Sea Ice Detection from RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarization SAR Imagery Based on Co- and Cross-Polarization Ratio
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. SAR Polarimetric Parameters
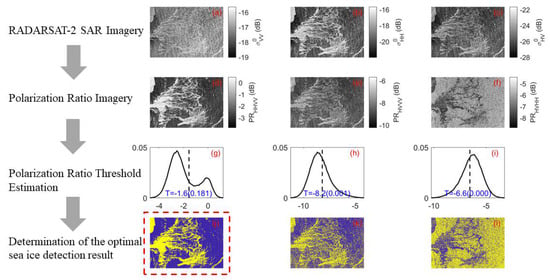
2.3. Sea Ice Detection Method Based on PR
- (1)
- SAR image pre-processing:
- (2)
- Low backscatter area detection:
- (3)
- PR threshold estimation:
- (4)
- Segmentation of PR images:
- (5)
- Determination of the optimal sea ice detection result:
3. Results
3.1. Polarimetric Characteristics of Sea Ice and OW
3.1.1. Backscattering Characteristics of Sea Ice and OW
3.1.2. PR Characteristics of Sea Ice and OW
3.2. Accuracy Assesment
3.2.1. Statistical Validation
3.2.2. Case Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effectiveness of SSIM
4.2. Effect of Incidence Angles on PR Threshold
4.3. The Wind Effects on PR
4.4. Performance Comparison to Other Algorithms
4.5. Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Function | Coefficients | CMOD5.N | CMODH |
|---|---|---|---|
| −0.6878 | −0.7272 | ||
| −0.7957 | −1.1901 | ||
| 0.3380 | 0.3396 | ||
| −0.1728 | 0.0867 | ||
| 0.0000 | 0.0030 | ||
| 0.0040 | 0.0117 | ||
| 0.1103 | 0.1291 | ||
| 0.0159 | 0.0835 | ||
| 6.7329 | 4.0925 | ||
| 2.7713 | 1.2111 | ||
| −2.2885 | −1.1197 | ||
| 0.4971 | 0.5790 | ||
| −0.7250 | −0.6045 | ||
| 0.0450 | 0.1183 | ||
| 0.0066 | 0.0089 | ||
| 0.3222 | 0.2196 | ||
| 0.0120 | 0.0175 | ||
| 22.700 | 24.442 | ||
| 2.0813 | 1.9834 | ||
| 3.0000 | 6.7814 | ||
| 8.3659 | 7.9479 | ||
| −3.3428 | −4.6964 | ||
| 1.3236 | −0.4370 | ||
| 6.2437 | 5.4712 | ||
| 2.3893 | 0.6394 | ||
| 0.3249 | 0.6733 | ||
| 4.1590 | 3.4332 | ||
| 1.6930 | 0.3670 |
References
- DeRepentigny, P.; Jahn, A.; Holland, M.M.; Smith, A. Arctic sea ice in two configurations of the CESM2 during the 20th and 21st centuries. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2020JC016133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannuzel, D.; Tedesco, L.; Van Leeuwe, M.; Campbell, K.; Flores, H.; Delille, B.; Miller, L.; Stefels, J.; Assmy, P.; Bowman, J. The future of Arctic sea-ice biogeochemistry and ice-associated ecosystems. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, D.; Community, S. Arctic sea ice in CMIP6. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Wang, J.; Beletsky, D.; Overland, J.; Ikeda, M.; Wan, L. Accelerated decline of summer Arctic sea ice during 1850–2017 and the amplified Arctic warming during the recent decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gersten, R.; Stock, L. Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Risi, C.; Codron, F.; He, X.; Poulsen, C.J.; Wei, Z.; Chen, D.; Li, S.; Bowen, G.J. Acceleration of western Arctic sea ice loss linked to the Pacific North American pattern. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivy, A.; Howell, S.E.; Alt, B.; McCourt, S.; Chagnon, R.; Crocker, G.; Carrieres, T.; Yackel, J.J. Trends and variability in summer sea ice cover in the Canadian Arctic based on the Canadian Ice Service Digital Archive, 1960–2008 and 1968–2008. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C03007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zeng, J.; Liang, S.; Zhang, P.; Tang, F.; Chen, S.; Ma, X. Spatial and temporal variations of Arctic sea ice from 2002 to 2017. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Spreen, G.; Pang, S. Arctic sea ice circulation and drift speed: Decadal trends and ocean currents. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2013, 118, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylek, P.; Folland, C.; Klett, J.D.; Wang, M.; Hengartner, N.; Lesins, G.; Dubey, M.K. Annual mean arctic amplification 1970–2020: Observed and simulated by CMIP6 climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.E.; Ballinger, T.J.; Euskirchen, E.S.; Hanna, E.; Mård, J.; Overland, J.E.; Tangen, H.; Vihma, T. Extreme weather and climate events in northern areas: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 209, 103324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.; Lund, M.; Skov, K.; Abermann, J.; López-Blanco, E.; Scheller, J.; Scheel, M.; Jackowicz-Korczynski, M.; Langley, K.; Murphy, M. Multiple ecosystem effects of extreme weather events in the Arctic. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Gloersen, P.; Campbell, W.J. Determination of sea ice parameters with the Nimbus 7 SMMR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1984, 89, 5355–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Cavalieri, D.J. An enhancement of the NASA Team sea ice algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.; Sullivan, C. Satellite microwave and in situ observations of the Weddell Sea ice cover and its marginal ice zone. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1986, 91, 9663–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.; Tonboe, R.; Kern, S.; Schyberg, H. Improved retrieval of sea ice total concentration from spaceborne passive microwave observations using numerical weather prediction model fields: An intercomparison of nine algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 374–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, E.; Matzler, C.; Grenfell, T.C. A model for retrieving total sea ice concentration from a spaceborne dual-polarized passive microwave instrument operating near 90 GHz. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; Heygster, G. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.; Lambe, A.; Agnew, T. A new algorithm (ECICE) to estimate ice concentration from remote sensing observations: An application to 85-GHz passive microwave data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 4104–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.; Dabboor, M. Polarimetric SAR Applications of Sea Ice: A Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 6627–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Huang, W.; Mahdianpari, M. A meta-analysis of sea ice monitoring using spaceborne polarimetric SAR: Advances in the last decade. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6158–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.P.; Yackel, J.J. Evaluation of C-band SAR polarimetric parameters for discrimination of first-year sea ice types. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldsetzer, T.; Yackel, J. Sea ice type and open water discrimination using dual co-polarized C-band SAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 35, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.P.; Yackel, J.J.; Geldsetzer, T. Analysis of consistency in first-year sea ice classification potential of C-band SAR polarimetric parameters. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 39, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabboor, M.; Montpetit, B.; Howell, S. Assessment of the high resolution SAR mode of the RADARSAT constellation mission for first year ice and multiyear ice characterization. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. SVM-based sea ice classification using textural features and concentration from RADARSAT-2 dual-pol ScanSAR data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhvatkina, N.; Korosov, A.; Muckenhuber, S.; Sandven, S.; Babiker, M. Operational algorithm for ice–water classification on dual-polarized RADARSAT-2 images. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Gu, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, G. Sea ice classification using TerraSAR-X ScanSAR data with removal of scalloping and interscan banding. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Korosov, A.A.; Babiker, M.; Won, J.-S.; Hansen, M.W.; Kim, H.-C. Classification of sea ice types in Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar images. Cryosphere 2019, 14, 2629–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Perrie, W. Arctic Sea Ice and Open Water Classification from Spaceborne Fully Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4203713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.; Wang, Z.; Clausi, D.A. Automated ice–water classification using dual polarization SAR satellite imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Li, F.; Heygster, G.; Zhang, S. Antarctic sea-ice classification based on conditional random fields from RADARSAT-2 dual-polarization satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2451–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q. Extraction of sea ice cover by Sentinel-1 SAR based on support vector machine with unsupervised generation of training data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 3040–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.S.; Nandan, V.; Singha, S.; Howell, S.E.; Geldsetzer, T.; Yackel, J.; Montpetit, B. C-and L-band SAR signatures of Arctic sea ice during freeze-up. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Clausi, D.A. Unsupervised segmentation of synthetic aperture radar sea ice imagery using a novel Markov random field model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulze, H.; Korosov, A.; Brajard, J. Classification of sea ice types in Sentinel-1 SAR data using convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghian, S.; Ullah, H.; Kræmer, T.; Hughes, N.; Eltoft, T.; Marinoni, A. Sea ice classification of SAR imagery based on convolution neural networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Huang, W.; Mahdianpari, M. Eastern Arctic Sea Ice Sensing: First Results from the RADARSAT Constellation Mission Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chu, Q.; Liu, L. An improved sea ice classification algorithm with Gaofen-3 dual-polarization SAR data based on deep convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gelis, I.; Colin, A.; Longepe, N. Prediction of categorized sea ice concentration from Sentinel-1 SAR images based on a fully convolutional network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5831–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Scott, K.A.; Clausi, D.A. Sea Ice Concentration Estimation: Using Passive Microwave and SAR Data With a U-Net and Curriculum Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5339–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, H. Development of a dual-attention U-Net model for sea ice and open water classification on SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4010205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xie, T.; Perrie, W.; Yang, J. Deep Learning-Based Sea Ice Classification with Sentinel-1 and AMSR-2 Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 5514–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Luo, X.; Wu, Z.; Qin, X.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Shang, J.; Zhao, D. Multi-Featured Sea Ice Classification with SAR Image Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, S.; Bertoia, C. Study of multi-polarization C-band backscatter signatures for Arctic sea ice mapping with future satellite SAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 27, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, W. Mapping of different sea ice regimes using images from Sentinel-1 and ALOS synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Perrie, W.; Wei, C.; Zhao, L. Discrimination of open water from sea ice in the Labrador Sea using quad-polarized synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, V.N.; Fan, S.; Zhang, B.; Mouche, A.A.; Chapron, B. On quad-polarized SAR measurements of the ocean surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8362–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Jurkevich, L.; Dewaele, P.; Wambacq, P.; Oosterlinck, A. Speckle filtering of synthetic aperture radar images: A review. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 8, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topouzelis, K.; Kitsiou, D. Detection and classification of mesoscale atmospheric phenomena above sea in SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J. Oil spill detection from SAR intensity imagery using a marked point process. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, J.; Brenning, A. A comparative study of different classification techniques for marine oil spill identification using RADARSAT-1 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W. Cross-polarized synthetic aperture radar: A new potential measurement technique for hurricanes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, G.R. Theories for the interaction of electromagnetic and oceanic waves—A review. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1978, 13, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronovich, A. Small-slope approximation for electromagnetic wave scattering at a rough interface of two dielectric half-spaces. Waves Random Media 1994, 4, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. Comparison of C-band scatterometer CMOD5. N equivalent neutral winds with ECMWF. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Mouche, A.; Lu, Y.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. A geophysical model function for wind speed retrieval from C-band HH-polarized synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Perrie, W.; Hwang, P.A.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X. A hurricane wind speed retrieval model for C-band RADARSAT-2 cross-polarization ScanSAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4766–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Frequency band | C-band (5.405 GHz) |
| Product type | Single Look Complex (SLC) |
| Beam mode | Fine Quad Polarization |
| Polarization | HH VV HV VH |
| Incidence angle range | 19–49° |
| Scene size (Rg × Az) | 25 × 25 km |
| Pixel spacing (Rg × Az) | 4.7 × 5.1 m |
| Spatial resolution (Rg × Az) | 5.2 × 7.6 m |
| Noise equivalent sigma zero (NESZ) | −36.5 ± 3 dB |
| Revisit time | 24 days |
| PR Used | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Co-pol ratio: HH/VV | 0.83 |
| Cross-pol ratio: HV/VV | 0.79 |
| Cross-pol ratio: HV/HH | 0.77 |
| PR combinations: HH/VV + HV/VV + HV/HH | 0.96 |
| PR Used | HH/VV | HV/VV | HV/HH |
|---|---|---|---|
| HH/VV | 51 | 3 | 0 |
| HV/VV | 3 | 62 | 0 |
| HV/HH | 1 | 0 | 11 |
| Number of SAR images | 54 | 65 | 11 |
| Accuracy | 0.93 | 0.95 | 1 |
| Overall accuracy | 0.95 | ||
| Method | Reference | Data | Parameter | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision tree | [23] | ENVISAT ASAR dual-polarization imagery | Co-pol ratio (VV/HH) | 0.85 |
| K-means | [22,24] | RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization SAR imagery | Co-pol ratio (HH/VV) | 0.82 |
| K-means | [22,24] | RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization SAR imagery | Cross-pol ratio (HH/HV) | 0.78 |
| X-Bragg backscatter model | [47] | RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization SAR imagery | Co-pol ratio (VV/HH) | 0.82 |
| Our algorithm | Our paper | RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization SAR imagery | Co-pol ratio (HH/VV), Cross-pol ratios (HV/VV, HV/HH) | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Xie, T.; Perrie, W.; Yang, J. Sea Ice Detection from RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarization SAR Imagery Based on Co- and Cross-Polarization Ratio. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030515
Zhao L, Xie T, Perrie W, Yang J. Sea Ice Detection from RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarization SAR Imagery Based on Co- and Cross-Polarization Ratio. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(3):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030515
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li, Tao Xie, William Perrie, and Jingsong Yang. 2024. "Sea Ice Detection from RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarization SAR Imagery Based on Co- and Cross-Polarization Ratio" Remote Sensing 16, no. 3: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030515
APA StyleZhao, L., Xie, T., Perrie, W., & Yang, J. (2024). Sea Ice Detection from RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarization SAR Imagery Based on Co- and Cross-Polarization Ratio. Remote Sensing, 16(3), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030515