Improving the Detection Effect of Long-Baseline Lightning Location Networks Using PCA and Waveform Cross-Correlation Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Network and Data
3. Method
3.1. Real-Time Data Compression
3.2. Location Algorithm
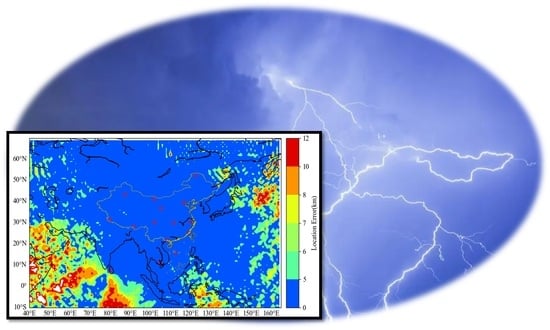
3.3. Simulated Analysis
4. Results
4.1. The Location Result of Cross-Correlation Method
4.2. The Location Result of Envelope Peak Method
5. Discussion
5.1. Relative Detection Efficiency
5.2. Relative Location Accuracy
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- An LEMP waveform compression method based on PCA is proposed and applied for the first time, which realizes real-time compression and the efficient transmission of LEMP waveform data. The compression time for each data point is less than 1 ms.
- (2)
- The cross-correlation technique of the long-baseline LEMP waveform is proposed. On the one hand, the influence of noise on location accuracy is minimized, and on the other hand, the accuracy of calculating the signal arrival time difference is improved.
- (3)
- The relative detection efficiency and relative location accuracy of the waveform cross-correlation method and envelope peak method were evaluated with ADTD data. The detection performance of the long-baseline lightning location network can be further improved by using waveform cross-correlation technology. The lightning location accuracy can be better than 4.5 km, and the relative detection efficiency can reach 69%. It should be emphasized that the location accuracy of the proposed method is twice higher than that of the envelope peak method.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nag, A.; Murphy, M.J.; Schulz, W.; Cummins, K.L. Lightning locating systems: Insights on characteristics and validation techniques. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Z.; Mardiana, R.; Ushio, T. Broadband and narrowband RF interferometers for lightning observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3189–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. Observations on the leader-return stroke of cloud-to-ground lightning with the broadband interferometer. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhou, B.-H.; Shi, L.-H.; Dong, W.-S.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Gao, T.-C. An improved method for broadband interferometric lightning location using wavelet transforms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D18211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, W.; Wu, T.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y. Observation of compact intracloud discharges using VHF broadband interferometers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D01203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Qie, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, D. Using lightning locating system based on time-of-arrival technique to study three-dimensional lightning discharge processes. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budden, K.G.I. The propagation of a radio-atmospheric. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1951, 42, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.; Jones, D.L.; Rodger, C.J. ELF and VLF radio waves. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 1689–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowden, R.L.; Brundell, J.B.; Rodger, C.J. VLF lightning location by time of group arrival (TOGA) at multiple sites. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R.K.; Inan, U.S.; Cummins, K.L. Long-range lightning geolocation using a VLF radio atmospheric waveform bank. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, A.T.; Businger, S.; Cummins, K.L.; Demetriades, N.W.S.; Murphy, M.; Pifer, B. Development of a Long-Range Lightning Detection Network for the Pacific: Construction, Calibration, and Performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, C.J.; Werner, S.; Brundell, J.B.; Lay, E.H.; Thomson, N.R.; Holzworth, R.H.; Dowden, R.L. Detection efficiency of the VLF World-Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN): Initial case study. Ann. Geophys. 2006, 24, 3197–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, C.J.; Brundell, J.B.; Holzworth, R.H.; Lay, E.H. Growing detection efficiency of the World Wide Lightning Location Network. Amer. IOP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1118, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, C.J.; Brundell, J.B.; Hutchins, M.; Holzworth, R.H. The world wide lightning location network (WWLLN): Update of status and applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 16–23 August 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, F.; Yuan, S.; Chang, S.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q. Asia-Pacific Lightning Location Network (APLLN) and Preliminary Performance Assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, W.; Qu, X. Source Locating Algorithm for Ultra-long Baseline Lightning Detection System Based on TDOA. High Volt. Eng. 2020, 46, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P. Compression of large data grids for Internet transmission. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringnér, M. What is principal component analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadima, J.; Cerdeira, J.O.; Minhoto, M. Computational aspects of algorithms for variable selection in the context of principal components. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2004, 47, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratius, V.; Jannesari, A.; Tichy, W.F. Parallelizing Bzip2: A Case Study in Multicore Software Engineering. IEEE Softw. 2009, 26, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, J.L.; Sleator, D.D.; Tarjan, R.E.; Wei, V.K. A Locally adaptive data-compression scheme. Commun. ACM 1986, 29, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.L. An experimental study of the remote location of lightning flashes using a VLF arrival time difference technique. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 112, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.D.; Schmidt, K.; Laroche, P.; Blanchet, P.; Oettinger, W.P.; Defer, E.; Dziewit, Z.; Konarski, J. LINET—An international lightning detection network in Europe. Atmos. Res. 2009, 91, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, C.J.; Cummins, K.L.; Kehoe, K.E.; Krider, E.P. National Lightning Detection Network (NLDN) performance in southern Arizona, Texas, and Oklahoma in 2003–2004. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D05208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shi, L.; Qiu, S.; Liu, H.; Dong, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Fine Three-Dimensional VHF Lightning Mapping Using Waveform Cross-Correlation TOA Method. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2019EA000832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.G.; Akita, M.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Edens, H.E.; Kawasaki, Z.; Stanley, M.A. Continuous broadband digital interferometry of lightning using a generalized cross-correlation algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3134–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Cummer, S.A.; Solanki, R.; Weinert, J.; McTague, L.; Katko, A.; Barrett, J.; Zigoneanu, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, W. A low-frequency near-field interferometric-TOA 3-D Lightning Mapping Array. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7777–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Lightning Mapping With an Array of Fast Antennas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, P.M.; Christian, H.J.; Stewart, M.; Burchfield, J.; Podgorny, S.; Corredor, D.; Hall, J.; Kuznetsov, E.; Franklin, V. Characterization and applications of VLF/LF source locations from lightning using the Huntsville Alabama Marx Meter Array. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 3120–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshak, W.J.; Solakiewicz, R.J.; Blakeslee, R.J.; Goodman, S.J.; Christian, H.J.; Hall, J.M.; Bailey, J.C.; Krider, E.P.; Bateman, M.G.; Boccippio, D.J.; et al. North Alabama Lightning Mapping Array (LMA): VHF source retrieval algorithm and error analyses. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, C.J.; Brundell, J.B.; Dowden, R.L. Location accuracy of VLF World-Wide Lightning Location (WWLL) network: Post-algorithm upgrade. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qie, X.S.; Wang, D.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Su, D.B.; Wang, Z.C.; Liu, D.X.; Wu, Z.J.; Sun, Z.L.; Tian, Y. Beijing Lightning Network (BLNET) and the observation on preliminary breakdown processes. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowden, R.L.; Holzworth, R.H.; Rodger, C.J.; Lichtenberger, J.; Thomson, N.R.; Jacobson, A.R.; Lay, E.; Brundell, J.B.; Lyons, T.J.; O’Keefe, S.; et al. World-Wide Lightning Location Using VLF Propagation in the Earth-Ionosphere Waveguide. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2008, 50, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Chang, S.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, F.; Gao, C. Classification of VLF/LF Lightning Signals Using Sensors and Deep Learning Methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

















| Data Number | bzip2 Lossless Compression | PCA Lossy Compression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption of Time (s) | Compressibility (%) | Consumption of Time (s) | Compressibility (%) | |
| 100 | 0.84 | 0.63 | 0.0882 | 0.09 |
| 200 | 1.83 | 0.63 | 0.1764 | 0.09 |
| 300 | 2.75 | 0.66 | 0.2646 | 0.09 |
| 400 | 3.76 | 0.63 | 0.3528 | 0.09 |
| 500 | 4.48 | 0.60 | 0.441 | 0.09 |
| 600 | 5.57 | 0.63 | 0.5292 | 0.09 |
| 700 | 6.49 | 0.64 | 0.6174 | 0.09 |
| 800 | 8.55 | 0.72 | 0.7056 | 0.09 |
| Cross-Correlation Method | Envelope Peak Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke number | 10,604 | 9470 |
| Homologous events with ADTD | 8700 | 5345 |
| Detection efficiency relative to ADTD | 69% | 42.4% |
| Location accuracy relative to ADTD | 4.5 km | 9.9 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Fu, L. Improving the Detection Effect of Long-Baseline Lightning Location Networks Using PCA and Waveform Cross-Correlation Methods. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050885
Zhang T, Wang J, Ma Q, Fu L. Improving the Detection Effect of Long-Baseline Lightning Location Networks Using PCA and Waveform Cross-Correlation Methods. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(5):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050885
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ting, Jiaquan Wang, Qiming Ma, and Liping Fu. 2024. "Improving the Detection Effect of Long-Baseline Lightning Location Networks Using PCA and Waveform Cross-Correlation Methods" Remote Sensing 16, no. 5: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050885
APA StyleZhang, T., Wang, J., Ma, Q., & Fu, L. (2024). Improving the Detection Effect of Long-Baseline Lightning Location Networks Using PCA and Waveform Cross-Correlation Methods. Remote Sensing, 16(5), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050885