Anisotropic Green Tide Patch Information Extraction Based on Deformable Convolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
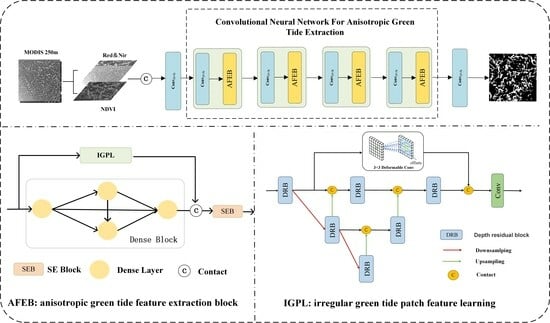
2. Methods
2.1. AGE-Net
2.2. Irregular Green Tide Patch Feature Learning Module
2.3. Experimental Environment and Settings
2.4. Evaluation
3. Research Area and Data Pre-Processing
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Preprocessing
4. Results
4.1. Experiments
4.1.1. Comparative Experiment
4.1.2. Interference Experiment
4.1.3. Ablation Experiment
4.1.4. Model Performance Analysis and Parameterization Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Zheng, W.; Li, F. Application of Himawari-8 Data to Enteromorpha Prolifera Dynamically Monitoring in the Yellow Sea. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2017, 28, 714–723. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Q.G.; An, D.Y.; Zheng, X.Y.; Wei, Z.N.; Wang, X.H.; Li, L.; Tian, L.Q.; Chen, J. Monitoring Seaweed Aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with Multiple Sensors for Managing the Disaster of Macroalgal Blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.W.; Gong, J.L.; Liu, R.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Liang, X.J. Remote sensing estimation of the biomass of floating Ulva prolifera and analysis of the main factors driving the interannual variability of the biomass in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.E.; Cui, T.W.; Cui, W.L. Analysis of Confusion Factors in Extracting Green Tide Remote Sensing Information from Multiple Source Satellites. Remote Sens. Inf. 2015, 30, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.W.; Lin, M.S.; Zhang, Y.G. Progress in China’s Ocean Satellite and Its Applications. JRS 2016, 20, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, J.H. Analysis of the Monitoring Capability of Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using Multi source and Multi resolution Remote Sensing Images. J. Qingdao Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2018, 31, 95–101, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.B.; Gao, Z.Q.; Xu, F.X.; Ai, J.Q.; Ning, J.C.; Shang, W.T.; Jiang, X.P. Remote Sensing Analysis of the Evolution of Enteromorpha Prolifera in the South Yellow Sea in 2017 Based on GOCI. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.H.; Su, J.; Sheng, H. Feasibility Study on Utilizing Geostationary Orbital Satellites for Operational Monitoring of Green Tide. Acta Laser Biol. Sin. 2018, 27, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, Y.Q.; Yan, Q.Y. Improving Spaceborne GNSS-R Algal Bloom Detection with Meteorological Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, J.; Bai, T. Analysis of the Drift Path of the Yellow Sea Green Tide in 2008 and 2009. Mar. Sci. 2014, 38, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.J.; Cao, C.H.; Huang, J.; Cao, Y.J.; Gao, S. Preliminary Study on Numerical Simulation of Emergency Tracing of the Yellow Sea Green Tide. Mar. Sci. 2011, 35, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.Q.; Guo, H.; Zhang, A.D. Study on Spatial-temporal Distribution Characteristics of Enteromorpha Prolifera in Shandong Peninsula Waters from 2008 to 2012. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2014, 34, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.L.; Huang, R.; Yuan, K.L. Characteristics of Green Tide Disasters in the Eastern Coast of Shandong Peninsula. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.Y. Research on Remote Sensing Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Deep Convolutional Networks. Eng. Technol. Part II 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Huang, J.; Cui, T.W.; Xiao, Y.F.; Cai, X.Q. Capability Comparison of 5 Vegetation Indices for Detecting the Green Tide in Different Development Phases and the Application. Acta Laser Biol. Sin. 2014, 23, 590–595. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.A.; Fearns, P.; Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D.Y. Quantification of Floating Macroalgae Blooms using the Scaled Algae Index. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean 2013, 118, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Dong, J.Y.; Sun, F.F.; Bing, L. Object-oriented random forest classification for Enteromorpha prolifera detection with SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Virtual Reality and Visualization (ICVRV), Hangzhou, China, 24–26 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.M.; Li, P.X.; Yang, J.; Shi, L.; Li, X.M.; Zhao, J.Q. Ulva prolifera detection with dual-polarization GF-3 SAR data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 502, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbos, P.J. Beyond Regression: New Tools for Prediction and Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. Ph.D. Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y. Intelligent Signal Processing; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 306–351. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ashish, V.; Noam, S.; Niki, P.; Jakob, U.; Llion, J.; Aidan, N.G.; Lukasz, K.; Illia, P. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30, pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.M.; Fu, K.; Sun, H.; Sun, X.; Yan, M.L. Automatic Water-Body Segmentation From High-Resolution Satellite Images via Deep Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Jin, S.G.; Liu, S.C.; Jia, Y.; Zhen, Y.Q.; Chen, T.X.; Huang, W.M. Inland Water Mapping Based on GA-LinkNet From CyGNSS Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.G.; Li, X.H.; Wu, J.; Ren, G.B.; Lu, Y. Tiny-Scene Embedding Network for Coastal Wetland Mapping Using Zhuhai-1 Hyperspectral Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.Q.; Chi, M.M. RSImageNet: A Universal Deep Semantic Segmentation Lifecycle for Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 68254–68267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, X.F.; Kong, F.Z.; Yu, R.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y. AlgaeNet: A Deep Learning Framework to Detect Floating Green Algae from Optical and SAR Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2782–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.F. Distribution Characteristics of Green Algae in Yellow Sea Using a Deep Learning Automatic Detection Procedure. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3499–3501. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano-Verdejo, J.; Lazcano-Hernandez, H.E.; Cabanillas-Terán, N. ERISNet: Deep neural Network for Sargassum Detection along the Coastline of the Mexican Caribbean. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.G.; Zhang, H.Q.; Jing, W.; Liu, H.; Cui, J. SRSe-Net: Super-resolution-based Semantic Segmentation Network for Green Tide Extraction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Y. Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. UNet: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.Y.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.X.; Wang, L.B.; Atkinson, P.M. ABCNet: Attentive bilateral contextual network for efficient semantic segmentation of Fine-Resolution remotely sensed imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 181, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI (0.05) | 91.38 | 86.45 | 75.21 | 0.8043 | 64.10 |
| RVI (1.10) | 90.79 | 89.95 | 69.26 | 0.7826 | 62.65 |
| SVM | 91.50 | 89.41 | 55.96 | 0.6884 | 52.48 |
| U-Net | 92.30 | 89.11 | 61.65 | 0.7288 | 57.33 |
| ABC-Net | 91.83 | 83.17 | 64.31 | 0.7253 | 56.90 |
| Algae-Net | 93.09 | 81.31 | 76.38 | 0.7877 | 64.97 |
| SRSe-Net | 93.86 | 82.84 | 79.98 | 0.8138 | 68.61 |
| AGE-Net | 94.07 | 79.43 | 87.28 | 0.8317 | 71.19 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score | IoU(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI (0.30) | 78.90 | 99.97 | 23.93 | 0.3862 | 23.93 |
| RVI (0.19) | 76.01 | 99.95 | 13.49 | 0.2378 | 13.49 |
| SVM | 85.67 | 88.31 | 55.73 | 0.6833 | 51.90 |
| U-Net | 87.06 | 82.46 | 74.39 | 0.7058 | 59.23 |
| ABC-Net | 82.99 | 78.21 | 53.62 | 0.6362 | 46.65 |
| Algae-Net | 86.68 | 75.63 | 76.69 | 0.7615 | 61.49 |
| SRSe-Net | 87.93 | 80.54 | 74.46 | 0.7738 | 63.11 |
| AGE-Net | 88.59 | 78.86 | 80.42 | 0.7963 | 66.16 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 93.37 | 77.80 | 84.62 | 0.8107 | 6.62 |
| Baseline + IGPL | 93.64 | 78.57 | 85.38 | 0.8183 | 7.39 |
| Baseline + SEB | 93.99 | 82.06 | 82.19 | 0.8212 | 7.17 |
| AGE-Net | 94.07 | 79.43 | 87.28 | 0.8317 | 7.46 |
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value | F1-Score | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimizer | SGD | 0.8243 | 0.7091 |
| SGDM | 0.8317 | 0.7119 | |
| ADAM | 0.8311 | 0.7110 | |
| Batch size | 16 | 0.8298 | 0.7012 |
| 8 | 0.8315 | 0.7119 | |
| 4 | 0.8292 | 0.7082 | |
| 2 | 0.8216 | 0.6972 | |
| Learning rate | 0.004 | 0.8317 | 0.7119 |
| 0.001 | 0.8257 | 0.7031 | |
| 0.0001 | 0.8132 | 0.6851 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Anisotropic Green Tide Patch Information Extraction Based on Deformable Convolution. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071162
Cui B, Liu M, Chen R, Zhang H, Zhang X. Anisotropic Green Tide Patch Information Extraction Based on Deformable Convolution. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(7):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071162
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Binge, Mengting Liu, Ruipeng Chen, Haoqing Zhang, and Xiaojun Zhang. 2024. "Anisotropic Green Tide Patch Information Extraction Based on Deformable Convolution" Remote Sensing 16, no. 7: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071162
APA StyleCui, B., Liu, M., Chen, R., Zhang, H., & Zhang, X. (2024). Anisotropic Green Tide Patch Information Extraction Based on Deformable Convolution. Remote Sensing, 16(7), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071162