite Remote-Sensing Data
2.4. MERRA-2 Reanalysis Dataset
2.5. Data Comparison Method
2.6. Gravity-Wave Power–Frequency Spectrum
2.7. Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability
2.8. Gravity-Wave Energy
3. Results
3.1. Time-Series Analysis of Temperature and Wind-Field Profiles
3.2. Comparison of Temperature, Pressure and Wind-Field Data
3.3. Atmospheric Gravity-Wave Spectrum Analysis
3.4. The Interrelationship between KHI and the Gravity-Wave Energy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Z.; Sheng, Z.; Wan, L.; Shi, H.; Jiang, Y. Comprehensive assessment of the accuracy of the data from near space meteorological rocket sounding. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 62, 199601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; He, M. Statistical Characteristics of Inertial Gravity Waves Over a Tropical Station in the Western Pacific Based on High-Resolution GPS Radiosonde Soundings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.M.; Yang, Z.X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.D.; Huang, C.M.; Yi, F.; Hu, F. A Statistical Study of Inertia Gravity Waves in the Lower Stratosphere Over the Arctic Region Based on Radiosonde Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 4958–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Liu, L.; Wan, W. A global morphology of gravity wave activity in the stratosphere revealed by the 8-year SABER/TIMED data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D21101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ern, M.; Trinh, Q.T.; Preusse, P.; Gille, J.C.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Russell, J.M., III; Riese, M. GRACILE: A comprehensive climatology of atmospheric gravity wave parameters based on satellite limb soundings. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 857–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaifler, N.; Kaifler, B.; Dörnbrack, A.; Rapp, M.; Hormaechea, J.L.; de la Torre, A. Lidar observations of large-amplitude mountain waves in the stratosphere above Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyard, T.P.; Wright, C.J.; Hindley, N.P.; Halloran, G.; Krisch, I.; Kaifler, B.; Hoffmann, L. Atmospheric Gravity Waves in Aeolus Wind Lidar Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL092756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.J.; Guo, W.; Yang, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, X.; Hu, X. Global Stratopheric Gravity Wave Characteristics by Aura/MLS and TIMED/SABER Observation Data. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2022, 42, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckermann, S.D.; Hirota, I.; Hocking, W.K. Gravity wave and equatorial wave morphology of the stratosphere derived from long-term rocket soundings. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 121, 149–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.C.S.; Shao, S.; Cai, J.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Shi, H. Method for Evaluation Uncertainty of Wind Measurements for Mete-orological Sounding Rocket. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Sheng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liao, Q. Data Analysis of the TK-1G Sounding Rocket Installed with a Satellite Navigation System. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, C.; Robinet, J.C.; Roblin, C. On using computational aeroacoustics for long-range propagation of infrasounds in realistic atmospheres. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L14814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Torkar, K.M.; Singer, W.; Strelnikova, I.; Rapp, M.; Robertson, S. Signatures of mesospheric particles in ionospheric data. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wan, L.; Fan, Z. A Study of Atmospheric Temperature and Wind Profiles Obtained from Rocketsondes in the Chinese Midlatitude Region. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Cao, Y.; Shi, W. The study of in situ wind and gravity wave determination by the first passive falling-sphere experiment in China’s northwest region. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 182, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Li, J.W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, S.D.; Shi, W.L. Characteristics of Stratospheric Winds over Jiuquan (41.1° N, 100.2° E) Using Rocketsonde Data in 1967–2004. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Xu, J.; Shi, D.; Wei, F.; Wang, L. Observations of the first meteorological rocket of the Meridian Space Weather Monitoring Project. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; He, M. Identification of stratospheric disturbance information in China based on round-trip intelligent sounding system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023; EGUsphere [preprint]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M.; Zhao, S.; Xia, X. Impacts of Stratospheric Polar Vortex Shift on the East Asian Trough. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 5605–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Yi, F.; Huang, C.M.; Huang, K.M. High vertical resolution analyses of gravity waves and turbulence at a midlatitude station. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D02103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sheng, Z.; He, M. The Interaction Between the Turbulence and Gravity Wave Observed in the Middle Stratosphere Based on the Round-Trip Intelligent Sounding System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, R.L.A.; Larsen, M.F.; Azeem, I.; Stevens, M.H.; Williams, B.P.; Collins, R.L.; Li, J. In Situ Observations of Neutral Shear Instability in the Statically Stable High-Latitude Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere During Quiet Geomagnetic Conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA027972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Fritts, D.C.; Liu, A.Z.; Lund, T.S.; Liu, H.L. Gravity Waves Emitted from Kelvin-Helmholtz Instabilities. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL102674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdilghanie, A.M.; Diamessis, P.J. The internal gravity wave field emitted by a stably stratified turbulent wake. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 720, 104–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.H.; Fritts, D.C.; Gelinas, L.J.; Rudy, R.J.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Liu, A.Z. Kelvin-Helmholtz Billow Interactions and Instabilities in the Mesosphere Over the Andes Lidar Observatory: 1. Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Shao, J. Inertia-gravity wave energy and instability drive turbulence evidence from a near-global high-resolution radiosonde dataset. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 58, 2927–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, J.M.; Hedin, A.E.; Drob, D.P.; Aikin, A.C. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: Statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drob, D.P.; Emmert, J.T.; Crowley, G.; Picone, J.M.; Shepherd, G.G.; Skinner, W.R.; Hays, P.B.; Niciejewski, R.J.; Larsen, M.F.; She, C.; et al. An empirical model of the Earth’s horizontal wind fields: HWM07. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, A12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ern, M.; Diallo, M.; Preusse, P.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Schwartz, M.J.; Wu, Q.; Riese, M. The semiannual oscillation (SAO) in the tropical middle atmosphere and its gravity wave driving in reanalyses and satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 13763–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezac, L.; Jian, Y.; Yue, J.; Russell, J.M.; Kutepov, A.; Garcia, R.; Walker, K.; Bernath, P. Validation of the global distribution of CO2 volume mixing ratio in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere from SABER. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12067–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xue, X.; Chen, T. An investigation of the global morphology of stratosphere gravity waves based on COSMIC observations. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 3668–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.D.; Huang, C.M.; Huang, K.M.; Gong, Y.; Gan, Q. The vertical wave number spectra of potential energy density in the stratosphere deduced from the COSMIC satellite observation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 145, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis, 1980 Onward. Part I: System Description and Data Assimilation Evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargan, K.; Coy, L.; Molod, A.M.; McCarty, W.R.; Pawson, S. Structure and Dynamics of the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation in MERRA-2. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 5339–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.R.; Kumar, K.K. TIMED/SABER observations of global gravity wave climatology and their interannual variability from stratosphere to mesosphere lower thermosphere. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 1489–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramitha, M.; Venkat Ratnam, M.; Taori, A.; Krishna Murthy, B.V.; Pallamraju, D.; Vijaya Bhaskar Rao, S. Evidence for tropospheric wind shear excitation of high-phase-speed gravity waves reaching the mesosphere using the ray-tracing technique. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2709–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.; Vadas, S.L.; Bossert, K.; Harvey, V.L.; Zulicke, C.; Hoffmann, L. A High-Resolution Whole-Atmosphere Model With Resolved Gravity Waves and Specified Large-Scale Dynamics in the Troposphere and Stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfler, A.; Harvey, B.; Methven, J.; Doyle, J.D.; Rahm, S.; Reitebuch, O.; Weiler, F.; Witschas, B. Observation of Jet Stream Winds during NAWDEX and Characterization of Systematic Meteorological Analysis Errors. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2020, 148, 2889–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.-Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, X.-C.; Xiao, C.-Y. Comparison of temperature measurements between COSMIC atmospheric radio occultation and SABER/TIMED. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 2152–2162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.R.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, J.K. Assessment of COSMIC radio occultation retrieval product using global radiosonde data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ho, S.P.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Hunt, D.; Kuo, Y.H. Assessment of radiosonde temperature measurements in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere using COSMIC radio occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladstädter, F.; Steiner, A.K.; Schwärz, M.; Kirchengast, G. Climate intercomparison of GPS radio occultation, RS90/92 radiosondes and GRUAN from 2002 to 2013. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsberg, E.E.; Marshall, B.T.; Garcia-Comas, M.; Krueger, D.; Lingenfelser, G.S.; Martin-Torres, J.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Russell, J.M.; Smith, A.K.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Assessment of the quality of the Version 1.07 temperature-versus-pressure profiles of the middle atmosphere from TIMED/SABER. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D17101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Q.; Sheng, Z.; Shi, H.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhou, C.J. A Characterization of the Quality of the Stratospheric Temperature Distributions from SABER based on Comparisons with COSMIC Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C.; Alexander, M.J. Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, A.; Gerding, M.; Lübken, F.-J. Characteristics of stratospheric turbulent layers measured by LITOS and their relation to the Richardson number. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 10605–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, G.; Sommer, S.; Schult, C.; Latteck, R.; Chau, J.L. Observation of Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities and gravity waves in the summer mesopause above Andenes in Northern Norway. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6721–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckermann, S.D. Effect of background winds on vertical wavenumber specrta of atmospheric gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 14097–14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.J.; Grimsdell, A.W.; Stephan, C.C.; Hoffmann, L. MJO-Related Intraseasonal Variation in the Stratosphere: Gravity Waves and Zonal Winds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Sheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Liao, Q.; Chang, S. Different Influences on ‘Wave Turbopause’ Exerted by 6.5 DWs and Gravity Waves. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric turbulence over China estimated using operational high-resolution soundings. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.; Wang, L.; Lund, T.; Thorpe, S. Multi-scale dynamics of Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities. Part 1. Secondary instabilities and the dynamics of tubes and knots. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 941, A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Lund, T.; Werne, J.; Wang, L.; Fritts, D.C. Gravity Wave Instability Dynamics at High Reynolds Numbers. Part I: Wave Field Evolution at Large Amplitudes and High Frequencies. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1126–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Lund, T.; Werne, J.; Wang, L.; Fritts, D.C. Gravity Wave Instability Dynamics at High Reynolds Numbers. Part II: Turbulence Evolution, Structure, and Anisotropy. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1149–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| COSMIC | 8.54 | 3.34 | 12.0% | 3.9 |
| SABER | 15.56 | 5.38 | 23.0% | 6.8 |
| MSIS | 11.12 | 5.38 | 18.2% | 6.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; He, Y.; Leng, H. Analysis of Atmospheric Elements in Near Space Based on Meteorological-Rocket Soundings over the East China Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020402
Song Y, He Y, Leng H. Analysis of Atmospheric Elements in Near Space Based on Meteorological-Rocket Soundings over the East China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020402
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yuyang, Yang He, and Hongze Leng. 2024. "Analysis of Atmospheric Elements in Near Space Based on Meteorological-Rocket Soundings over the East China Sea" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020402
APA StyleSong, Y., He, Y., & Leng, H. (2024). Analysis of Atmospheric Elements in Near Space Based on Meteorological-Rocket Soundings over the East China Sea. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020402